Abstract
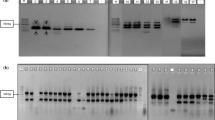
Sarcoplasmic proteins of four colour varieties of Siamese fighting fish, Betta splendens Regan, were analysed by isoelectric focusing (IEF). Genetic polymorphisms were detected in six loci having isoelectric points: 4.92-5.00 (Sp-1), 5.33-5.48 (Sp-2), 5.90 (Sp-3), 6.31-6.35 (Sp-4), 6.58-6.70 (Sp-5) and 6.90 (Sp-6). For the Sp-1, Sp-2, Sp-4 and Sp-5 loci, there were two co-dominant alleles. At Sp-3 and Sp-6, one allele was dominant and the other null. Individuals within each locus were classified into phenotypes A, AB and B. Only homozygotes were found at Sp-2. Allele frequencies were calculated for each locus and tested for accordance with the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Observed values for each phenotype at Sp-1, Sp-3, Sp-4, Sp-5 and Sp-6 agreed well with the expected ones. At Sp-2, genotypic frequencies for each variety deviated markedly (p < 0.01) from the equilibrium. When tested for homogeneity, no significant differences (p ≥ 0.95) in gene frequencies were found among the varieties except at Sp-2. Band sharing index (BSI), computed using the BIO-GENE v5.04 program, revealed high intravariety genetic similarities (0.701-0.740) and slightly above-average intervariety values (0.550-0.583). In this study, we estimated the levels of genetic variability in B. splendens, and proposed a genetic model for each polymorphic locus.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allendorf, F.W. and Utter, F.M. (1979) Population genetics. In: Fish Physiology, Vol. VIII (eds W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall and J.R. Brett) Academic Press: New York, pp. 407–454.
Dinesh, K.R., Lim, T.M., Chan, W.K. and Phang, V.P.E. (1996) Genetic variation inferred from RAPD fingerprinting in three species of tilapia. Aquaculture International 4, 19–30.
Hanzawa, N. and Taniguchi, N. (1982) Isoelectric focusing patterns of sarcoplasmic protein of the Japanese dace, genus Tribolodon. Report of the Usa Marine Biological Institute 4, 51–54.
Khoo, G., Chan, S.Y., Lim, T.M. and Phang, V.P.E. (1996) Isoelectric focusing: a rapid method for identification and differentiation of teleost species. Malaysian Journal of Science 17A, 11–17.
Kirpichnikov, V.S. (1981) The fighting fish and the paradise fish (Anabantidae). In: Genetic Bases of Fish Selection (transl. G.G. Gause) Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp. 97–98.
Lee, C.K. (1986) The fighting fish. In: Goldfish and Tropical Fish (3rd edn) Tropical Press, Kuala Lumpur, pp. 23–27.
Lucas, G.A. (1968) A Study of Variation in the Siamese Fighting Fish, Betta splendens, with Emphasis on Colour Mutants and the Problem of Sex Determination. PhD thesis, Iowa Ames State University, Iowa, 201 pp.
Lundstrom, R.C. and Roderick, S.A. (1979) Fish species identification by thin-layer iso-electric focusing of sarcoplasmic proteins. Science Tools 26, 38–43.
Macaranas, J.M., Taniguchi, N., Pante, M.J.R., Capili, J.B. and Pullin, R.S.V. (1986) Electrophoretic evidence for extensive hybrid gene introgression into commercial Oreochromis niloticus (L.) stocks in the Philippines. Aquaculture and Fisheries Management 17, 249–258.
McAndrew, B.J. and Majumdar, K.C. (1983) Tilapia stock identification using electrophoretic markers. Aquaculture 30, 249–261.
Meisfjord, J. and Nævdal, G. (1994) Using isoelectric focusing to discern enzyme variation in Northeast Atlantic stocks of the harp seal (Phoca groenlandica). Hereditas 121, 273–281.
Moav, R., Brody, T., Wohlfarth, G. and Hulata, G. (1976) Applications of electrophoretic genetic markers to fish breeding 1. Advantages and methods. Aquaculture 9, 217–228.
Nei, M. and Li, W.H. (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 76, 5269–5273.
Ng, C.S., Low, L.K., Lam, C.P. and Yamada, J. (1986) Thin layer polyacrylamide iso-electric focusing as a method for species identification of tropical fishes. Singapore Journal of Primary Industries 14, 36–45.
Purdom, C.E. (1993) Genetics and Fish Breeding. Chapman & Hall: London, 277 pp.
Regan, C.T. (1910) The Asiatic fishes of the family Anabantidae. Proceedings of The Zoological Society of London 1909[1910], 767–787.
Santos, E.E.M. and Ng, C.S. (1993) Evidence for genetic variation in the sarcoplasmic protein of Nemipterus peronii (Valenciennes). Asian Fisheries Science 6, 265–270.
Sodsuk, P. and McAndrew, B.J. (1991) Molecular systematics of three tilapiine genera Tilapia, Sarotherodon and Oreochromis using allozyme data. Journal of Fish Biology 39(Supplement A), 301–308.
Sokal, R.R. and Rohlf, F.J. (1981) Analysis of frequencies. In: Biometry. The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, (2nd edn) W.H. Freeman and Co., New York, pp. 691–778.
Strickberger, M.W. (1990) Probability and statistical testing. In: Genetics (3rd edn) Macmillan Publishing Co., New York, pp. 126–146.
Sumantadinata, K. and Taniguchi, N. (1982) Biochemical genetic variations in black seabream. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries 48, 143–149.
Sundt, R.C., Dahle, G. and Nævdal, G. (1994) Genetic variation in the hooded seal, Cystophora cristata, based on enzyme polymorphism and multi-locus DNA fingerprinting. Hereditas 121, 147–155.
Taniguchi, N., Sumantadinata, K., Suzuki, A. and Yamada, J. (1982) Genetic variations in isoelectric focusing pattern of sarcoplasmic protein of black seabream. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries 48, 139–141.
Taniguchi, N., Macaranas, J.M. and Pullin, R.S.V. (1985) Introgressive hybridization in cultured tilapia stocks in the Philippines. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries 51, 1219–1224.
Toom, P.M., Ward, C.F. and Weber, J.R. (1982) Identification of fish species by isoelectric focusing. In Chemistry and Biochemistry of Marine Food Products (eds R.E. Martin, G.J. Flick, C.E. Hebard and D.R. Ward) AVI Publishing Co., Connecticut, pp. 51–65.
Wallbrunn, H.M. (1958) Genetics of the Siamese fighting fish, Betta splendens. Genetics 43, 289–298.
Wilkinson, L. (1988) SYSTAT: The System for Statistics (Version 4) STYSTAT, Inc.: Evanston, Illinois.
Yamada, J. and Suzuki, A. (1982) Identification of fish species by thin layer isoelectric focusing of sarcoplasmic proteins. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries 48, 73–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoo, G., Loh, E.Y., Lim, T.M. et al. Genetic variation in different varieties of Siamese fighting fish using isoelectric focusing of sarcoplasmic proteins. Aquaculture International 5, 537–549 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018357400571
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018357400571