Abstract
Purpose. To study the influence of GI hydrodynamics and drug particle size on felodipine absorption in the dog.
Methods. Labradors fistulated at midjejunum were used to selectively study the influence of hydrodynamics and particle size on the in vivodissolution and absorption of the poorly soluble, lipophilic drug felodipine. A combination of infusion and oral administration of either normal saline or a 5% glucose solution was used to maintain “fasted” and establish “fed” state motility patterns, respectively. The absorption characteristics of both a micronized (8 μm) and a coarse fraction (125 μm) of felodipine were subsequently studied under these two motility patterns.
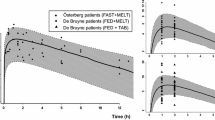
Results. A reduction in particle size led up to an approximate 22-fold increase in maximum plasma concentration and up to an approximate 14-fold increase in area under the curve, with a commensurate decrease in the time at which the maximum plasma concentration occurred. Although the absorption of felodipine from the solution and micronized suspension was not influenced by a change in the hydrodynamics, felodipine was absorbed from the coarse suspension almost twice as well in the “fed” state as under “fasted” conditions.
Conclusions. Absorption from coarse suspensions of felodipine was sensitive to luminal hydrodynamics, whereas micronized suspensions were not. However, the particle size seems to have a much more important influence on the bioavailability of felodipine than the hydrodynamics per se.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. A. Noyes and W. R. Whitney. Ñber die Auflösungsgeschwindigkeit von festen Stoffen in ihren eigenen Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 23:689–692 (1897).
W. Nernst. Theorie der Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit in heterogenen Systemen. Z. Phys. Chem. 47:52–55 (1904).
E. Brunner. Theorie der Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit in heterogenen Systemen. Z. Phys. Chem. 47:56–102 (1904).
V. G. Levich. Physicochemical Hydrodynamics Prentice Hall, Engelwood Cliffs, New Jersey, 1962.
R. M. Atkinson, C. Bedford, K. J. Child, and E. G. Tomich. Effect of particle size on blood griseofulvin levels in man. Nature 193:588–589 (1962).
A. Jounela, P. Pentikainen, and A. Sothmann. Effect of particle size on the bioavailability of digoxin. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 8:365–370 (1975).
M. Wilsson-Rahmberg and O. Jonsson. Method for long-term intestinal access in the dog. Lab. Anim. 31:231–240 (1997).
M. L. Siegle, H. R. Schmid, and H. J. Ehrlein. Effects of ileal infusions of nutrients on motor patterns of canine small intestine. Am. J. Physiol. 259:G78–G85 (1990).
W. Brener, T. R. Hendrix, and P. R. McHugh. Regulation of the gastric emptying of glucose. Gastroenterology 85:76–82 (1983).
T. B. Buxton, J. K. Crockett, W. L. Moore, and J. P. Rissing. Protein precipitation by acetone for the analysis of polyethylene glycol in intestinal perfusion fluid. Gastroenterology 76:820–824 (1979).
M. Ahnoff. Determination of felodipine in plasma by capillary gas chromatography with electron capture detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2:519–526 (1984).
N. Kaneniwa and N. Watari. Dissolution of slightly soluble drugs. I. Influence of particle size on dissolution behavior. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 22:1699–705 (1974).
M. Kraml, J. Dubuc, and R. Gaudry. Gastrointestinal absorption of griseofulvin: 2. Influence of particle size in man. Antibiot Chemother. 12:239–242 (1962).
S. Lin, J. Menig, and L. Lachman. Interdependence of physiological surfactant and drug particle size on the dissolution behavior of water-insoluble drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 57:2143–2148 (1968).
M. Efentakis and J. B. Dressman. Gastric juice as a dissolution medium: surface tension and pH. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 23:97–102 (1998).
P. E. Luner and D. VanDer Kamp. Wetting behaviour of bile salt-lipid dispersions and dissolution media patterned after intestinal fluids. J. Pharm. Sci. 90:348–359 (2001).
N. Kaneniwa and N. Watari. Dissolution of slightly soluble drugs. III. Surface condition of powder particles and their initial dissolution behavior. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 25:867–75 (1977).
R. G. Compton, P. J. Daly, and W. A. House. The dissolution of Iceland spar crystals: the effect of surface morphology. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 113:12–20 (1986).
A. Rubinstein. Gastrointestinal physiological variables affecting the performance of oral sustained release dosage forms. In A. Yacobi and E. Halperin (Ed.) Oral Sustained Release Formulations: Design and Evaluation, Pergamon Press, New York, 1988 chapter 6 pp. 123–156.
P. M. Armenante and D J. Kirwan. Mass transfer to microparticles in agitated systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 44:2781–2796 (1989).
P. Harriott. Mass transfer to particles A. I. Ch. E. J. 8:93–102 (1962).
P. Harriott. Mass transfer to particles: part 2. Suspended in a pipeline. A. I. Ch. E. J. 8:93–102 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scholz, A., Abrahamsson, B., Diebold, S.M. et al. Influence of Hydrodynamics and Particle Size on the Absorption of Felodipine in Labradors. Pharm Res 19, 42–46 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013651215061
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013651215061