Abstract
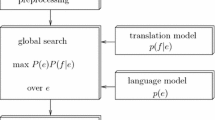
This article presents statistical language translation models,called “dependency transduction models”, based on collectionsof “head transducers”. Head transducers are middle-out finite-state transducers which translate a head word in a source stringinto its corresponding head in the target language, and furthertranslate sequences of dependents of the source head into sequencesof dependents of the target head. The models are intended to capturethe lexical sensitivity of direct statistical translation models,while at the same time taking account of the hierarchical phrasalstructure of language. Head transducers are suitable for directrecursive lexical translation, and are simple enough to be trainedfully automatically. We present a method for fully automatictraining of dependency transduction models for which the only inputis transcribed and translated speech utterances. The method has beenapplied to create English–Spanish and English–Japanese translationmodels for speech translation applications. The dependencytransduction model gives around 75% accuracy for an English–Spanishtranslation task (using a simple string edit-distance measure) and70% for an English–Japanese translation task. Enhanced with targetn-grams and a case-based component, English–Spanish accuracy is over76%; for English–Japanese it is 73% for transcribed speech, and60% for translation from recognition word lattices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alshawi, H., A. L. Buchbaum, and F. Xia: 1997, ‘A Comparison of Head Trandsucers and Transfer for a Limited Domain Translation Application’, 35th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and 8th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Madrid, pp. 360–365.
Alshawi, H., S. Bangalore, and S. Douglas: 1998a, ‘Automatic Acquisition of Hierarchical Transduction Models for Machine Translation’, 98: 36th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and 17th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Montreal, pp. 41–47.
Alshawi, H., S. Bangalore, and S. Douglas: 1998, ‘Learning Phrase-Based Head Transduction Models for Translation of Spoken Utterances’, 5th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSPL98), Sydney, pp. 2767–2770.
Brown, P., J. Cocke, S. D. Pietra, V. D. Pietra, J. Lafferty, R. Mercer, and P. Rossin: 1990, ‘A Statistical Approach to Machine Translation’, Computational Linguistics 16, 79–85.
Brown, P., S. D. Pietra, V. D. Pietra, and R. Mercer: 1993, ‘The Mathematics ofMachine Translation: Parameter Estimation’, Computational Linguistics 19, 263–312.
Booth, T.: 1969, ‘Probabilistic Representation of Formal Languages’, Conference Record of 1969 Tenth Annual IEEE Symposium on Switching and Automata Theory, Waterloo, Ontario, pp. 74–81.
Collins, M. J.: 1996, ‘A New Statistical Parser Based on Bigram Lexical Dependencies’, 34th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Santa Cruz, CA, pp. 184–191.
Early, J.: 1970, ‘An Efficient Context-Free Parsing Algorithm’, Communications of the ACM 14, 61–74.
Gale, W. and K. Church: 1991, ‘Identifying Word Correspondences in Parallel Texts’, [DARPA] Workshop on Speech and Natural Language Processing, Asilomar, CA, pp. 152–157.
Hirschman, L., M. Bates, D. Dahl, W. Fisher, J. Garofolo, D. Pallett, K. Hunicke-Smith, P. Price, A. Rudnicky, and E. Tzoukermann: 1993, ‘Multi-Site Data Collection and Evaluation in Spoken Language Understanding’, Human Language Technology Workshop, San Francisco, pp. 19–24.
Hudson, R.: 1984, Word Grammar, Blackwell, Oxford.
McCord, M.: 1988, ‘A Multi-Target Machine Translation System’, Proceedings of the International Conference on Fifth Generation Computer Systems, Tokyo, pp. 1141–1149.
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology): 1997, Speech Recognition Scoring Package, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD.
Sumita, E. and H. Iida: 1995, ‘Heterogeneous Computing for Example-Based Translation of Spoken Language’, Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Theoretical and Methodological Issues in Machine Translation TMI 95, Leuven, pp. 273–286.
van Noord, G., J. Dorrepaal, P. van der Eijk, M. Florenza, H. Huessink, and L. des Tombe: 1991, ‘An Overview of Mimo2’, Machine Translation 6, 201–214.
Vilar, J., V. M. Jiménez, J. C. Amengual, A. Castellanos, D. LLorens, and E. Vidal: 1996, ‘Text and Speech Translation by Means of Subsequential Transducers’, Natural Language Engineering 2, 351–354.
Worm, K. L.: 1998, ‘A Model for Robust Processing of Spontaneous Speech by Integrating Viable Fragments’, 98: 36th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and 17th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Montreal, pp. 1403–1407.
Wu, D.: 1997, ‘Stochastic Inversion Transduction Grammars and Bilingual Parsing of Parallel Corpora’, Computational Linguistics 23, 377–404.
Younger, D.: 1967, ‘Recognition and Parsing of Context-Free Languages in Time n 3', Information and Control 10, 189–208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshawi, H., Bangalore, S. & Douglas, S. Head-Transducer Models for Speech Translation and Their Automatic Acquisition from Bilingual Data. Machine Translation 15, 105–124 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011187330969
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011187330969