Abstract
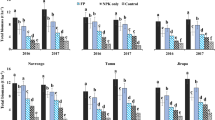
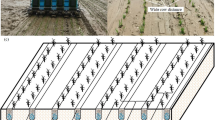
The recovery of applied nitrogen by rice is low due to several loss processes operating in the ricefields. Split application of fertilizer suggested for increasing nitrogen-use efficiency is often not practical in rainfed lowland rice due to adverse soil–water situations. Hence, the entire required amount of N has to be applied in one single application when the water regime is favorable. A single broadcast application, however, increases N loss. Deep placement of urea supergranules (USG) has been proven to improve N fertilizer efficiency. The placement technology is best suited to conditions where the predominant N loss mechanism is ammonia volatilization rather than leaching or denitrification. Deep placement of USG thus has greater benefit over surface split application on soils with moderate to heavy texture, low permeability and percolation rate, and high cation exchange capacity and pH. Environments and management factors conducive to high ammonia volatilization potential would benefit most from deep-placement technology. Improved N recovery and efficiency of USG has been well-documented for lowland rice, but its market availability and methods to achieve placement pose problems. The technology has very limited adoption because USG is not commercially available or manufactured in most countries, and labor requirement is high with hand placement. Manual application creates more difficulties in handling the granules, besides taking 36–42 more hours per hectare, than 2 split broadcast applications of prilled urea. Applicators developed so far have not worked satisfactorily under standing water conditions and in direct-seeded rice conditions due to hardness of the soil. Hence, it is necessary to develop a suitable applicator to overcome these difficulties. Alternatively, for direct-seeded rice, N-fertilizers can be subsoil-banded near seedrows. The placement technology, if adopted by the farmers of the potential lowland areas in eastern India, is expected to give an additional production of 5.6 million tons of rice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanian V, Morales AC, Cruz RT & Abdul Rachman S (1997) On-farm adaptation of knowledge-intensive nitrogen management technologies for rice systems. Paper presented at the ‘International Workshop on Natural Resource Management in Rice Systems: Technology Adaptation for Efficient Nutrient Use’, Bogor, Indonesia, 2–5 December 1996. 26 p
Cao ZH, De Datta SK & Fillery IRP (1984) Nitrogen-15 balance and residual effects of urea-N in wetland rice fields as affected by deep placement techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48: 203–208
Chalam AB, Chakravorti SP & Mohanty SK (1989) Comparative efficiency of urea super granule and prilled urea for lowland rice Oryza sativa using 15N. Indian J Agric Sci 59: 400–1
Crasswell ET, De Datta SK, Obscemea WN & Hartantyo Mq (1981) Time and mode of nitrogen fertilizer application to tropical rice. Fert Res 2: 247–259
Daftardar SY & Savant SK (1995). Evaluation of environmentally friendly fertilizer management for rainfed lowland rice on tribal farmers' fields in India. pp 173–186. In: Fragile Lives in Fragile Ecosystems. Proceedings of the International Rice Research Conference; 13–17 Feb 1995. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, PO Box 933, Manila, Philippines
De Datta SK & Patrick WH Jr (1986) Nitrogen Economy of Flooded Rice Soils. Martinus Nijhof Publishers, Dordrecht, the Netherlands
De Datta SK & Buresh RJ (1989) Integrated nitrogen management in irrigated rice. Adv Soil Sci 10:143–169
Devasenapathy P & Palaniappan SP (1995) Band placement of urea solution increases N-use efficiency in transplanted lowland rice. Int Rice Res Notes 20:19
FAAS (Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences) (1994) A studying report on urea deep-point applicator in paddy field. Mimeo 10 p FAAS, Fuzhou, Fujian 350003, China
Fillery IRP & Vlek PLG (1986) Reappraisal of the significance of ammonia volatilization as an N loss mechanism in flooded rice fields. Fert Res 9: 79–98
Godwin DC, Singh U, Buresh RJ & De Datta SK (1990) Modeling of nitrogen dynamics in relation to rice growth and yield. Trans. 14th Int Cong Soil Sci, Kyoto, Japan IV: 320–325
IFA-IFDC-FAO (1992) Fertilizer Use by Crop. Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, Italy
INSFFER (International Network on Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Evaluation for Rice) (1985) Summary reports on the fifth international trial on nitrogen fertilizer efficiency in irrigated wetland rice (1981–1984). IRRI, Los Banos, PO Box 933, Manila, Philippines
INSFFER (International Network on Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Evaluation for Rice) (1986) Progress Report on the First International Trial on Comparison of Hand and Machine Applied Prilled Urea and Urea Supergranules in Lowland Rice (1984–1985). IRRI, Los Banos, PO Box 933, Manila, Philippines
Katyal JC, Singh B, Sharma VK & Crasswell ET (1985) Efficiency of some modified urea fertilizer for lowland rice grown on a permeable soil. Fert Res 6:279–290
Kumar V & Kaore SV (1989) Use of urea super granule in rice — IFFCO's experience. In: Kumar et al. (eds) Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Use, Vol III. Urea Supergranules for Increasing Nitrogen Use Efficiency, pp 138–143. Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative (IFFCO), New Delhi-110 019, India
Kumar V, Shrotriya GC & Kaore SV (eds) (1989) Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Use, Vol III. Urea Supergranules for Increasing Nitrogen-use Efficiency, 143 p. Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative (IFFCO), New Delhi-110 019, India
Kumar K, Thangaraju M & Kannaiyan S (1995) Use of nitrification inhibitors and nitrogen-use efficiency in lowland rice soil. In: Kannaiyan S (ed) Rice Management Biotechnology, pp 101–116. Associated Publishing Co., New Delhi, India
Lapitan JA, Khan AU, Calabio J & Bautista (1985) Evaluation of fertilizer placement machines and their current developments. Paper presented at the International Rice Research Conference, IRRI, Los Banos, Philippines, 1–5 June 1985. Mimeo 25 p
Mahapatra P, Panda D & Mohanty SK (1990) Efficiency of urea based fertilizers for wetland rice Oryza sativa. J Agric Sci (Cambridge), 113: 187–191
Misra C, Mohanty BC, Das BS & Savant NK (1995) Relationship between some selected soil properties and yield of transplanted rice fertilized with urea briquettes. Oryza 32: 178–183
Mohanty SK & Dash RN (1982) Chemistry of waterlogged soils. In: Wetlands: Ecology and Management, pp 389–396. National Institute of Ecology and International Scientific Publications, Jaipur, India
Mohanty SK, Chakravorti SP & Bhadrachalam A (1989) Nitrogen balance studies in rice using 15N labeled urea and urea super granules. J Agric Sci (Cambridge) 113: 119–121
Pande HK & Mohanty SK (1986) Consolidated report on ICAR coordinated project on chemistry of submerged soils under rice cultivation in high rainfall areas. Central Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, India. 150 p
Patel SK, Panda D & Mohanty SK (1989) Relative ammonia loss from urea based fertilizers applied to rice under different hydrological situations. Fert Res 19: 113–119
Patel SK, Panda D & Mohanty SK (1990) Leaching loss of nitrogen from urea based fertilizers applied to rice under different hydrological conditions. Oryza 27: 342–345
Prasad R & De Datta SK (1979) Increasing fertilizer nitrogen efficiency in wetland rice. In: Nitrogen and Rice, pp 465–485. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines
Rai OP, Singh NB & Singh RA (1991) Effect of varying doses of nitrogen applied in different forms on the yield and nitrogen efficiency of rice. Oryza 28: 167–170
Rao MV, Padalia CR, Rao KS, Prasad M, Reddy MD, Manna GB, Chandra D & Singh J (1989) Comprehensive studies on use of urea supergranules. In: Kumar V, Shrotriya GC and Kaore SV (eds) Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Use, Vol III. Urea Supergranules for Increasing Nitrogen-use Efficiency, pp 97–113. Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative (IFFCO), New Delhi-110 019, India
Rao KS & Moorthy BTS (1993) Effect of different urea formulations on the yield of medium and long duration varieties of rice. Oryza 30: 129–132
Roger PA & Watanabe I (1986) Technologies for utilizing biological nitrogen fixation in wetland rice: Potentialities, current usage and limiting factors. Fert Res 9:39–77
Sarvanan A, Velu V & Ramanathan km (1988) Effect of source of methods of nitrogen application on volatilization loss of ammonia and yield of rice under submerged of Cauvery Delta, India. Oryza 23: 145–148
Savant NK & De Datta SK (1982) Nitrogen transformation in wetland rice soils. Adv Agron 35:241–294
Savant NK, Ongkingco PS, Zarate IV, Torrizo FM & Stangel PJ (1991) Urea briquette applicator for transplanted rice. Fert Res 28: 323–331
Savant NK, Ongkingco PS, Garcia FD, Dhane SS, Khadse RR, Chavan SA & Rao KS (1992) Agronomic performance of urea briquette applicator in transplanted rice. Fert Res 32: 139–142
Savant NK & Stangel PJ (1997) Urea briquettes containing diammonium phosphate: a potential new NP fertilizer for transplanted rice. Fert Res (in press)
Schnier HF, De Datta SK, Mengel K, Marqueses EP & Faronilo JE (1988) Nitrogen-use efficiency, floodwater properties and nitrogen-15 balance in transplanted lowland rice as affected by liquid band placement. Fert Res 16: 241–255
Schnier HF, De Datta SK, Fagi AM, Eaqub M, Ahmed F, Tejaswarana R & Mazid A (1993) Yield response of wetland rice to band placement of urea solution in various soils in the tropics. Fert Res 36: 221–227
Sharma AR (1994) Fertilizer management in lowland rice under excess water condition. Fert News 39(5): 35–44
Sharma SK (1995) Urea super granules — its performance and prospects for rice production. In: Kannaiyan S (ed) Rice Management Biotechnology, pp 117–134. Associated Publishing Co., New Delhi, India
Shoji S & Kanno H (1994) Use of olefin-coated fertilizers for increasing fertilizer efficiency and reducing nitrate leaching and nitrous oxide emissions. Fert Res 39(2): 147–152
Shukla RK, Sharma RS & Chipde SJ (1993) Improvement of N-use efficiency in transplanted rice. Oryza 30: 259–261
Singh U & Thornton PK (1992) Using crop models for sustainability and environmental quality assessment. Outlook Agric 21(3): 209–218
Singh U & Buresh RJ (1994) Fertilizer technology for increased fertilizer efficiency in paddy rice fields. In: Proceedings of the 15th World Cong Soil Sci, pp 643–653. Acapulco, Mexico
Singh U, Cassman KG, Ladha JK & Bronson KF (1995) Innovative nitrogen management strategies for lowland rice systems. In: Fragile Lives in Fragile Ecosystems, pp 230–254. Proceedings of the International Rice Research Conference; 13–17 Feb 1995. International Rice Research Institute, P.O. Box 933, Manila, Philippines
Stangel PJ (1989) Urea supergranule for transplanted rice. IFDC Research Review. In: V. Kumar et al.(eds) Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Use, Vol III, pp 1–9. Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative (IFFCO) Limited, New Delhi, India
Subbiah SV (1992) Agronomic efficiency of modified urea materials. Oryza 29: 374–375
Tandon HLS (1989) Urea super granule for increasing nitrogen efficiency in rice. An overview. In: Kumar V et al. (eds) Soil Fertility and Fertilizer Use, Vol III, pp 10–22. IFFCO Ltd., New Delhi, India
Tyagi RC, Singh H, Rammohan Rao DS, Singh T & Singh BR (1994) Effect of levels, sources and time of nitrogen application in transplanted rice. Oryza 31: 297–300
Wetselaar R (1985) Deep-point placed urea in a flooded soil: A mechanistic view. In: Special Publication SP-6. pp 7–14. International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC), Muscle Shoals, USA
Yamada Y, Ahmad A, Alcantara A & Khan NH (1979) Nitrogen efficiency study under flooded paddy conditions. In: Proc. of Final INPUTS Review Meeting, pp 39–74, East West Center, Honolulu, Hawaii
Zhu ZL, Cai GX, Simpson JR, Zhang SL, Chen DL, Jackson AV & Freney JR (1989) Processes of nitrogen loss from fertilizers applied to flooded rice fields on calcareous soil in north-central China. Fert Res 18: 101–115
Zhu Z (1990) Management of nitrogen fertilizers for flooded rice in relation to nitrogen transformations, IV, pp 337–342 Trans 14th Int Cong Soil Sci, Kyoto Japan
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, S., Singh, U., Balasubramanian, V. et al. Nitrogen deep-placement technologies for productivity, profitability, and environmental quality of rainfed lowland rice systems. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 53, 43–57 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009731922431
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009731922431