Abstract
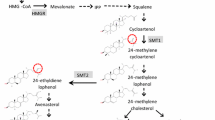
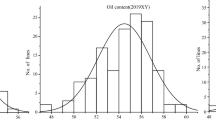
Undesirable characteristic of rapeseed oil is a relatively high level of linolenic acid (18:3), which is easily oxidized leading to rancidity and a shortened shelf life of the oil. Previous attempts to reduce linolenic acid levels in rapeseed oil through breeding have been impaired by complex genetics and strong environmental sensitivity of this trait. Therefore, our objective was to develop molecular markers for low linolenic acid that could facilitate the breeding of low linolenic rapeseed. Bulked segregant analysis was employed to identify two RAPD markers associated with 18:3 in a doubled haploid population segregating for linolenic and erucic acid levels. Based on analysis of individual DH lines, the markers RM350 and RM574, representing two independent loci, accounted for a total of 39% of the genetic variability in this population. This marker RM350 alone accounted for 25% genetic variation for this trait with no evidence of recombination. Significant interlocus interaction found between the markers RM350 and RM574 suggested that epistasis was involved in the genetic control of 18:3 level in this population. Another marker designated as RM322, which was independent of the other two, was found significantly associated with the erucic acid level and oil content. RAPD markers identified in this study should be a useful tool for the early detection of low linolenic, or low or high erucic acid genotypes in rapeseed breeding programs based on doubled haploids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannon, C.D., G.J. Breen, J.D. Craske, N.T. Hai & K.L. O'Rourke, 1982. Analysis of fatty acid methyl esters with accuracy and reliability. Jour Chromatograph 247: 71–89.
Chen, J. & W.D. Beversdorf, 1990. Fatty acid inheritance in microspore-derived populations of spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 80: 465–469.
Diepenbrock, W. & R.F. Wilson, 1987. Genetic regulation of linolenic acid concentration in rapeseed. Crop Sci 27: 75–77.
Dorrell, D.G. & R.K. Downey, 1964. The inheritance of erucic acid level in rapeseed (Brassica campestris). Can Jour Plant Sci 44: 499–504.
Downey, R.K. & B.M. Craig, 1964. Genetic control of fatty acid biosynthesis in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Jour Am Oil Chem Soc 41: 475–478.
Edwards, K., C. Johnstone & Thompson, 1991. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of the plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 1349.
Gomez, K.A. & A.A. Gomez, 1984. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. Second Edition. John Willey & Sons, New York, USA.
Harvey, B.L. & R.K. Downey, 1964. The inheritance of erucic acid content in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Can Jour Plant Sci 44: 104–111.
Hu, J., C. Quiros, P. Arus, D. Struss & G. Röbbelen, 1995. Mapping of a gene determining linolenic acid concentration in rapeseed with DNA-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 90: 258–262.
Jourdren, C., P. Barret, R. Horvais, R. Delourme & M. Renard, 1996a. Identification of RAPD markers linked to linolenic acid genes in rapeseed. Euphytica 90: 351–357.
Jourdren, C., P. Barret, R. Horvais, N. Foisset, R. Delourme & M. Renard, 1996b. Identification of RAPD markers linked to loci controlling erucic acid acid level in rapeseed. Molecular Breeding 2: 61–71.
Kilian, A., B.J. Stefansson, M.A. Saghai-Maroof & A. Kleinhofs, 1994. RFLP markers linked to the durable rust resistance gene Rpg1 in barley. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 7: 298–301.
Kondra, Z.P. & P.M. Thomas, 1975. Inheritance of oleic, linoleic, and linolenic acids in seed oil of rapeseed (Brassica napus). Can Jour Plant Sci 55: 205–210.
Lander, E.S., P. Green, J. Abrahamson, A. Barlow, M.J. Daley, S.E. Lincoln & L. Newburn, 1987. An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1: 174–181.
Luchs, W. & W. Friedt, 1994. The major oil crops. In: Dennis Murphy (Ed), Designer Oil Crops. Breeding, Processing and Biotechnology. VCH, Weinheim, Germany.
Michelmore, R.W., I. Paran & R.V. Kesseli, 1991. Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 9828–9832.
Miklas, P.N., J.R. Stavely & J.D. Kelly, 1993. Identification and potential use of a molecular marker for rust resistance on common bean. Theor Appl Genet 86: 705–712.
Paran, I. & R.W. Michelmore, 1993. Development of reliable PCR based markers linked to downy resistance genes in lettuce. Theor Appl Genet 85: 985–993.
Polsoni, L., L.S. Kott and W.D. Beversdorf, 1988. Large scale microspore culture technique for mutation, selection studies in Brassica napus L. Can Jour Bot 66: 1681–1685.
Rajcan, I., L.S. Kott, W.D. Beversdorf & K.J. Kasha, 1997. Performance of doubled haploid populations segregating for linolenic acid levels in spring rapeseed. Crop Sci 37: 1438–1442.
Röbbelen, G. and Nitsch, A. 1975. Genetical and physiological investigations on mutants for polyenoic fatty acids in rapeseed, Brassica napus L. I. Selection and description of new mutants. Plant Breeding 75: 93–105.
Röbbelen, G. & W. Thies, 1980. Biosynthesis of seed oil and breeding for improved oil quality of rapeseed. In: S. Tsunoda, K. Hinata & C. Gomez-Campo (Eds), Brassica Crops and Wild Allies, pp. 253–283. Japn Sci Soc Press, Tokyo.
Roy, N.N. & A.W. Tarr, 1985. IXLIN-an interspecific source for high linoleic and low linolenic acids in rapeseed (Brasica napus L.). Z Pflanzenzüchtg 95: 201–209.
SAS Institute, Inc. 1988. SAS/STAT User's guide, Release 6.03 Edition. Cary, NC.
Siebel, J. & K.P. Pauls, 1989. Inheritance patterns of erucic acid content in populations of Brassica napus microspore-derived spontaneous diploids. Theor Appl Genet 77: 489–494.
Stefansson, B.R. & F.W. Hougen, 1964. Selection of rape plants (Brassica napus) with seed oil practically free from erucic acid. Can Jour Plant Sci 44: 359–364.
Stefansson, B.R. & A.K. Storgaard, 1969. Correlation involving oil and fatty acids in rapeseed. Can Jour Plant Sci 49: 573–580.
Tanhuanpaa, P.K., J.P. Vilkki & H.J. Vilkki, 1995. Association of a RAPD marker with linolenic acid concentration in the seed oil of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Genome 38: 414–416.
Thomas, P.M. & Z.P. Kondra, 1973. Maternal effects on the oleic, linoleic, and linolenic acid content of rapeseed oil. Can Jour Plant Sci 53: 221–225.
Thormann, C.E., J. Romero, J. Mantet & T.C. Osborn, 1996. Mapping loci controlling the concentrations of erucic and linolenic acids in seed oil of Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Genet 93: 282–286.
Welsh, J. & M. McClelland, 1990. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 7213–7218.
Williams, J.G.K., A.R. Kubelik, K.J. Livak, J.A. Rafalski & S.V. Tingey, 1990. DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18: 6531–6535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajcan, I., Kasha, K., Kott, L. et al. Detection of molecular markers associated with linolenic and erucic acid levels in spring rapeseed (Brassica napur L.). Euphytica 105, 173–181 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003494217074
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003494217074