Abstract
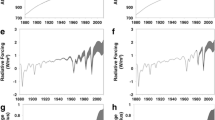
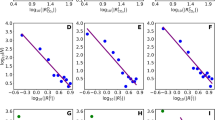
We analyse spatio-temporal patterns of near-surface temperature change to provide an attribution of twentieth century climate change. We apply an “optimal detection” methodology to seasonal and annual data averaged over a range of spatial and temporal scales. We find that solar effects may have contributed significantly to the warming in the first half of the century although this result is dependent on the reconstruction of total solar irradiance that is used. In the latter half of the century, we find that anthropogenic increases in greenhouses gases are largely responsible for the observed warming, balanced by some cooling due to anthropogenic sulphate aerosols, with no evidence for significant solar effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M. R. and S. F. B. Tett: 1999, ‘Checking for model consistency in optimal fingerprinting’, Cli. Dyn. 15, 419–434.
Haigh, J. D.: 1999, ‘A GCM study of climate change in response to the 11-year solar cycle’, Q. J. R. Met. Soc. 125, 871–892.
Hasselmann, K.: 1993, ‘Optimal fingerprints for the detection of Time-dependent Climate Change’, J. Clim. 6, 1957–1971.
Hegerl, G. C., K. Hasselman, U. Cubasch, J. F. B. Mitchell, E. Roeckner, R. Voss, and J. Waskewitz: 1997, ‘Multi-fingerprint detection and attribution analysis of greenhouse gas, greenhouse gasplus-aerosol and solar forced climate change’, Cli. Dyn. 13, 613–634.
Hegerl, G. C., P. A. Stott, S. F. B. Tett, J. F. B. Mitchell, M. R. Allen, and U. Cubasch: 1999, ‘Optimal detection and attribution of climate change: sensitivity of results to climate model differences’, Climate Dynamics, in press.
Hoyt, D. V. and K. H. Schatten: 1993, ‘A discussion of plausible solar irradiance variations, 1700–1992’, J. Geophys. Res. 98, 18,895–18,906.
Johns, T. C., R. E. Carnell, J. F. Crossley, J. M. Gregory, J. F. B. Mitchell, C. A. Senior, S. F. B. Tett, and R. A. Wood: 1997, ‘The second Hadley Centre coupled ocean-atmosphere GCM: model description, spinup and validation’, Cimate Dynamics 13, 103–134.
Lean, J., J. Beer, and R. Bradley: 1995, ‘Reconstruction of solar irradiance since 1610: implications for climate change’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 22, 3195–3198.
Parker, D. E., P. D. Jones, C. K. Folland, and A. Bevan: 1994, ‘Interdecadal changes of surface temperature since the late nineteenth century’, J. Geophys. Res. 99, 14,373–14,399.
Stott, P. A. and S. F. B. Tett: 1998, ‘Scale-dependent detection of climate change’, J. Climate 11, 3282–3294.
Stott, P. A., S. F. B. Tett, G. S. Jones, M. R. Allen, W. J. Ingram, and J. F. B. Mitchell: 1999, ‘Attribution of twentieth century temperature change to natural and an thropogenic causes’, Climate Dynamics, submitted.
Tett, S. F. B., P. A. Stott, M. R. Allen, W. J. Ingram, and J. F. B. Mitchell: 1999, ‘Causes of twentieth century temperature change near the Earth's surface’, Nature 399, 569–572.
Willson, R. C.: 1997, ‘Total solar irradiance trend during solar cycles 21 and 22’, Science 277, 1963–1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stott, P., Tett, S., Jones, G. et al. Anthropogenic and natural causes of twentieth century temperature change. Space Science Reviews 94, 337–344 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026743928439
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026743928439