Abstract
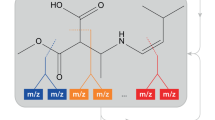
Surface-induced ion activation in combination with a database search strategy based on the Patchwork concept is applied to the determination of peptide sequences. Surface-induced dissociation (SID) is performed in a tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer and in a hybrid sector/time-of-flight mass spectrometer in order to evaluate the importance of accurate mass analysis of the SID fragment ions for peptide identification. The modified Patchwork approach is based on piecing together the peptide blocks in a bidirectional way, simultaneously using low-mass fragments originating from the C-terminus and N-terminus of the molecule, and relying on the measurement of the peptide’s molecular weight with moderate mass accuracy. The results from this analysis are used as search filters in MASCOT’s (http://www.matrixscience.com) Sequence Query search engine, with the simultaneous addition of the full MS/MS peak list. SID is performed with collision targets coated with pure and mixed composition self-assembled monolayers produced by fluorocarbon and hydrocarbon alkanethiolate solutions of varying chemical composition. The resulting MS/MS spectra produced on pure and mixed hydrocarbon SAMs are submitted to the modified version of Patchwork sequencing. It is found that hydrocarbon surfaces improve the relative abundance of larger fragments. Under the moderate mass accuracy conditions (±0.3 u) offered by our linear-TOF-SID instrument, it is found that increasing the abundance of larger fragments dramatically improves the sequencing scores.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yates, J. R. Mass Spectrometry and the Age of the Proteome. J. Mass Spectrom. 1998, 33, 1–19.
Yates, J. R. Database Searching Using Mass Spectrometry Data. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 893–900.
Simpson, R. J.; Connelly, L. M.; Eddes, J. S.; Pereira, J. J.; Moritz, R. L.; Reid, G. E. Proteomic Analysis of the Human Colon Carcinoma Cell Line (LIM 1215): Development of a Membrane Protein Database. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 1707–1732.
Washburn, M. P.; Wolters, D.; Yates, J. R. Large-Scale Analysis of the Yeast Proteome by Multidimensional Protein Identification Technology. Nat. Biotech. 2001, 19, 242–247.
Peng, J. M.; Elias, J. E.; Thoreen, C. C. Evaluation of Multidimensional Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/LC-MS/MS) for Large-Scale Protein Analysis: The Yeast Proteome. J. Prot. Res. 2003, 2, 43–50.
Gevaert, K.; Van Damme, J.; Goethals, M. Chromatographic Isolation of Methionine-Containing Peptides for Gel-Free Proteome Analysis—Identification of More than 800 Escherichia Coli Proteins. Mol. Cell. Prot. 2002, 1, 896–903.
Domon, B.; Alving, K.; He, T. Enabling Parallel Protein Analysis through Mass Spectrometry. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2002, 4, 577–586.
Gras, R.; Muller, M. Computational Aspects of Protein Identification by Mass Spectrometry. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2001, 3, 526–532.
Tabb, D. L.; Smith, L. L.; Breci, L. A. Statistical Characterization of Ion Trap Mass Spectra from Doubly Charged Tryptic Peptides. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1155–1163.
Dongre, A. R.; Jones, J. L.; Somogyi, A.; Wysocki, V. H. Influence of Peptide Composition, Gas-Phase Basicity, and Chemical Modification on Fragmentation Efficiency: Evidence for the Mobile Proton Model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8365–8374.
Laskin, J.; Denisov, E.; Futrell, J. A Comparative Study of Collision-Induced and Surface-Induced Dissociation. 1. Fragmentation of Protonated Dialanine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 9703–9714.
Laskin, J.; Denisov, E.; Futrell, J. Comparative Study of Collision-Induced and Surface-Induced Dissociation. 2: Fragmentation of Small Alanine-Containing Peptides in FT-ICR MS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 1895–1900.
Senko, M. W.; Speir, J. P.; McLafferty, F. W. Collisional Activation of Large Multiply Charged Ions Using Fourier Transform Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2801–2808.
Feng, R.; Konishi, Y. Analysis of Antibodies and Other Large Glycoproteins in the Mass Range of 150,000–200,000 Da by Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 2090–2095.
Dongre, A. R.; Somogyi, A.; Wysocki, V. H. Surface-Induced Dissociation: An Effective Tool to Probe Structure, Energetics, and Fragmentation Mechanisms of Protonated Peptides. J. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 31, 339–350.
DeKrey, M. J.; Kenttamaa, H. I.; Wysocki, V. H.; Cooks, R. G. Energy Deposition in [Fe(CO)5]+·Upon Collision with a Metal Surface. Org. Mass Spectrom 1986, 21, 193–195.
Clauser, K. R.; Baker, P.; Burlingame, A. L. Role of Accurate Mass Measurement (+/− 10 ppm) in Protein Identification Strategies Employing MS or MS MS and Database Searching. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2871–2882.
Perkins, D. N.; Pappin, D. J. C.; Creasy, D. M.; Cottrell, J. S. Probability-Based Protein Identification by Searching Sequence Databases Using Mass Spectrometry Data. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 3551–3567.
Schlosser, A.; Lehmann, W. D. Patchwork Peptide Sequencing: Extraction of Sequence Information from Accurate Mass Data of Peptide Tandem Mass Spectra Recorded at High Resolution. Proteomics 2002, 2, 524–533.
Smith, D. L.; Wysocki, V. H.; Colorado, R.; Shmakova, O. E.; Graupe, M.; Lee, T. R. Low-Energy Ion-Surface Collisions Characterize Alkyl and Fluoroalkyl-Terminated Self-Assembled Monolayers on Gold. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3895–3902.
Nikolaev, E. N.; Somogyi, A.; Smith, D. L.; Gu, C.; Wysocki, V. H.; Martin, C. D.; Samuelson, G. L. Implementation of Low-Energy Surface-Induced Dissociation (eV SID) and High-Energy Collision-Induced Dissociation (keV CID) in a Linear Sector-TOF Hybrid Tandem Mass Spectrometer. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 212, 535–551.
Kimmel, J. R.; Engelke, F.; Zare, R. N. Novel Method for the Production of Finely Spaced Bradbury-Nielson Gates. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 4354–4357.
Grill, V.; Shen, J.; Evans, C.; Cooks, R. G. Collisions of Ions with Surfaces at Chemically Relevant Energies: Instrumentation and Phenomena. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 3149–3179.
McLuckley, S. A.; Wells, M. Mass Analysis at the Advent of the 21st Century. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 571–606.
Cotter, R. J. The New Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 445A-451A.
Beck, R. D.; St. John, P.; Homer, M. L.; Whetten, R. L. Impact-Induced Cleaving and Melting of Alkali-Halide Nanocrystals. Science 1991, 253, 879–883.
de Maaijer-Gielbert, J.; Beijersbergen, J. H. M.; Kistemaker, P. G.; Weeding, T. L. Surface-Induced Dissociation of Benzene on a PFPE Liquid Insulator in a Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 1996, 153, 119–128.
Haney, L. L.; Riederer, D. E. Delayed Extraction for Improved Resolution of Ion/Surface Collision Products by Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 397, 225–233.
Kimura, T.; Sugai, T.; Shinohara, H. Surface-Induced Fragmentation of Higher Fullerenes and Endohedral Metallofullerenes. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 9681–9687.
Williams, E. R.; Fang, L.; Zare, R. N. Surface Induced Dissociation for Tandem Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Processes 1993, 123, 233–241.
Fernandez, F. M., Smith, D. L., Somogyi, A., Yang, X., Wysocki, V. H. Comparison of Surface Energy Transfer by Low-energy Collisions on Mixed Self-Assembled Monolayers in a Sector/TOF Mass Spectrometer and in a Dual Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer, submitted.
Laskin, J.; Futrell, J. H. Energy Transfer in Collisions of Peptide Ions with Surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 3413–3420.
Meroueh, O.; Hase, W. L. Effect of Surface Stiffness on the Efficiency of Surface-Induced Dissociation. Phys. Chem., Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 2306–2314.
Schultz, D. G.; Wainhaus, S. B.; Hanley, L. L.; de Sainte Claire, P.; Hase, W. L. Classical Dynamics Simulations of SiMe +3 Ion-Surface Scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 106, 10337–10348.
Meroueh, O.; Hase, W. L. Dynamics of Energy Transfer in Peptide-Surface Collisions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 124, 1524–1531.
Alves, C.; Porter, M. D. Atomic Force Microscopic Characterization of a Fluorinated Alkanethiolate Monolayer at Gold and Correlations to Electrochemical and Infrared Reflection Spectroscopic Structural Descriptions. Langmuir 1993, 9, 3507–3512.
Schönherr, H.; Vancso, G. J. Lattice Imaging of Self-Assembled Monolayers of Partially Fluorinated Disulfides and Thiols on Sputtered Gold by Atomic Force Microscopy. Langmuir 1997, 13, 3769–3774.
Cohen, S. R.; Naaman, R.; Sagiv, J. Translational Energy Transfer from Molecules and Atoms to Adsorbed Organic Monolayers of Long-Chain Amphiphiles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 1208–1211.
Tsao, M. W.; Hoffmann, C. L.; Rabolt, J. F.; Johnson, H. E.; Castner, D. G.; Erdelen, C.; Ringsdorf, H. Studies of Molecular Orientation and Order in Self-Assembled Semifluorinated N-Alkanethiols: Single and Dual Component Mixtures. Langmuir 1997, 13, 4317–4322.
Stone, E.; Gillig, K. J.; Ruotolo, B.; Fuhrer, K.; Gonin, M.; Schultz, A.; Russell, D. H. Surface-Induced Dissociation on a MALDI-Ion Mobility-Orthogonal Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer: Sequencing Peptides from an “In-Solution” Protein Digest. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 2233–2238.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published online October 23, 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, F.M., Smith, L.L., Kuppannan, K. et al. Peptide sequencing using a patchwork approach and surface-induced dissociation in sector-TOF and dual quadrupole mass spectrometers. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 14, 1387–1401 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasms.2003.09.003
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasms.2003.09.003