Abstract
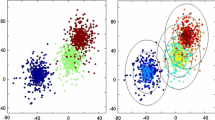
In this paper, we propose self-semi-supervised clustering, a new clustering method for large scale data with a massive null group. Self-semi-supervised clustering is a two-stage procedure: preselect a part of “null” group from the data in the first stage and apply semi-supervised clustering to the rest of the data in the second stage, allowing them to be assigned to the null group. We evaluate the performance of the proposed method using a simulation study and demonstrate the method in the analysis of time course gene expression data from a longitudinal study of Influenza A virus infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu, S., Davidson, I., & Wagstaff, K. (2008). Constrained clustering: Advanced in algorithms, theory, and application. New York: Chapman and Hall/CRC.
Bermejo-Martin, J. F., Martin-Loeches, I., Rello, J., Antón, A., Almansa, R., Xu, L., et al. (2010). Host adaptive immunity deficiency in severe pandemic influenza. Clinical Care, 14, R167.
Bozdogan, H., & Sclove, S. L. (1984). Multi-sample cluster analysis using Akaike’s information criterion. Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 36, 163–180.
Brown, R. L., Durbin, J., & Evans, J. M. (1975). Techniques for testing the constancy of regression relations over time. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 37, 149–192.
Celeux, G., & Soromenho, G. (1996). An entropy criterion for assessing the number of clusters in a mixture model. Journal of Classification, 13, 195–212.
Dasgupta, A., & Raftery, A. E. (1998). Detecting features in spatial point processes with clutter via model-based clustering. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 93, 294–302.
Fan, J., & Fan, Y. (2008). High-dimensional classification using features annealed independence rules. The Annals of Statistics, 36, 2605–2637.
Fraley, C., & Raftery, A. E. (1998). How many clusters? Which clustering method? Answers via model-based cluster analysis. The Computer Journal, 41, 578–588.
Fraley, C., & Raftery, A. E. (2002). Model-based clustering, discriminant analysis, and density estimation. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 97, 611–631.
Herberg, J. A., Kaforou, M., Gormley, S., Sumner, E. R., Patel, S., Jones, K. D. J., et al. (2013). Transcriptomic profiling in childhood H1N1/09 influenza reveals reduced expression of protein sysnthesis genes. The Journal of Infectious Diseases, 208(10), 1664–1668.
Hong, S., Kim, Y., & Park, T. (2014). Practical issues in screening and variable selection in genome-wide association analysis. Cancer Informatics, 13(Suppl 7), 55–65.
Huang, J.-T. & Hasegawa-Johnson, M. (2009). On semi-supervised learning of Gaussian mixture models for phonetic classification. In Proceedings of the North American Chapter of the Association for Compuational Linguistics—Human Language Technologies Workshop on Semi-supervised Learning for Natural Language Processing, pp. 75–83.
Ji, P., & Jin, J. (2012). UPS delivers optimal phase diagram in high dimensional variable selection. The Annals of Statistics, 40, 73–103.
Keribin, C. (2000). Consistent estimation of the order of mixture models. Sankhya. The Indian Journal of Statistics, Series A, 62, 49–66.
Law, M.H.C., Topchy, A., & Jain, A.K. (2005). Model-based clustering with probabilistic constraints. In Proceedings of the 2005 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 641–645.
Lee, K. E., Lim, J., Won, J.-H., Lee, S., & Lee, S.-J. (2015). Finding standard dental arch forms from a nationwide standard occlusion study using a Gaussian functional mixture model. Journal of the Korean Statistical Society, 44, 477–489.
Lim, J., Wang, X., Lee, S., & Jung, S.-H. (2008). A distribution-free test of constant mean in linear mixed effects models. Statistics in Medicine, 27, 3833–3846.
Lu, Z., & Leen, T. K. (2007). Penalized probabilistic clustering. Neural Computation, 19, 1528–1567.
Luan, Y., & Li, H. (2003). Clustering of time-course gene expression data using a mixed-effects model with B-splines. Bioinformatics, 19, 474–482.
Melnykov, V., Melykov, I., & Michael, S. (2016). Semi-supervised model-based clustering with positive ad negative constraints. Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, 10, 327–349.
Pan, W., Shen, X., Jiang, A., & Hebbel, R. (2006). Semisupervised learning via penalized mixture model with application to microaaray sample classification. Bioinformatics, 22, 2388–2395.
Park, C., Ahn, J., Hendry, M., & Jang, W. (2011). Analysis of long period variable stars with nonparametric tests for trend detection. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 106, 832–845.
Ramilo, O., Allman, W., Chung, W., Mejias, A., Ardura, M., Glaser, C., et al. (2007). Gene expression patterns in blood leukocytes discriminate patients with acute infections. Blood, 109, 2066–2077.
Schwarz, G. E. (1978). Estimating the dimensions of a model. The Annals of Statistics, 6, 461–464.
Shental, N., Bar-Hiller, A., Hertz, T., & Weinshall, D. (2003). Computing Gaussian mixture models with EM using equivalence constraints. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 465–472.
Wagstaff, K., Cardi, C., Rogers, S., & Schroedl, S. (2001). Constrained K-means clustering with background knowledge. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 577–584.
Wasserman, L., & Roeder, K. (2009). High-dimensional variable selection. The Annals of Statistics, 37, 2178–2201.
Woods, C. W., McClain, M. T., Chen, M., Zaas, A. K., Nicholson, B. P., Varkey, J., et al. (2013). A host transcriptional signature for presymptomatic detection of infection in humans exposed to influenza H1N1 or H3N2. PLos One, 8(1), e52198.
Yang, Y., Huang, N., Hao, L., & Kong, W. (2017). A clustering-based approach for efficient identification of microRNA combinatorial biomarkers. BMC Genomics, 18(Suppl 2), 210.
Yeung, K. Y., Fraley, C., Murua, A., Raftery, A. E., & Ruzzo, W. L. (2001). Model-based clustering and data transformations for gene expression data. Bioinformatics, 17, 977–87.
Yu, D., Lee, S. H., Lim, J., Xiao, G., Craddock, R. C., & Biswal, B. B. (2018). Fused lasso regression for identifying differential correlations in brain connectome graphs. Statistical Analysis and Data Mining, 11(5), 203–226.
Zhai, Y., Franco, L. M., Atmar, R. L., Quarles, J. M., Arden, N., Bucasas, K. L., et al. (2015). Host transcriptional response to influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections? A prospective cohort study. PLOS Pathogen, 11(6), e1004869.
Zaas, A. K., Chen, M., Varkey, J., Veldman, T., Hero, A. O, I. I. I., Lucas, J., et al. (2009). Gene expression signatures diagnose influenza and other symptomatic respiratory viral infections in humans. Cell Host & Microbe, 6(3), 207–217.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the new faculty research fund of Ajou University and National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant nos: 2012R1A1A3013075, 2017R1A2B2012264).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, S., Choi, H., Lim, J. et al. Self-semi-supervised clustering for large scale data with massive null group. J. Korean Stat. Soc. 49, 161–176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42952-019-00005-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42952-019-00005-z