Abstract
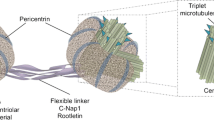
Centrosomes are the major microtubule-organizing center (MTOC), which are important cytoplasmic organelles regulating cell cycle, cell morphology, genomic stability, etc. The role of centrosomes on genomic stability has been reported in different conditions. Centrosomal proteins such as centrin2, pericentrin (PCNT), CEP164 have been reported to facilitate DNA damage repair. Various DNA damage response (DDR) proteins locate on centrosomes or microtubules, such as ATM, ATR, DNA-PKcs, 53BP1, etc. Meanwhile, microtubules serve as the “highway” for the transportation of DNA damage proteins into the nucleus. Microtubules have also been discovered to regulate the DNA double strands breaks (DSBs) mobility in DSBs repair. In this review, we first summarize the association between centrosome, microtubules, and DDR. Further, we discuss the new progression on how cells coordinate DDR with microtubule dynamics to facilitate DSBs repair.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Satta, M., & Matheu, A. (2018). Primary cilium and glioblastoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol, 10, 1758835918801169.
Antonczak, A. K., Mullee, L. I., Wang, Y., Comartin, D., Inoue, T., Pelletier, L., & Morrison, C. G. (2016). Opposing effects of pericentrin and microcephalin on the pericentriolar material regulate CHK1 activation in the DNA damage response. Oncogene, 35, 2003–2010.
Araki, M., Masutani, C., Takemura, M., Uchida, A., Sugasawa, K., Kondoh, J., Ohkuma, Y., & Hanaoka, F. (2001). Centrosome protein centrin 2/caltractin 1 is part of the xeroderma pigmentosum group C complex that initiates global genome nucleotide excision repair. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 18665–18672.
Barton, O., Naumann, S. C., Diemer-Biehs, R., Kunzel, J., Steinlage, M., Conrad, S., Makharashvili, N., Wang, J., Feng, L., Lopez, B. S., et al. (2014). Polo-like kinase 3 regulates CtIP during DNA double-strand break repair in G1. The Journal of Cell Biology, 206, 877–894.
Biehs, R., Steinlage, M., Barton, O., Juhasz, S., Kunzel, J., Spies, J., Shibata, A., Jeggo, P. A., & Lobrich, M. (2017). DNA double-strand break resection occurs during non-homologous end joining in G1 but is distinct from resection during homologous recombination. Molecular Cell, 65(671–684), e675.
Bourke, E., Dodson, H., Merdes, A., Cuffe, L., Zachos, G., Walker, M., Gillespie, D., & Morrison, C. G. (2007). DNA damage induces Chk1-dependent centrosome amplification. EMBO Reports, 8, 603–609.
Bozulic, L., Surucu, B., Hynx, D., & Hemmings, B. A. (2008). PKBalpha/Akt1 acts downstream of DNA-PK in the DNA double-strand break response and promotes survival. Molecular Cell, 30, 203–213.
Breslow, D. K., & Holland, A. J. (2019). Mechanism and regulation of centriole and cilium biogenesis. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 88, 691–724.
Brodie, K. M., & Henderson, B. R. (2012). Characterization of BRCA1 protein targeting, dynamics, and function at the centrosome: A role for the nuclear export signal, CRM1, and Aurora A kinase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287, 7701–7716.
Brodie, K. M., Mok, M. T., & Henderson, B. R. (2012). Characterization of BARD1 targeting and dynamics at the centrosome: The role of CRM1, BRCA1 and the Q564H mutation. Cellular Signalling, 24, 451–459.
Brown, A., & Zhang, R. (2020). Primary cilia: A closer look at the antenna of cells. Current Biology : CB, 30, R1494–R1496.
Brown, N., & Costanzo, V. (2009). An ATM and ATR dependent pathway targeting centrosome dependent spindle assembly. Cell Cycle, 8, 1997–2001.
Buttrick, G. J., Beaumont, L. M., Leitch, J., Yau, C., Hughes, J. R., & Wakefield, J. G. (2008). Akt regulates centrosome migration and spindle orientation in the early Drosophila melanogaster embryo. The Journal of Cell Biology, 180, 537–548.
Buttrick, G. J., & Wakefield, J. G. (2008). PI3-K and GSK-3: Akt-ing together with microtubules. Cell Cycle, 7, 2621–2625.
Caridi, C. P., D’Agostino, C., Ryu, T., Zapotoczny, G., Delabaere, L., Li, X., Khodaverdian, V. Y., Amaral, N., Lin, E., Rau, A. R., et al. (2018). Nuclear F-actin and myosins drive relocalization of heterochromatic breaks. Nature, 559, 54–60.
Chavali, P. L., Putz, M., & Gergely, F. (2014). Small organelle, big responsibility: The role of centrosomes in development and disease (p. 369). Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society of London.
Chen, T. Y., Huang, B. M., Tang, T. K., Chao, Y. Y., Xiao, X. Y., Lee, P. R., Yang, L. Y., & Wang, C. Y. (2021). Genotoxic stress-activated DNA-PK-p53 cascade and autophagy cooperatively induce ciliogenesis to maintain the DNA damage response. Cell Death and Differentiation, 28, 1865–1879.
Chow, K. H., Factor, R. E., & Ullman, K. S. (2012). The nuclear envelope environment and its cancer connections. Nature Reviews Cancer, 12, 196–209.
Clement, C. A., Ajbro, K. D., Koefoed, K., Vestergaard, M. L., Veland, I. R., Henriques de Jesus, M. P., Pedersen, L. B., Benmerah, A., Andersen, C. Y., Larsen, L. A., et al. (2013). TGF-beta signaling is associated with endocytosis at the pocket region of the primary cilium. Cell Reports, 3, 1806–1814.
Conduit, P. T., Wainman, A., & Raff, J. W. (2015). Centrosome function and assembly in animal cells. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 16, 611–624.
Conroy, P. C., Saladino, C., Dantas, T. J., Lalor, P., Dockery, P., & Morrison, C. G. (2012). C-NAP1 and rootletin restrain DNA damage-induced centriole splitting and facilitate ciliogenesis. Cell Cycle, 11, 3769–3778.
Dawe, H. R., Farr, H., & Gull, K. (2007). Centriole/basal body morphogenesis and migration during ciliogenesis in animal cells. Journal of Cell Science, 120, 7–15.
Dellino, G. I., Palluzzi, F., Chiariello, A. M., Piccioni, R., Bianco, S., Furia, L., De Conti, G., Bouwman, B. A. M., Melloni, G., Guido, D., et al. (2019). Release of paused RNA polymerase II at specific loci favors DNA double-strand-break formation and promotes cancer translocations. Nature Genetics, 51, 1011.
Dobrzynska, A., Gonzalo, S., Shanahan, C., & Askjaer, P. (2016). The nuclear lamina in health and disease. Nucleus, 7, 233–248.
Dodson, H., Bourke, E., Jeffers, L. J., Vagnarelli, P., Sonoda, E., Takeda, S., Earnshaw, W. C., Merdes, A., & Morrison, C. (2004). Centrosome amplification induced by DNA damage occurs during a prolonged G2 phase and involves ATM. EMBO Journal, 23, 3864–3873.
Dodson, H., Wheatley, S. P., & Morrison, C. G. (2007). Involvement of centrosome amplification in radiation-induced mitotic catastrophe. Cell Cycle, 6, 364–370.
Estrem, C., & Moore, J. K. (2020). Help or hindrance: How do microtubule-based forces contribute to genome damage and repair? Current Genetics, 66, 303–311.
Fan, G., Sun, L., Meng, L., Hu, C., Wang, X., Shi, Z., Hu, C., Han, Y., Yang, Q., Cao, L., et al. (2021). The ATM and ATR kinases regulate centrosome clustering and tumor recurrence by targeting KIFC1 phosphorylation. Nature Communications, 12, 20.
Fang, E. F., Scheibye-Knudsen, M., Chua, K. F., Mattson, M. P., Croteau, D. L., & Bohr, V. A. (2016). Nuclear DNA damage signalling to mitochondria in ageing. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 17, 308–321.
Farber-Katz, S. E., Dippold, H. C., Buschman, M. D., Peterman, M. C., Xing, M., Noakes, C. J., Tat, J., Ng, M. M., Rahajeng, J., Cowan, D. M., et al. (2014). DNA damage triggers Golgi dispersal via DNA-PK and GOLPH3. Cell, 156, 413–427.
Fraser, M., Harding, S. M., Zhao, H., Coackley, C., Durocher, D., & Bristow, R. G. (2011). MRE11 promotes AKT phosphorylation in direct response to DNA double-strand breaks. Cell Cycle, 10, 2218–2232.
Fu, J., Hagan, I. M., & Glover, D. M. (2015). The centrosome and its duplication cycle. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 7, a015800.
Goetz, S. C., & Anderson, K. V. (2010). The primary cilium: A signalling centre during vertebrate development. Nature Reviews. Genetics, 11, 331–344.
Griffith, E., Walker, S., Martin, C. A., Vagnarelli, P., Stiff, T., Vernay, B., Al Sanna, N., Saggar, A., Hamel, B., Earnshaw, W. C., et al. (2008). Mutations in pericentrin cause Seckel syndrome with defective ATR-dependent DNA damage signaling. Nature Genetics, 40, 232–236.
Hauer, M. H., & Gasser, S. M. (2017). Chromatin and nucleosome dynamics in DNA damage and repair. Genes & Development, 31, 2204–2221.
Jackson, S. P., & Bartek, J. (2009). The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature, 461, 1071–1078.
Jette, N., & Lees-Miller, S. P. (2015). The DNA-dependent protein kinase: A multifunctional protein kinase with roles in DNA double strand break repair and mitosis. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 117, 194–205.
Johnson, C. A., & Collis, S. J. (2016). Ciliogenesis and the DNA damage response: A stressful relationship. Cilia, 5, 19.
Khodjakov, A., & Rieder, C. L. (1999). The sudden recruitment of gamma-tubulin to the centrosome at the onset of mitosis and its dynamic exchange throughout the cell cycle, do not require microtubules. The Journal of Cell Biology, 146, 585–596.
Lawo, S., Hasegan, M., Gupta, G. D., & Pelletier, L. (2012). Subdiffraction imaging of centrosomes reveals higher-order organizational features of pericentriolar material. Nature Cell Biology, 14, 1148–1158.
Lawrimore, J., Barry, T. M., Barry, R. M., York, A. C., Friedman, B., Cook, D. M., Akialis, K., Tyler, J., Vasquez, P., Yeh, E., et al. (2017). Microtubule dynamics drive enhanced chromatin motion and mobilize telomeres in response to DNA damage. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 28, 1701–1711.
Lei, K., Zhu, X., Xu, R., Shao, C., Xu, T., Zhuang, Y., & Han, M. (2012). Inner nuclear envelope proteins SUN1 and SUN2 play a prominent role in the DNA damage response. Current Biology : CB, 22, 1609–1615.
Li, W., Bai, X., Li, J., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Zhao, H., Liu, L., Ding, M., Wang, Q., Shi, F. Y., et al. (2019). The nucleoskeleton protein IFFO1 immobilizes broken DNA and suppresses chromosome translocation during tumorigenesis. Nature Cell Biology, 21, 1273–1285.
Lobrich, M., & Jeggo, P. (2017). A process of resection-dependent nonhomologous end joining involving the goddess artemis. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 42, 690–701.
Loffler, H., Fechter, A., Liu, F. Y., Poppelreuther, S., & Kramer, A. (2013). DNA damage-induced centrosome amplification occurs via excessive formation of centriolar satellites. Oncogene, 32, 2963–2972.
Lottersberger, F., Karssemeijer, R. A., Dimitrova, N., & de Lange, T. (2015). 53BP1 and the LINC complex promote microtubule-dependent DSB mobility and DNA repair. Cell, 163, 880–893.
Lukas, J., & Lukas, C. (2013). Molecular biology. Shielding broken DNA for a quick fix. Science, 339, 652–653.
Ma, S., Rong, Z., Liu, C., Qin, X., Zhang, X., & Chen, Q. (2021). DNA damage promotes microtubule dynamics through a DNA-PK-AKT axis for enhanced repair. Journal of Cell Biology. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201911025
Marnef, A., & Legube, G. (2017). Organizing DNA repair in the nucleus: DSBs hit the road. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 46, 1–8.
Matsuzawa, A., Kanno, S., Nakayama, M., Mochiduki, H., Wei, L., Shimaoka, T., Furukawa, Y., Kato, K., Shibata, S., Yasui, A., et al. (2014). The BRCA1/BARD1-interacting protein OLA1 functions in centrosome regulation. Molecular Cell, 53, 101–114.
Mennella, V., Agard, D. A., Huang, B., & Pelletier, L. (2014). Amorphous no more: Subdiffraction view of the pericentriolar material architecture. Trends in Cell Biology, 24, 188–197.
Mennella, V., Keszthelyi, B., McDonald, K. L., Chhun, B., Kan, F., Rogers, G. C., Huang, B., & Agard, D. A. (2012). Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence microscopy reveals a domain of the centrosome critical for pericentriolar material organization. Nature Cell Biology, 14, 1159–1168.
Monnich, M., Borgeskov, L., Breslin, L., Jakobsen, L., Rogowski, M., Doganli, C., Schroder, J. M., Mogensen, J. B., Blinkenkjaer, L., Harder, L. M., et al. (2018). CEP128 localizes to the subdistal appendages of the mother centriole and regulates TGF-beta/BMP signaling at the primary cilium. Cell Reports, 22, 2584–2592.
Morrison, C. G. (2021). Primary cilia and the DNA damage response: Linking a cellular antenna and nuclear signals. Biochemical Society Transactions, 49, 829–841.
Mullee, L. I., & Morrison, C. G. (2016). Centrosomes in the DNA damage response–the hub outside the centre. Chromosome Research : An International Journal on the Molecular, Supramolecular and Evolutionary Aspects of Chromosome Biology, 24, 35–51.
Nigg, E. A. (2007). Centrosome duplication: Of rules and licenses. Trends in Cell Biology, 17, 215–221.
Nigg, E. A., & Holland, A. J. (2018). Once and only once: Mechanisms of centriole duplication and their deregulation in disease. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 19, 297–312.
Nishi, R., Okuda, Y., Watanabe, E., Mori, T., Iwai, S., Masutani, C., Sugasawa, K., & Hanaoka, F. (2005). Centrin 2 stimulates nucleotide excision repair by interacting with xeroderma pigmentosum group C protein. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 25, 5664–5674.
Ochi, T., Blackford, A. N., Coates, J., Jhujh, S., Mehmood, S., Tamura, N., Travers, J., Wu, Q., Draviam, V. M., Robinson, C. V., et al. (2015). DNA repair. PAXX, a paralog of XRCC4 and XLF, interacts with Ku to promote DNA double-strand break repair. Science, 347, 185–188.
Palazzo, R. E., Vogel, J. M., Schnackenberg, B. J., Hull, D. R., & Wu, X. (2000). Centrosome maturation. Current Topics in Developmental Biology, 49, 449–470.
Pan, Y. R., & Lee, E. Y. (2009). UV-dependent interaction between Cep164 and XPA mediates localization of Cep164 at sites of DNA damage and UV sensitivity. Cell Cycle, 8, 655–664.
Park, J., Welner, R. S., Chan, M. Y., Troppito, L., Staber, P. B., Tenen, D. G., & Yan, C. T. (2016). The DNA ligase IV syndrome R278H mutation impairs B lymphopoiesis via error-prone nonhomologous end-joining. Journal of Immunology, 196, 244–255.
Penfield, L., Wysolmerski, B., Mauro, M., Farhadifar, R., Martinez, M. A., Biggs, R., Wu, H. Y., Broberg, C., Needleman, D., & Bahmanyar, S. (2018). Dynein pulling forces counteract lamin-mediated nuclear stability during nuclear envelope repair. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 29, 852–868.
Poruchynsky, M. S., Komlodi-Pasztor, E., Trostel, S., Wilkerson, J., Regairaz, M., Pommier, Y., Zhang, X., Kumar Maity, T., Robey, R., Burotto, M., et al. (2015). Microtubule-targeting agents augment the toxicity of DNA-damaging agents by disrupting intracellular trafficking of DNA repair proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112, 1571–1576.
Pugacheva, E. N., Jablonski, S. A., Hartman, T. R., Henske, E. P., & Golemis, E. A. (2007). HEF1-dependent Aurora A activation induces disassembly of the primary cilium. Cell, 129, 1351–1363.
Reiter, J. F., & Leroux, M. R. (2017). Genes and molecular pathways underpinning ciliopathies. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 18, 533–547.
Riballo, E., Kuhne, M., Rief, N., Doherty, A., Smith, G. C., Recio, M. J., Reis, C., Dahm, K., Fricke, A., Krempler, A., et al. (2004). A pathway of double-strand break rejoining dependent upon ATM, Artemis, and proteins locating to gamma-H2AX foci. Molecular Cell, 16, 715–724.
Rosin, N., Elcioglu, N. H., Beleggia, F., Isguven, P., Altmuller, J., Thiele, H., Steindl, K., Joset, P., Rauch, A., Nurnberg, P., et al. (2015). Mutations in XRCC4 cause primary microcephaly, short stature and increased genomic instability. Human Molecular Genetics, 24, 3708–3717.
Rothballer, A., & Kutay, U. (2013). The diverse functional LINCs of the nuclear envelope to the cytoskeleton and chromatin. Chromosoma, 122, 415–429.
Roukos, V., Voss, T. C., Schmidt, C. K., Lee, S., Wangsa, D., & Misteli, T. (2013). Spatial dynamics of chromosome translocations in living cells. Science, 341, 660–664.
Saji, M., Vasko, V., Kada, F., Allbritton, E. H., Burman, K. D., & Ringel, M. D. (2005). Akt1 contains a functional leucine-rich nuclear export sequence. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 332, 167–173.
Saladino, C., Bourke, E., Conroy, P. C., & Morrison, C. G. (2009). Centriole separation in DNA damage-induced centrosome amplification. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 50, 725–732.
Schrank, B. R., Aparicio, T., Li, Y., Chang, W., Chait, B. T., Gundersen, G. G., Gottesman, M. E., & Gautier, J. (2018). Nuclear ARP2/3 drives DNA break clustering for homology-directed repair. Nature, 559, 61–66.
Shen, K., Wang, Y., Brooks, S. C., Raz, A., & Wang, Y. A. (2006). ATM is activated by mitotic stress and suppresses centrosome amplification in primary but not in tumor cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 99, 1267–1274.
Shokrollahi, M., & Mekhail, K. (2021). Interphase microtubules in nuclear organization and genome maintenance. Trends in Cell Biology, 31, 721–731.
Sivasubramaniam, S., Sun, X., Pan, Y. R., Wang, S., & Lee, E. Y. (2008). Cep164 is a mediator protein required for the maintenance of genomic stability through modulation of MDC1, RPA, and CHK1. Genes & Development, 22, 587–600.
Starr, D. A. (2011). KASH and SUN proteins. Current Biology : CB, 21, R414-415.
Suizu, F., Hirata, N., Kimura, K., Edamura, T., Tanaka, T., Ishigaki, S., Donia, T., Noguchi, H., Iwanaga, T., & Noguchi, M. (2016). Phosphorylation-dependent Akt-Inversin interaction at the basal body of primary cilia. The EMBO Journal, 35, 1346–1363.
Sun, S., Fisher, R. L., Bowser, S. S., Pentecost, B. T., & Sui, H. (2019). Three-dimensional architecture of epithelial primary cilia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116, 9370–9379.
Tian, Y., Wei, C., He, J., Yan, Y., Pang, N., Fang, X., Liang, X., & Fu, J. (2021). Superresolution characterization of core centriole architecture. The Journal of Cell Biology. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202005103
Tibelius, A., Marhold, J., Zentgraf, H., Heilig, C. E., Neitzel, H., Ducommun, B., Rauch, A., Ho, A. D., Bartek, J., & Kramer, A. (2009). Microcephalin and pericentrin regulate mitotic entry via centrosome-associated Chk1. The Journal of Cell Biology, 185, 1149–1157.
Villumsen, B. H., Danielsen, J. R., Povlsen, L., Sylvestersen, K. B., Merdes, A., Beli, P., Yang, Y. G., Choudhary, C., Nielsen, M. L., Mailand, N., et al. (2013). A new cellular stress response that triggers centriolar satellite reorganization and ciliogenesis. The EMBO Journal, 32, 3029–3040.
Wakefield, J. G., Stephens, D. J., & Tavare, J. M. (2003). A role for glycogen synthase kinase-3 in mitotic spindle dynamics and chromosome alignment. Journal of Cell Science, 116, 637–646.
Wang, C. Y., Huang, E. Y., Huang, S. C., & Chung, B. C. (2015). DNA-PK/Chk2 induces centrosome amplification during prolonged replication stress. Oncogene, 34, 1263–1269.
Wang, C. Y., Kao, Y. H., Lai, P. Y., Chen, W. Y., & Chung, B. C. (2013). Steroidogenic factor 1 (NR5A1) maintains centrosome homeostasis in steroidogenic cells by restricting centrosomal DNA-dependent protein kinase activation. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 33, 476–484.
Wang, G., Chen, Q., Zhang, X., Zhang, B., Zhuo, X., Liu, J., Jiang, Q., & Zhang, C. (2013). PCM1 recruits Plk1 to the pericentriolar matrix to promote primary cilia disassembly before mitotic entry. Journal of Cell Science, 126, 1355–1365.
Woodbine, L., Gennery, A. R., & Jeggo, P. A. (2014). The clinical impact of deficiency in DNA non-homologous end-joining. DNA Repair, 16, 84–96.
Yoshino, Y., Qi, H., Fujita, H., Shirota, M., Abe, S., Komiyama, Y., Shindo, K., Nakayama, M., Matsuzawa, A., Kobayashi, A., et al. (2018). BRCA1-interacting protein OLA1 requires interaction with BARD1 to regulate centrosome number. Molecular Cancer Research, 16, 1499–1511.
Zhang, J., Xu, J., Wang, G., Sun, P., Yan, T., & Zhao, X. (2016). WTIP interacts with BRCA2 and is essential for BRCA2 centrosome localization in cervical cancer cell. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 294, 1311–1316.
Zhao, J., Zou, Y., Liu, H., Wang, H., Zhang, H., Hou, W., Li, X., Jia, X., Zhang, J., Hou, L., et al. (2014). TEIF associated centrosome activity is regulated by EGF/PI3K/Akt signaling. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1843, 1851–1864.
Zheng, P., Chen, Q., Tian, X., Qian, N., Chai, P., Liu, B., Hu, J., Blackstone, C., Zhu, D., Teng, J., et al. (2018). DNA damage triggers tubular endoplasmic reticulum extension to promote apoptosis by facilitating ER-mitochondria signaling. Cell Research, 28, 833–854.
Zhu, S., Paydar, M., Wang, F., Li, Y., Wang, L., Barrette, B., Bessho, T., Kwok, B. H., & Peng, A. (2020). Kinesin Kif2C in regulation of DNA double strand break dynamics and repair. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.53402
Funding
Q. Chen is supported by Grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1003400), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32170698, 31770868).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Liu, X. & Chen, Q. Centrosome, microtubule and DNA damage response. GENOME INSTAB. DIS. 3, 163–171 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42764-022-00068-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42764-022-00068-z