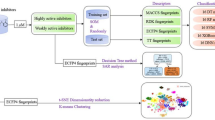
Abstract
Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a promising target for cancer treatment, developing new effective Hsp90 inhibitors is of great significance in anticancer therapy. In this study, 20 machine learning models were constructed on 1321 molecules in order to precisely classify highly active and weakly active Hsp90 inhibitors. Six types of fingerprints including MACCS keys (MACCS), Extended connectivity fingerprints with radius 2 (ECFP_4), PubChem fingerprints, Estate fingerprints, Substructure fingerprints and 2D atom pairs fingerprints were applied to characterize Hsp90 inhibitors. Five machine learning algorithms containing support vector machine (SVM), decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) and multilayer perceptron (MLP) were utilized to develop classification models. The best RF and SVM models resulted in MCC values of 0.8070 and 0.8003, respectively. The fingerprints of these best models were analyzed by information gain (IG) method. Based on the IG analysis, we found some favorable substructures of highly active Hsp90 inhibitors. Moreover, we clustered 1321 Hsp90 inhibitors into eight subsets, further analyzed and summarized the structural characteristics of each subset. It was found that purine scaffold and resorcinol appeared frequently in highly active Hsp90 inhibitors.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Reaxys: Elsevier Information Systems GmbH. https//www.reaxys.com/, Accessed October 20, 2020.
SONNIA, version 4.2. Molecular Networks GmbH, Germany and Altamira, LLC, USA. http://www.molecular-networks.com.
RDKit: Open-Source Cheminformatics Software. http://www.rdkit.org.
Weka, version 3.8.1. https://www.cs.waikato.ac.nz/ml/weka/.
References
Abbasi, M., Sadeghi-Aliabadi, H., Amanlou, M.: Prediction of new Hsp90 inhibitors based on 3,4-isoxazolediamide scaffold using QSAR study, molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation. Daru 25(1), 17 (2017)
Al-Sha’er, M.A., Mansi, I., Khanfar, M., Abudayyh, A.: Discovery of new heat shock protein 90 inhibitors using virtual co-crystallized pharmacophore generation. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 31(sup4), 64–77 (2016)
Bhat, R., Tummalapalli, S.R., Rotella, D.P.: Progress in the discovery and development of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 57(21), 8718–8728 (2014)
Breiman, L.: Random forsets. Mach. Learn. 45, 5–32 (2001)
Brown, D.E., Corruble, V., Pitttard, C.L.: A comparison of decision tree classifiers with backpropagation neural networks for multimodal classification problems. Pattern Recogn. 26(6), 953–961 (1993)
Canonici, A., Qadir, Z., Conlon, N.T., Collins, D.M., O’Brien, N.A., Walsh, N., Eustace, A.J., O’Donovan, N., Crown, J.: The HSP90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 inhibits growth of HER2 positive and trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cells. Invest. New. Drugs. 36(4), 581–589 (2018)
Cavenagh, J., Oakervee, H., Baetiong-Caguioa, P., Davies, F., Gharibo, M., Rabin, N., Kurman, M., Novak, B., Shiraishi, N., Nakashima, D., Akinaga, S., Yong, K.: A phase I/II study of KW-2478, an Hsp90 inhibitor, in combination with bortezomib in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Br. J. Cancer. 117(9), 1295–1302 (2017)
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V.: Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20, 273–297 (1995)
Costa, T., Raghavendra, N.M., Penido, C.: Natural heat shock protein 90 inhibitors in cancer and inflammation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 189, 112063 (2020)
Eccles, S.A., Massey, A., Raynaud, F.I., Sharp, S.Y., Box, G., Valenti, M., Patterson, L., de Haven Brandon, A., Gowan, S., Boxall, F., Aherne, W., Rowlands, M., Hayes, A., Martins, V., Urban, F., Boxall, K., Prodromou, C., Pearl, L., James, K., Matthews, T.P., Cheung, K.M., Kalusa, A., Jones, K., McDonald, E., Barril, X., Brough, P.A., Cansfield, J.E., Dymock, B., Drysdale, M.J., Finch, H., Howes, R., Hubbard, R.E., Surgenor, A., Webb, P., Wood, M., Wright, L., Workman, P.: NVP-AUY922: a novel heat shock protein 90 inhibitor active against xenograft tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Cancer. Res. 68(8), 2850–2860 (2008)
Friedman, J.H.: Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 29(5), 1189–1232 (2001)
Ge, J., Normant, E., Porter, J.R., Ali, J.A., Dembski, M.S., Gao, Y., Georges, A.T., Grenier, L., Pak, R.H., Patterson, J., Sydor, J.R., Tibbitts, T.T., Tong, J.K., Adams, J., Palombella, V.J.: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of hydroquinone derivatives of 17-amino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin as potent, water-soluble inhibitors of Hsp90. J. Med. Chem. 49(15), 4606–4615 (2006)
Halko, N., Martinsson, P.G., Tropp, J.A.: Finding structure with randomness: probabilistic algorithms for constructing approximate matrix decompositions. SIAM Rev. 53(2), 217–288 (2011)
He, Q., Chu, H., Wang, Y., Guo, H., Wang, Y., Wang, S., Feng, Z., Xie, X.Q., Hu, Y., Liu, H., Lin, Z.: In silico design novel vibsanin B derivatives as inhibitor for heat shock protein 90 based on 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 38, 1–12 (2019)
Heikamp, K., Bajorat, J.: Fingerprint design and engineering strategies: rationalizing and improving similarity search performance. Future. Med. Chem. 4(15), 1945–1959 (2012)
Hofmann, T., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.J.: Kernel methods in machine learning. Ann. Stat. 36(3), 1171–1220 (2008)
Immormino, R.M., Kang, Y., Chiosis, G., Gewirth, D.T.: Structural and quantum chemical studies of 8-aryl-sulfanyl adenine class Hsp90 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 49(16), 4953–4960 (2006)
Infante, J.R., Weiss, G.J., Jones, S., Tibes, R., Bauer, T.M., Bendell, J.C., Hinson, J.M., Jr., Von Hoff, D.D., Burris, H.A., Orlemans, E.O., Ramanathan, R.K.: Phase I dose-escalation studies of SNX-5422, an orally bioavailable heat shock protein 90 inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer. 50(17), 2897–2904 (2014)
Jhaveri, K., Taldone, T., Modi, S., Chiosis, G.: Advances in the clinical development of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) inhibitors in cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1823(3), 742–755 (2012)
Jiang, F., Wang, H.J., Jin, Y.H., Zhang, Q., Wang, Z.H., Jia, J.M., Liu, F., Wang, L., Bao, Q.C., Li, D.D., You, Q.D., Xu, X.L.: Novel tetrahydropyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidines as potent inhibitors of chaperone heat shock protein 90. J. Med. Chem. 59(23), 10498–10519 (2016)
Jung, J., Kwon, J., Hong, S., Moon, A.N., Jeong, J., Kwon, S., Kim, J.A., Lee, M., Lee, H., Lee, J.H., Lee, J.: Discovery of novel heat shock protein (Hsp90) inhibitors based on luminespib with potent antitumor activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 30(12), 127165 (2020)
Kanungo, T., Mount, D.M., Netanyahu, N.S., Piatko, C.D., Silverman, R., Wu, A.Y.: An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(7), 881–892 (2002)
Le Brazidec, J.Y., Kamal, A., Busch, D., Thao, L., Zhang, L., Timony, G., Grecko, R., Trent, K., Lough, R., Salazar, T., Khan, S., Burrows, F., Boehm, M.F.: Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new class of geldanamycin derivatives as potent inhibitors of Hsp90. J. Med. Chem. 47(15), 3865–3873 (2004)
Li, Z., Jia, L., Wang, J., Wu, X., Hao, H., Xu, H., Wu, Y., Shi, G., Lu, C., Shen, Y.: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 17-arylmethylamine-17-demethoxygeldanamycin derivatives as potent Hsp90 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 85, 359–370 (2014b)
Liu, Y., Liu, X., Li, L., Dai, R., Shi, M., Xue, H., Liu, Y., Wang, H.: Identification and structure-activity studies of 1,3-dibenzyl-2-aryl imidazolidines as novel Hsp90 inhibitors. Molecule. 24(11), 2105 (2019)
Mettu, A., Talla, V., Bajaj, D.M., Subhashini, N.J.P.: Design, synthesis, and molecular docking studies of novel pyrazolyl 2-aminopyrimidine derivatives as HSP90 inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 352(10), e1900063 (2019)
Miura, T., Fukami, T.A., Hasegawa, K., Ono, N., Suda, A., Shindo, H., Yoon, D.O., Kim, S.J., Na, Y.J., Aoki, Y., Shimma, N., Tsukuda, T., Shiratori, Y.: Lead generation of heat shock protein 90 inhibitors by a combination of fragment-based approach, virtual screening, and structure-based drug design. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21(19), 5778–5783 (2011)
Niculaescu, O.: Classifying data with decision trees. XRDS. 24(4), 55–57 (2018)
Pedregosa F., Varoquaux G., Gramfort A., Michel V., Thirion B., Grisel O., Blondel M., Prettenhofer P., Weiss R., Dubourg V., Vanderplas J., Passons A., Cournapeau D., Brucher M., Perrot M., Duchesnay E.: Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2825–2830 (2011)
Robert, M.I., Yan, L.K., Gabriela, C., Daniel, T.G.: Structural and quantum chemical studies of 8-aryl-sulfanyl adenine class Hsp90 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 49(16), 4953–4960 (2006)
Roe, S.M., Prodromou, C., O’Brien, R., Ladbury, J.E., Piper, P.W., Pearl, L.H.: Structural basis for inhibition of the Hsp90 molecular chaperone by the antitumor antibiotics radicicol and geldanamycin. J. Med. Chem. 42(2), 260–266 (1999)
Sausville, E.A., Tomaszewski, J.E., Ivy, P.: Clinical development of 17-allylamino, 17-demethoxygeldanamycin. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 3(5), 377–383 (2003)
Shen, J., Cheng, F., Xu, Y., Li, W., Tang, Y.: Estimation of ADME properties with substructure pattern recognition. J. Chem. Inf. Mode. 50(6), 1034–1041 (2010)
Sun, J., Lin, C., Qin, X., Dong, X., Tu, Z., Tang, F., Chen, C., Zhang, J.: Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3,5-disubstituted-4-alkynylisoxozales as a novel class of HSP90 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25(16), 3129–3134 (2015)
Talebi, N., Nasrabadi, A.M., Mohammad-Rezazadeh, I.: Estimation of effective connectivity using multi-layer perceptron artificial neural network. Cogn. Neurodyn. 12(1), 21–42 (2018)
Whitesell, L., Mimnaugh, E.G., Costa, B.D., Myers, C.E., Neckers, L.M.: Inhibition of heat shock protein Hsp90-pp6Ov-src heteroprotein complex formation by benzoquinone ansamycins: essential role for stress proteins in oncogenic transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91(18), 8324–8328 (1994)
Willett, P.: Similarity-based virtual screening using 2D fingerprints. Drug. Discov. Today. 11(23–24), 1046–1053 (2006)
Yan, A.X., Grant, G.H., Richards, W.G.: Dynamics of conserved waters in human Hsp90: implications for drug design. J. R. Soc. Interface. 5(supp3), S199–S205 (2008)
Yap, C.W.: PaDEL-descriptor: an open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J. Comput. Chem. 32(7), 1466–1474 (2011)
Yong, K., Cavet, J., Johnson, P., Morgan, G., Williams, C., Nakashima, D., Akinaga, S., Oakervee, H., Cavenagh, J.: Phase I study of KW-2478, a novel Hsp90 inhibitor, in patients with B cell malignancies. Br. J. Cancer. 114(1), 7–13 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21675010), and “Chemical Grid Project” of Beijing University of Chemical Technology. We thank the Molecular Networks GmbH, Nuremberg, Germany for providing the programs CORINA Symphony and SONNIA for our scientific work.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Additional information
This paper is submitted for possible publication in the Special Issue on HPC in Life Science and Medical Science.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
42514_2021_84_MOESM3_ESM.docx
All optimum parameters of 20 classification models can be found in docx files named The optimum parameters.docx (DOCX 19 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Tian, Y. & Yan, A. SAR study on inhibitors of Hsp90α using machine learning methods. CCF Trans. HPC 3, 353–364 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42514-021-00084-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42514-021-00084-7