Abstract
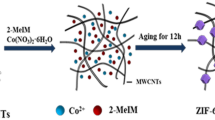
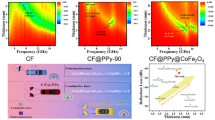
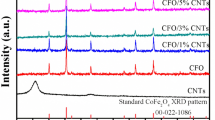
The composite structure of Co beads (200–300 nm) threaded by carbon nanotubes has been synthesized through a facile solvothermal method followed by a carbon reduction process. A carbon layer of ca. 5 nm was coated on the surface of Co beads to form a core-shell structure (CNTs/Co@C), in favor of the anti-oxidation of Co nanoparticles. The CNTs/Co@C hybrid showed a saturation magnetization (M s) of 82.5 emu g−1 and a larger H c value of 258.8 Oe than bulk Co (ca. 10 Oe). Served as an EM wave absorption material, the epoxy resin composites consisting of 60 wt% and 40 wt% CNTs/Co@C hybrid exhibited effective EM absorption (RL < − 10 dB) over the frequency ranges of 1.5–15 and 1.6–20 GHz with the matching thicknesses of 1.0–7.5 and 1.0–10.0 mm, respectively. The superior EM absorption performances of CNTs/Co@C hybrid containing strong absorption, wide frequency range, thin thickness, and light weight are mainly attributed to the synergy of magnetic loss from Co beads and dielectric loss from carbon nanotubes, as well as remarkable impedance matching.

The composite structure of Co beads threaded by carbon nanotubes synthesized through a facile solvothermal method followed by a carbon reduction process exhibit superior electromagnetic wave absorption properties.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang F, Liu J, Kong J, Zhang Z, Wang X, Itoh M, Machida K (2011) Template free synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of monodispersed hollow magnetite nano-spheres. J Mater Chem 21:4314–4320
Lu M, Cao W, Shi H, Fang X, Yang J, Hou Z, Jin H, Wang W, Yuan J, Cao M (2014) Multi-wall carbon nanotubes decorated with ZnO nanocrystals: mild solution-process synthesis and highly efficient microwave absorption properties at elevated temperature. J Mater Chem A 2:10540–10547
Liang C, Liu C, Wang H, Wu L, Jiang Z, Xu Y, Shen B, Wang Z (2014) SiC–Fe3O4 dielectric–magnetic hybrid nanowires:controllable fabrication, characterization and electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Chem A 2:16397–16402
Zhao B, Zhao W, Shao G, Fan B, Zhang R (2015) Morphology-control synthesis of a core-shell structured NiCu alloy with tunable electromagnetic-wave absorption capabilities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:12951–12960
Liu X, Chen Y, Cui X, Zeng M, Yu R, Wang G (2015) Flexible nanocomposites with enhanced microwave absorption properties based on Fe3O4/SiO2 nanorods and polyvinylidene fluoride. J Mater Chem A 3:12197–12204
Liu J, Cao M, Luo Q, Shi H, Wang W, Yuan J (2016) Electromagnetic property and tunable microwave absorption of 3D nets from nickel chains at elevated temperature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:22615–22622
Qiang R, Du Y, Zhao H, Wang Y, Tian C, Li Z, Han X, Xu P (2015) Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption. J Mater Chem A 3:13426–13434
Lü Y, Wang Y, Li H, Lin Y, Jiang Z, Xie Z, Kuang Q, Zheng L (2015) MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:13604–13611
Feng J, Pu F, Li Z, Li X, Hu X, Bai J (2016) Interfacial interactions and synergistic effect of CoNi nanocrystals and nitrogen-doped graphene in a composite microwave absorber. Carbon 104:214–225
Wang L, Jia X, Li Y, Yang F, Zhang L, Liu L, Ren X, Yang H (2014) Synthesis and microwave absorption property offlexible magnetic film based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Mater Chem A 2:14940–14946
Tsonos C, Soin N, Tomara G, Yang B, Psarras GC, Kanapitsas A, Siores E (2016) Synthesis and microwave absorption property of flexible magnetic film based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6:1919–1924
Pan G, Zhu J, Ma S, Sun G, Yang X (2013) Synthesis and microwave absorption property of flexible magnetic film based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:12716–12724
Shen J, Yao Y, Liu Y, Leng J (2016) Tunable hierarchical Fe nanowires with a facile template-free approach for enhanced microwave absorption performance. J Mater Chem C 4:7614–7621
He C, Qiu S, Wang X, Liu J, Luan L, Liu W, Itoh M, Machida K (2012) Facile synthesis of hollow porous cobalt spheres and their enhanced electromagnetic properties. J Mater Chem 22:22160–22166
Wang C, Han X, Zhang X, Hu S, Zhang T, Wang J, Du Y, Wang X, Xu P (2010) Controlled synthesis and morphology-dependent electromagnetic properties of hierarchical cobalt assemblies. J Phys Chem C 114:14826–14830
Zhao B, Guo X, Zhao W, Deng J, Shao G, Fan B, Bai Z, Zhang R (2016) Yolk-shell Ni@SnO2 composites with a designable interspace to improve the electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:28917–28925
Zhao B, Shao G, Fan B, Zhao W, Zhang R (2015) Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core–shell structure. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:2531–2539
Wang Z, Wu L, Zhou J, Jiang Z, Shen B (2014) Chemoselectivity-induced multiple interfaces in MWCNT/Fe3O4@ZnO heterotrimers for whole X-band microwave absorption. Nanoscale 6:12298–12302
Liu P, Huang Y, Yan J, Yang Y, Zhao Y (2016) Construction of CuS nanoflakes vertically aligned on magnetically decorated graphene and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:5536–5546
Han M, Yin X, Kong L, Li M, Duan W, Zhang L, Cheng L (2014) Graphene-wrapped ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Mater Chem A 2:16403–16409
Zhang X, Ji G, Liu W, Zhang X, Gao Q, Li Y, Du Y (2016) A novel Co/TiO2 nanocomposite derived from a metal–organic framework: synthesis and efficient microwave absorption. J Mater Chem C 4:1860–1870
Li N, Cao M, Hu C (2012) A simple approach to spherical nickel-carbon monoliths as light-weight microwave absorbers. J Mater Chem 22:18426–18432
Zhu J, Wei S, Haldolaarachchige N, Young D, Guo Z (2011) Electromagnetic field shielding polyurethane nanocomposites reinforced with core–shell Fe–silica nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 115:15304–15301
Feng C, Liu X, Sun Y, Jin C, Lv Y (2014) Enhanced microwave absorption of flower-like FeNi@C nanocomposites by dual dielectric relaxation and multiple magnetic resonance. RSC Adv 4:22170–22175
Wang H, Wu L, Jiao J, Zhou J, Xu Y, Zhang H, Jiang Z, Shen B, Wang Z (2015) Covalent interaction enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption in SiC/Co hybrid nanowires. J Mater Chem A 3:6517–6525
Li X, Feng J, Du Y, Bai J, Fan H, Zhang H, Peng Y, Li F (2015) One-pot synthesis of CoFe2O4/graphene oxide hybrids and their conversion into FeCo/graphene hybrids for lightweight and highly efficient microwave absorber. J Mater Chem A 3:5535–5546
Chen Y, Xiao G, Wang T, Ouyang Q, Qi L, Ma Y, Gao P, Zhu C, Cao M, Jin H (2011) Porous Fe3O4/carbon core/shell nanorods: synthesis and electromagnetic properties. J Phys Chem C 115:13603–13608
Micheli D, Vircella A, Pastore R, Marchetli M (2014) Ballistic and electromagnetic shielding behaviour of multifunctional Kevlar fiber reinforced epoxy composites modified by carbon nanotubes. Carbon 104:141–156
Song W, Cao M, Fan L, Lu M, Li Y, Wang C, Ju H (2014) Highly ordered porous carbon/wax composites for effective electromagnetic attenuation and shielding. Carbon 77:130–142
Zhan Y, Zhao R, Lei Y, Meng F, Zhong J, Liu X (2011) A novel carbon nanotubes/Fe3O4 inorganic hybrid material: synthesis, characterization and microwave electromagnetic properties. J Magn Magn Mater 323:1006–1010
Zhang S, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Jiao Q, Ni X, Wang Y, Cheng Y, Ding C (2017) Core/shell structured composites of hollow spherical CoFe2O4 and CNTs as absorbing materials. J Alloys Compd 694:309–312
Wen F, Zhang F, Liu Z (2011) Investigation on microwave absorption properties for multiwalled carbon nanotubes/Fe/Co/Ni nanopowders as lightweight absorbers. J Phys Chem C 115:14025–14030
Zhao H, Han X, Han M, Zhang L, Xu P (2010) Preparation and electromagnetic properties of multiwalled carbon nanotubes/Ni composites by γ-irradiation technique. Mater Sci Eng B 167:1–5
Singh BP, Saket DK, Singh AP, Pati S, Gupta TK, Singh VN, Dhakate SR, Dhawan SK, Kotnala RK, Mathur RB (2015) Microwave shielding properties of Co/Ni attached to single walled carbon nanotubes. J Mater Chem A 3:13203–13209
Bittencourt C, Felten A, Ghijsen J, Pireaux JJ, Drube W, Erni R, Van Tendeloo G (2007) Decorating carbon nanotubes with nickel nanoparticles. Chem Phys Letter 436:368–372
Bao T, Zhao Y, Su X, Duan Y (2011) A study of the electromagnetic properties of cobalt-multiwalled carbon nanotubes (Co-MWCNTs) composites. Mater Sci Eng B 176:906–912
Liu J, Itoh M, Machida K (2003) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of a-Fe/Fe3B/Y2O3 nanocomposites in gigahertz range. Appl Phys Lett 83:4017–4019
Li X, Gu H, Liu J, Wei H, Qiu S, Fu Y, Lv H, Lu G, Wang Y, Guo Z (2015) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes composited with nanomagnetite for anodes in lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 5:7237–7244
Lu M, Cao M, Chen Y, Cao W, Liu J, Shi H, Zhang D, Wang W, Yuan J (2015) Multiscale assembly of grape-like ferroferric oxide and carbon nanotubes: a smart absorber prototype varying temperature to tune intensities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:19408–19415
Bertram BD, Gerhardt RA (2011) Effects of frequency, percolation, and axisymmetric microstructure on the electrical response of hot-pressed alumina–silicon carbide whisker composites. J Am Ceram Soc 94:1125–1132
Du Y, Liu W, Qiang R, Wang Y, Han X, Ma J, Xu P (2014) Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core–shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:12997–13006
Kittel C (1948) On the theory of ferromagnetic resonance absorption. Phys Rev 73:155–161
Lv H, Ji G, Wang M, Shang C, Zhang H, Du Y (2014) Hexagonal-cone like of Fe50Co50 with broad frequency microwave absorption: effect of ultrasonic irradiation time. J Alloys Compd 615:1037–1042
Sun X, He J, Li G, Tang J, Wang T, Guo Y, Xue H (2013) Laminated magnetic graphene with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Mater Chem C 1:765–777
Yasir Rafique M, Panb L, Farid A (2016) From nano-dendrite to nano-sphere of Co100−xNix alloy: composition dependent morphology, structure and magnetic properties. J Alloys Compd 656:443–451
Wu M, Zhang Y, Hui S, Xiao T, Ge S, Hines W, Budnick J, Taylor G (2002) Microwave magnetic properties of Co50/(SiO2)50 nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 80:4404–4406
Smith D, Padilla W, Vier D, Nemat-Nasser S, Schultz S (2000) Composite medium with simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity. Physi Rev Letters 84:4184–4187
Kasagi T, Tsutaoka T, Hatakeyama K (2006) Negative permeability spectra in permalloy granular composite materials. Appl Phys Lett 88:172502
Deng L, Han M (2007) Microwave absorbing performances of multiwalled carbon nanotube composites with negative permeability. Appl Phys Lett 91:023119
Xiang J, Li J, Zhang X, Ye Q, Xu J, Shen X (2014) Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. J Mater Chem A 2:16905–16914
Liu Q, Zhang D, Han T (2008) Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous carbon/Co nanocomposites. Appl Phys Lett 93:013110
Wen S, Liu Y, Zhao X, Cheng J, Li H (2014) Facile synthesis of novel cobalt particles by reduction method and their microwave absorption properties. Powder Technol 264:128–132
Li H, Zhu H, Guo H, Yu L (2007) Investigation of the microwave-absorbing properties of Fe-filled carbon nanotubes. Mater Lett 61:3547–3550
Cui H, Li T, Zhao T, Liu H, Liu L, Zhang W (2013) Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of multi-wall carbon nanotube/Fe3O4 hybrid materials. New Carbon Mater 28:184–190
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51572157), the Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (2015JC016, 2015JC036), and the Science and Technology Development Plan (2014GGX102004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, N., Qiao, J., Liu, J. et al. Strengthened electromagnetic absorption performance derived from synergistic effect of carbon nanotube hybrid with Co@C beads. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 1, 149–159 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-017-0008-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-017-0008-z