Abstract
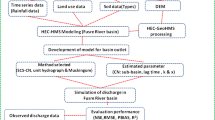
Streamflow forecasts are fundamental to the effective operation of flood control reservoirs and levee systems. Therefore, streamflow forecasting is of great importance. In this paper, the HEC-HMS conceptual model and SARIMA time-series model are compared to forecast streamflow in Maroon basin in the southwest of Iran to evaluate their ability and accuracy in monthly streamflow forecasting. First, the continuous rainfall–runoff was simulated monthly before the forecasting period by the HEC-HMS model. The monthly data from October 1991 to 2010 were used for verification. Also the data from 2011 to 2017 were used for calibrated HEC-HMS model. Streamflow forecast was conducted from 2018 to 2021 at the Idanak hydrometric station. To validate the SARIMA model based on the autocorrelation function, the partial autocorrelation of the residuals, Port-Manteau test, Akaike criterion and plotting the residual time series diagram on normal probability paper were used. The results showed that the accuracy of the HEC-HMS model in forecasting streamflow is higher than SARIMA model, the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of predicted and observed discharges for HEC-HMS and SARIMA models are 2.8 and 3.4 m3/s, respectively.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data not available.
Change history
05 June 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00862-x
References
Adnan RM, Petroselli A, Heddam S, Santos CAG, Kisi O (2021) Short term rainfall-runoff modelling using several machine learning methods and a conceptual event-based model. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 35(3):597–616
Anon (2000) Hydrologic modeling system HEC–HMS: technical reference manual. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Hydrologic Engineering Center, Davis, Calif
Bennett T (1998) MS thesis, Development and application of a continuous soil moisture accounting algorithm for the Hydrologic Engineering Center-Hydrologic Modeling System HEC-HMS, Dept. Of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Univ. of California, Davis, Calif
Box GEP, Jenkins GM, Reinsel GC (1994) Time Series Analysis Forecasting and Control, 3rd. ed., Englewood cliff, N.J Prentice Hall
Can I, Selim S (2009) Stochastic modeling of mean monthly flows of Carrasco river. In water and Environment Journal
Fathian F, Fakheri Fard A, Ouarda TBMJ, Dinpashoh Y, Mousavi-Nadoushani SS (2019a) Modeling streamflow time series using nonlinear SETAR-GARCH models. J Hydrol 573:82–97
Fathian F, Mehdizadeh S, Sales AK, Safari MJS (2019b) Hybrid models to improve the monthly river flow prediction: integrating artificial intelligence and non-linear time series models. J Hydrol 575:1200–1213
Gumindoga W, Rwasoka DT, Nhapi I, Dube T (2016) Ungauged runoff simulation in Upper Manyame Catchment, Zimbabwe: Application of the HEC-HMS model. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C. In: Press, Corrected Proof
HEC (2008) HEC-HMS, User’s manual version 3.3. Hydrologic engineering center, California
Hooshyaripor F, Faraji-Ashkavar S, Koohyian F, Tang Q, Noori R (2020) Annual flood damage influenced by El Niño in the Kan River basin, Iran. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 20(10):2739–2751
Khezrian NN, Hajjam S, Mirzaei A, Meshkavati AH (2012) Prediction of runoff of Tireh basin using quantitative prediction of rainfall as the WRF model output. J Clim Res 12:53–68 ((In Persian))
Koch R, Bene K (2013) Continuous hydrologic modeling with HMS in the Aggtelek Karst region. Hydrology 1(1):1–7
Mehdizadeh S, Fathian F, Adamowski JF (2019a) Hybrid artificial intelligence-time series models for monthly streamflow modeling. Appl Soft Comput 80:873–887
Mehdizadeh S, Fathian F, Safari MJS, Adamowski JF (2019b) Comparative assessment of time series and artificial intelligence models to estimate monthly streamflow: a local and external data analysis approach. J Hydrol 579:124225
Modaresi F, Araghinejad S, Ebrahimi K (2018) A comparative assessment of artificial neural network, generalized regression neural network, least-square support vector regression, and K-nearest neighbor regression for monthly streamflow forecasting in linear and nonlinear conditions. Water Resour Manage 32(1):243–258
Ni L, Wang D, Singh VP, Wu J, Wang Y, Tao Y, Zhang J (2019) Streamflow and rainfall forecasting by two long short-term memory-based models. J Hydrol 124296
Razmkhah H, Saghafian BA, Ali AM, Radmanesh F (2016) Rainfall_Runoff Modeling Considering Soil Moisture Accounting Algorithm, Case Study: Karoon III River Basin. Water Resour 43(4):699–710
Shafizadeh-Moghadam H, Valavi R, Shahabi H, Chapi K, Shirzadi A (2018) Novel forecasting approaches using combination of machine learning and statistical models for flood susceptibility mapping. J Environ Manag 217:1–11
Singh WR, Jain MK (2015) Continuous Hydrological Modeling using Soil Moisture Accounting Algorithm in Vamsadhara River Basin, India. J Water Resour Hydraulic Eng 4(4):398–408
Sintayehu LG (2015) Application of the HEC-HMS Model for Runoff Simulation of Upper Blue Nile River Basin. J Hydrol Curr Res 6(2):2–8
Supe MS, Taley SM, Kale MU (2015) Rainfall - Runoff Modeling using HEC-HMS for Van River Basin. Int J Res Eng Sci Technol 1(8):20–28
Tongal H, Booij MJ (2018) Simulation and forecasting of streamflows using machine learning models coupled with base flow separation. J Hydrol 564:266–282
Valipour M (2015) Long –term runoff using SARIMA and ARIMA models the United States. J Meteorol Appl 22:592–598
Valipour M, Banihabib M, E and Behbahani S. M. R. (2012) Monthly Inflow Forecasting Using Autoregressive Artificial Neural Network. J Appl Sci 12(20):2139–2147
Wei ZL, Xu YP, Sun HY, Xie W, Wu G (2018) Predicting the occurrence of channelized debris flow by an integrated cascading model: A case study of a small debris flow-prone catchment in Zhejiang Province, China. Geomorphology 308:78–90
Yurekli K, Kurunc K, Ozturk F (2005) Application of linear stochastic models to monthly flow data of kellkit stream. Ecol Model 183:67–75
Acknowledgements
This article has been prepared with the assistance and financial support of the Vice Chancellor for Research and Technology of University of Zabol and the grant number IR-UOZ-GR-0303, by which the author expresses his gratitude and appreciation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised due to change in the author name.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadpour, A., Mirhashemi, S., Haghighat jou, P. et al. Comparison of the monthly streamflow forecasting in Maroon dam using HEC-HMS and SARIMA models. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 8, 158 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00686-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-022-00686-1