Abstract
The global solar irradiance data plays a vital role in evaluating the performance of all the solar energy conversion devices. In general there are two methods to predict the performance of such irradiance, namely physical models and the machine learning models. This paper presents a generalized regression neural network model (a machine learning technique) for estimating the global solar irradiance using seasonal and meteorological factors as input parameters. Results obtained from this proposed generalized regression neural network approach are compared with the results estimated by extensively used machine learning based methodologies such as fuzzy and artificial neural network models. Such a comparative results clearly indicate that prediction accuracy of proposed generalized regression neural network model is in good agreement with experimentally measured values. The mean percentage error for using GRNN, fuzzy logic and artificial neural network are 3.55%, 4.64%, and 5.49%.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Code Availability
The paper includes all the codes related to the prediction.
Abbreviations
- D:
-
Day of the year
- H:
-
Monthly mean daily irradiance on horizontal surface
- \({\mathbf{H}}_{0}\) :
-
Mean clear sky daily irradiance
- \({\raise0.7ex\hbox{${\mathbf{H}}$} \!\mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\mathbf{H}} {{\mathbf{H}}_{0} }}}\right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \!\lower0.7ex\hbox{${{\mathbf{H}}_{0} }$}}\) :
-
Clearness index
- \({\mathbf{H}}_{{{\mathbf{meas}}}}\) :
-
Measured value of monthly mean daily irradiance on horizontal surface
- \({\mathbf{H}}_{{{\mathbf{estim}}}}\) :
-
Predicted value of monthly mean daily irradiance on horizontal surface
- S:
-
Monthly mean daily hours of bright sunshine
- \({\mathbf{S}}_{0}\) :
-
Monthly mean of maximum possible daily hours of bright sunshine
- \({\raise0.7ex\hbox{${\mathbf{S}}$} \!\mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\mathbf{S}} {{\mathbf{S}}_{0} }}}\right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \!\lower0.7ex\hbox{${{\mathbf{S}}_{0} }$}}\) :
-
Mean fraction possible sunshine hours
- T:
-
Monthly mean hourly temperature (°C)
- \({\mathbf{T}}_{0}\) :
-
Monthly mean hourly maximum possible temperature (°C)
- \({\raise0.7ex\hbox{${\mathbf{T}}$} \!\mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\mathbf{T}} {{\mathbf{T}}_{0} }}}\right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \!\lower0.7ex\hbox{${{\mathbf{T}}_{0} }$}}\) :
-
Ratio of monthly mean hourly temperature to monthly mean hourly maximum possible temperature
- \({\mathbf{T}}_{{\mathbf{a}}}\) :
-
Ambient temperature (°C)
- ω:
-
Hour angle
- \({{\varvec{\upomega}}}_{{\mathbf{s}}}\) :
-
Hour angle at sunset
- Ø:
-
Latitude of location
- δ:
-
Declination angle
- FL:
-
Fuzzy logic
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- GRNN:
-
Generalized regression neural network
- NN:
-
Neural network
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- K-NN:
-
K-nearest neighbor algorithm
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
References
Tien JM (2017) Internet of things, real-time decision making, and artificial intelligence. Ann Data Sci 4(2):149–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-017-0112-5
Olson DL, Shi Y (2007) Introduction to business data mining. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, New York
Shi Y, Tian YJ, Kou G, Peng Y, Li JP (2011) Optimization based data mining: theory and applications. Springer, Berlin
Sivakumar P, Christraj W, Sridharan M, Jayamalathi N (2012) Performance comparison of differently configured solar water heaters. Eur J Sci Res 91(1):23–31
Marimuthu M, Geetha P, Deepiha P, Sridharan M (2015) MATLAB simulation of transparent glass PV/T hybrid water collectors. In: IEEE 9th international conference on intelligent systems and control (ISCO), Coimbatore, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCO.2015.7282327
Voyant C, Notton G, Kalogirou S, Nivet M-L, Paoli C, Motte F, Fouilloy A (2017) Machine learning methods for solar radiation forecasting: a review. Renew Energy 105(2017):569–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2016.12.095
Wang L, Kisi O, Zounemat-Kermani M, Salazar GA, Zhu Z, Gong W (2016) Solar radiation prediction using different techniques: model evaluation and comparison. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 2016(61):384–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.04.024
Maier HR, Dandy GC (2000) Neural networks for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: a review of modelling issues and applications. Environ Modell Softw 15(1):101–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-8152(99)00007-9
Zeng J, Qiao W (2013) Short-term solar power prediction using a support vector machine. Renew Energy 52(1):118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2012.10.009
Orfila A, Ballester JL, Oliver R, Alvarez A, Tintoré J (2002) Forecasting the solar cycle with genetic algorithms. Astron Astrophys 386(1):313–318. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20020246
Chen SX, Gooi HB, Wang MQ (2013) Solar radiation forecast based on fuzzy logic and neural networks. Renew Energy 60:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2013.05.011
Bendu H, Deepak BBVL, Murugan S (2016) Application of GRNN for the prediction of performance 585 and exhaust emissions in HCCI engine using ethanol. Energy Convers Manag 122:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.05.061
Rizwan M, Jamil M, Kirmani S, Kothari DP (2014) Fuzzy logic based modeling and estimation of 573 global solar energy using meteorological parameters. Energy 70(6):685–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.04.057
Solar radiation handbook (2008) SEC & IMD, Pune. http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/srd-sec.pdf
Ghritlahre HK, Chandrakar P, Ahmad AA (2019) Comprehensive review on performance prediction of solar air heaters using artificial neural network. Ann Data Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-019-00236-1
Ghritlahre HK, Prasad RK (2018) Development of optimal ANN model to estimate the thermal performance of roughened solar air heater using two different learning algorithms. Ann Data Sci 5:453–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-018-0146-3
Sridharan M (2020) Application of generalized regression neural network in predicting the performance of solar photovoltaic thermal water collector. Ann Data Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-020-00273-1
Sridharan M (2020) Applications of artificial intelligence techniques in heat exchanger systems, advanced analytic and control techniques for thermal systems with heat exchangers. Academic Press, New York, pp 325–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819422-5.00015-3. ISBN: 978-0-12-819422-5
Sridharan M, Jayaprakash G, Chandrasekar M, Vigneshwar P, Paramaguru S, Amarnath K (2018) Prediction of solar photovoltaic/thermal collector power output using fuzzy logic. J Sol Energy Eng 140(6):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4040757
Sridharan M (2020) Application of generalized regression neural network in predicting the performance of natural convection solar dryer. J Sol Energy Eng 142(3):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4047824
Sridharan M (2020) Predicting performance of double pipe parallel and counter flow heat exchanger using fuzzy logic. J Therm Sci Eng Appl 12(3):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4044696
Sridharan M, Jayaprakash G (2019) Verification and validation of solar photovoltaic thermal water collectors performance using fuzzy logic. J Verif Valid Uncert 4(4):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4045895
Sridharan M (2020) Application of fuzzy logic expert system in predicting cold and hot fluid outlet temperature of counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger advanced analytic and control techniques for thermal systems with heat exchangers. Academic Press, New York, pp 307–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819422-5.00014-1. ISBN: 978-0-12-819422-5
Sridharan M, Shri Balaji S (2020) Application of generalized regression neural network in predicting the thermal performance of solar flat plate collector systems. J Therm Sci Eng Appl 13(2):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4047824
Sridharan M, Devi R, Dharshini CS, Bhavadarani M (2019) IoT Based performance monitoring and control in counter flow double pipe heat exchanger. Internet Things 5:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2018.11.002
Funding
There is no funding related to the content in this journal article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest related to this work.
Author contributions
The corresponding author is responsible for all the contributions in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendix 1
For the prediction of global solar irradiance at Jodhpur, Shillong, New Delhi, and Kolkata stations, Fuzzy logic based architecture has been developed and presented in Fig. 8. was proposed by [13] (Table 8).
Fuzzy logic based architecture suggested by [9] for prediction of global solar energy at Jodhpur, Shillong, New Delhi, and Kolkata stations
Appendix 2
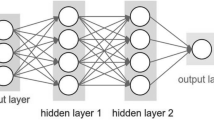
For the prediction of global solar irradiance at Jodhpur, Shillong, New Delhi, and Kolkata stations, ANN logic based architecture has been developed and presented in Fig. 9. was proposed by [13].
ANN model based architecture suggested by [9] for prediction of global solar energy at Jodhpur, Shillong, New Delhi, and Kolkata stations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sridharan, M. Generalized Regression Neural Network Model Based Estimation of Global Solar Energy Using Meteorological Parameters. Ann. Data. Sci. 10, 1107–1125 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-020-00319-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-020-00319-4