Abstract
Microplastics have emerged as an ubiquitous pollutant with severe environmental and human health hazards. Over the decades encountering these pollutants, microorganisms have evolved with the tool(s) to degrade different classes of plastic polymers. Several enzymes including depolymerases and lipases have been studied for the reduction of plastic toxicity. Since the degradation of plastic is a long process, thus, meta “omics” approaches have been employed to identify the active microbiota and microbial dynamics involved in the mitigation of microplastic-contaminated sites. Further, protein engineering approaches have opened new avenues to tackle this alarming situation. Increasing plastic contamination is serving as a breeding ground and carrier for spread of other persistent chlorinated pollutant. This review for the first time summarized a comprehensive report on microplastic sources, toxicity, and bio-based mitigation approaches. It covers deeper understanding about multi-omic approaches in microplastic research and engineering technologies in microplastic degradation. The guidelines and regulation to tackle the increasing pollution have been discussed. Knowledge gaps and opportunities have been comprehensively compiled that would aid the state-of-the-art information in the available literature for the researchers to further address this issue.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tran HT, Lin, C, Bui, XT, Nguyen, MK, Cao, NDT, Mukhtar, H, Hoang, HG, Varjani S, Ngo HH, Nghiem LD. Phthalates in the environment: characteristics, fate and transport, and advanced wastewater treatment technologies. Bioresour Technol. 2022;126249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126249
Singh K, Kashyap SK, Garg V. Use of zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model for research in toxicological studies. J Appl Nat Sci. 2021;13:846–52.
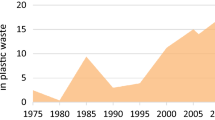
Lebreton L, Andrady A. Future scenarios of global plastic waste generation and disposal. Palgrave Commun Palgrave. 2019;5:1–11.
Ritchie H, Roser M. Plastic pollution. Published online at OurWorldInData.org. [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2021 Oct 10]. Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/plastic-pollution#total-plastic-waste-by-country
Wang C, Zhao J, Xing B. Environmental source, fate, and toxicity of microplastics. J Hazard Mater Elsevier. 2020;407:124357.
Chamas A, Moon H, Zheng J, Qiu Y, Tabassum T, Jang JH, et al. Degradation rates of plastics in the environment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng ACS Publications. 2020;8:3494–511.
Miloloža M, Kučić Grgić D, Bolanča T, Ukić Š, Cvetnić M, Ocelić Bulatović V, et al. Ecotoxicological assessment of microplastics in freshwater sources—a review. Water. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; 2021;13:56.
Guo X, Wang J. The chemical behaviors of microplastics in marine environment: a review. Mar Pollut Bull Elsevier. 2019;142:1–14.
Gaur VK, Sharma P, Gaur P, Varjani S, Ngo HH, Guo W, et al. Sustainable mitigation of heavy metals from effluents: toxicity and fate with recent technological advancements. Bioengineered Taylor & Francis. 2021;12:7297–313.
Gaur VK, Sharma P, Sirohi R, Varjani S, Taherzadeh MJ, Chang J-S, et al. Production of biosurfactants from agro-industrial waste and waste cooking oil in a circular bioeconomy: an overview. Bioresour Technol. Elsevier; 2021;126059.
Varjani S, Joshi R, Srivastava VK, Ngo HH, Guo W. Treatment of wastewater from petroleum industry: current practices and perspectives. Environ Sci Pollut Res Springer. 2020;27:27172–80.
Nair S. Plastic waste is India’s and the world’s most formidable environmental challenge today, and the COVID-19 pandemic has made matters worse: CSE. 2020.
Singh SG. Draft Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2021: addressing the bigger problem [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2021 Nov 20]. Available from: https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/waste/draft-plastic-waste-management-rules-2021-addressing-the-bigger-problem-75939
Gopinath KP, Nagarajan VM, Krishnan A, Malolan R. A critical review on energy, environmental and economic factors on various processes used to handle and recycle plastic wastes: development of a comprehensive index. J Clean Prod. Elsevier; 2020;123031.
Webb HK, Arnott J, Crawford RJ, Ivanova EP. Plastic degradation and its environmental implications with special reference to poly (ethylene terephthalate). Polymers (Basel). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; 2013;5:1–18.
Mishra B, Varjani S, Iragavarapu GP, Ngo HH, Guo W, Vishal B. Microbial fingerprinting of potential biodegrading organisms. Curr Pollut Reports Springer. 2019;5:181–97.
Varjani S, Rakholiya P, Shindhal T, Shah A V, Ngo HH. Trends in dye industry effluent treatment and recovery of value added products. J Water Process Eng. Elsevier; 2021;39:101734.
Dey TK, Uddin ME, Jamal M. Detection and removal of microplastics in wastewater: evolution and impact. Environ Sci Pollut Res. Springer; 2021;1–23.
Moharir RV, Kumar S. Challenges associated with plastic waste disposal and allied microbial routes for its effective degradation: a comprehensive review. J Clean Prod Elsevier. 2019;208:65–76.
Regar RK, Gaur VK, Bajaj A, Tambat S, Manickam N. Comparative microbiome analysis of two different long-term pesticide contaminated soils revealed the anthropogenic influence on functional potential of microbial communities. Sci Total Environ. 2019;681.
Jiang B, Jin N, Xing Y, Su Y, Zhang D. Unraveling uncultivable pesticide degraders via stable isotope probing (SIP). Crit Rev Biotechnol Taylor & Francis. 2018;38:1025–48.
Gaur VK, Gupta S, Pandey A. Evolution in mitigation approaches for petroleum oil-polluted environment: recent advances and future directions. Environ Sci Pollut Res. Springer; 2021;1–17.
Kaur I, Gaur VK, Regar RK, Roy A, Srivastava PK, Gaur R, et al. Plants exert beneficial influence on soil microbiome in a HCH contaminated soil revealing advantage of microbe-assisted plant-based HCH remediation of a dumpsite. Chemosphere. Elsevier; 2021;280:130690.
Horton AA, Barnes DKA. Microplastic pollution in a rapidly changing world: implications for remote and vulnerable marine ecosystems. Sci Total Environ. Elsevier; 2020;738:140349.
Verla AW, Enyoh CE, Verla EN, Nwarnorh KO. Microplastic–toxic chemical interaction: a review study on quantified levels, mechanism and implication. SN Appl Sci Springer. 2019;1:1–30.
Kershaw P. Sources, fate and effects of microplastics in the marine environment: a global assessment. International Maritime Organization; 2015.
Sridharan S, Kumar M, Singh L, Bolan NS, Saha M. Microplastics as an emerging source of particulate air pollution: a critical review. J Hazard Mater. Elsevier; 2021;126245.
Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Du F, Cai H, Wang G, Shi H. Microplastic fallout in different indoor environments. Environ Sci Technol ACS Publications. 2020;54:6530–9.
Bowley J, Baker-Austin C, Porter A, Hartnell R, Lewis C. Oceanic hitchhikers—assessing pathogen risks from marine microplastic. Trends Microbiol Elsevier. 2021;29:107–16.
Yan B, Liu Q, Li J, Wang C, Li Y, Zhang C. Microplastic pollution in marine environment: occurrence, fate, and effects (with a specific focus on biogeochemical carbon and nitrogen cycles). Microplastic Pollut. Springer Nature; 2021;105.
Horton AA, Dixon SJ. Microplastics: an introduction to environmental transport processes. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Water. Wiley Online Library; 2018;5:e1268.
Gallo F, Fossi C, Weber R, Santillo D, Sousa J, Ingram I, et al. Marine litter plastics and microplastics and their toxic chemicals components: the need for urgent preventive measures. Environ Sci Eur Springer. 2018;30:1–14.
Rochman CM, Hentschel BT, Teh SJ. Long-term sorption of metals is similar among plastic types: implications for plastic debris in aquatic environments. PLoS One. Public Library of Science San Francisco, USA; 2014;9:e85433.
Rios LM, Moore C, Jones PR. Persistent organic pollutants carried by synthetic polymers in the ocean environment. Mar Pollut Bull Elsevier. 2007;54:1230–7.
Karapanagioti HK, Ogata Y, Takada H. Eroded plastic pellets as monitoring tools for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH): laboratory and field studies. Glob NEST J Global Nest Journal. 2010;12:327–34.
Frias J, Sobral P, Ferreira AM. Organic pollutants in microplastics from two beaches of the Portuguese coast. Mar Pollut Bull Elsevier. 2010;60:1988–92.
Hirai H, Takada H, Ogata Y, Yamashita R, Mizukawa K, Saha M, et al. Organic micropollutants in marine plastics debris from the open ocean and remote and urban beaches. Mar Pollut Bull Elsevier. 2011;62:1683–92.
Heskett M, Takada H, Yamashita R, Yuyama M, Ito M, Geok YB, et al. Measurement of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in plastic resin pellets from remote islands: toward establishment of background concentrations for International Pellet Watch. Mar Pollut Bull Elsevier. 2012;64:445–8.
Zhu B-K, Fang Y-M, Zhu D, Christie P, Ke X, Zhu Y-G. Exposure to nanoplastics disturbs the gut microbiome in the soil oligochaete Enchytraeus crypticus. Environ Pollut Elsevier. 2018;239:408–15.
Enyoh CE, Shafea L, Verla AW, Verla EN, Qingyue W, Chowdhury T, et al. Microplastics exposure routes and toxicity studies to ecosystems: an overview. Environ Anal Heal Toxicol. Korean Society of Environmental Health and Toxicology & Korea Society for …; 2020;35.
Lu Y, Zhang Y, Deng Y, Jiang W, Zhao Y, Geng J, et al. Uptake and accumulation of polystyrene microplastics in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and toxic effects in liver. Environ Sci Technol ACS Publications. 2016;50:4054–60.
Duis K, Coors A. Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environ Sci Eur SpringerOpen. 2016;28:1–25.
Cox KD, Covernton GA, Davies HL, Dower JF, Juanes F, Dudas SE. Human consumption of microplastics. Environ Sci Technol ACS Publications. 2019;53:7068–74.
Westphalen H, Abdelrasoul A. Challenges and treatment of microplastics in water. Water Challenges an Urban World. BoD–Books on Demand; 2018;5:71–82.
Show PL, Thangalazhy-Gopakumar S, Foo DCY. Sustainable technologies for waste reduction and pollutants removals. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy; 2021;1.
Othman AR, Hasan HA, Muhamad MH, Ismail N, Abdullah SRS. Microbial degradation of microplastics by enzymatic processes: a review. Environ Chem Lett Springer. 2021;19:3057–73.
Ru J, Huo Y, Yang Y. Microbial degradation and valorization of plastic wastes. Front Microbiol. Frontiers; 2020;11:442.
Wei R, Zimmermann W. Microbial enzymes for the recycling of recalcitrant petroleum-based plastics: how far are we? Microb Biotechnol Wiley Online Library. 2017;10:1308–22.
Miri S, Saini R, Davoodi SM, Pulicharla R, Brar SK, Magdouli S. Biodegradation of microplastics: better late than never. Chemosphere. Elsevier; 2021;131670.
Chai WS, Tan WG, Munawaroh HSH, Gupta VK, Ho SS, Show PL. Multifaceted roles of microalgae in the application of wastewater biotreatment: a review. Environ. Pollut., 2021: 269: 116236.
Khandare SD, Chaudhary DR, Jha B. Marine bacterial biodegradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) plastic. Biodegradation Springer. 2021;32:127–43.
Hou L, Xi J, Liu J, Wang P, Xu T, Liu T, et al. Biodegradability of polyethylene mulching film by two Pseudomonas bacteria and their potential degradation mechanism. Chemosphere. Elsevier; 2022;286:131758.
Oviedo-Anchundia R, del Castillo DS, Naranjo-Mor&an J, Francois N, Alarc&on A, Villafuerte JS, et al. Analysis of the degradation of polyethylene, polystyrene and polyurethane mediated by three filamentous fungi isolated from the Antarctica. African J Biotechnol. Academic Journals; 2021;20:66–76.
Spina F, Tummino ML, Poli A, Prigione V, Ilieva V, Cocconcelli P, et al. Low density polyethylene degradation by filamentous fungi. Environ Pollut. Elsevier; 2021;274:116548.
Wang Z, Xin X, Shi X, Zhang Y. A polystyrene-degrading Acinetobacter bacterium isolated from the larvae of Tribolium castaneum. Sci Total Environ. Elsevier; 2020;726:138564.
Kumar AG, Hinduja M, Sujitha K, Rajan NN, Dharani G. Biodegradation of polystyrene by deep-sea Bacillus paralicheniformis G1 and genome analysis. Sci Total Environ. Elsevier; 2021;774:145002.
Chaudhary AK, Chaitanya K, Vijayakumar RP. Synergistic effect of UV and chemical treatment on biological degradation of polystyrene by Cephalosporium strain NCIM 1251. Arch Microbiol. Springer; 2021;1–9.
Skariyachan S, Taskeen N, Kishore AP, Krishna BV, Naidu G. Novel consortia of Enterobacter and Pseudomonas formulated from cow dung exhibited enhanced biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene. J Environ Manage. Elsevier; 2021;284:112030.
Jeon J-M, Park S-J, Choi T-R, Park J-H, Yang Y-H, Yoon J-J. Biodegradation of polyethylene and polypropylene by Lysinibacillus species JJY0216 isolated from soil grove. Polym Degrad Stab. Elsevier; 2021;191:109662.
Khandare SD, Chaudhary DR, Jha B. Bioremediation of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) films by marine bacteria. Mar Pollut Bull. Elsevier; 2021;169:112566.
Pardo-Rodríguez ML, Zorro-Mateus PJP. Biodegradation of polyvinyl chloride by Mucor sp and Penicillium sp isolated from soil. Rev Investig Desarro E INNOVACIÓN. 2021;11:387–400.
Roy R, Mukherjee G, Gupta A Das, Tribedi P, Sil AK. Isolation of a soil bacterium for remediation of polyurethane and low-density polyethylene: a promising tool towards sustainable cleanup of the environment. 3 Biotech. Springer; 2021;11:1–14.
Gao R, Sun C. A marine bacterial community that degrades poly (ethylene terephthalate) and polyethylene. bioRxiv. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2020;
Torena P, Alvarez‐Cuenca M, Reza M. Biodegradation of polyethylene terephthalate microplastics by bacterial communities from activated sludge. Can J Chem Eng. Wiley Online Library; 2021;
Liu R, Lai Q, Gu L, Yan P, Shao Z. Croceimicrobium hydrocarbonivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel marine bacterium isolated from a bacterial consortium that degrades polyethylene terephthalate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. Microbiology Society; 2021;71:4770.
Sarkhel R, Sengupta S, Das P, Bhowal A. Comparative biodegradation study of polymer from plastic bottle waste using novel isolated bacteria and fungi from marine source. J Polym Res Springer. 2020;27:1–8.
Moog D, Schmitt J, Senger J, Zarzycki J, Rexer K-H, Linne U, et al. Using a marine microalga as a chassis for polyethylene terephthalate (PET) degradation. Microb Cell Fact Springer. 2019;18:1–15.
Liu SY, Leung MM-L, Fang JK-H, Chua SL. Engineering a microbial ‘trap and release’ mechanism for microplastics removal. Chem Eng J. Elsevier; 2021;404:127079.
Pandey AK, Gaur VK, Udayan A, Varjani S, Kim S-H, Wong JWC. Biocatalytic remediation of industrial pollutants for environmental sustainability: research needs and opportunities. Chemosphere. Elsevier; 2021;272:129936.
Salvador M, Abdulmutalib U, Gonzalez J, Kim J, Smith AA, Faulon J-L, et al. Microbial genes for a circular and sustainable bio-PET economy. Genes (Basel). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; 2019;10:373.
Yoshida S, Hiraga K, Takehana T, Taniguchi I, Yamaji H, Maeda Y, et al. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly (ethylene terephthalate). Science (80- ). American Association for the Advancement of Science; 2016;351:1196–9.
Yan F, Wei R, Cui Q, Bornscheuer UT, Liu Y. Thermophilic whole-cell degradation of polyethylene terephthalate using engineered Clostridium thermocellum. Microb Biotechnol Wiley Online Library. 2021;14:374–85.
Wei R, Breite D, Song C, Gräsing D, Ploss T, Hille P, et al. Biocatalytic degradation efficiency of postconsumer polyethylene terephthalate packaging determined by their polymer microstructures. Adv Sci. Wiley Online Library; 2019;6:1900491.
Neelakanta G, Sultana H. The use of metagenomic approaches to analyze changes in microbial communities. Microbiol insights. SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, England; 2013;6:MBI-S10819.
Chandra A, Gaur V, Tripathi P. Microbiome analysis of rhizospheres of plant and winter-initiated ratoon crops of sugarcane grown in sub-tropical India: utility to improve ratoon crop productivity. 3 Biotech. Springer; 2021;11:1–11.
Purohit J, Chattopadhyay A, Teli B. Metagenomic exploration of plastic degrading microbes for biotechnological application. Curr Genomics Bentham Science Publishers. 2020;21:253–70.
Kumar AN, Kim G-B, Muhorakeye A, Varjani S, Kim S-H. Biopolymer production using volatile fatty acids as resource: effect of feast-famine strategy and lignin reinforcement. Bioresour Technol. Elsevier; 2021;326:124736.
Zhu F, Doyle E, Zhu C, Zhou D, Gu C, Gao J. Metagenomic analysis exploring microbial assemblages and functional genes potentially involved in di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate degradation in soil. Sci Total Environ. Elsevier; 2020;715:137037.
Qiu J, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Jiang J, Wu S, Li L, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel phthalate-degrading hydrolase from a soil metagenomic library. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. Elsevier; 2020;190:110148.
Michealsamy A, Thangamani L, Manivel G, Kumar P, Sundar S, Piramanayagam S, et al. Current research and applications of meta-omics stratagems in bioremediation: a bird’s-eye view. J Appl Biotechnol Reports. Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences; 2021;8:109–15.
Gravouil K, Ferru-Clément R, Colas S, Helye R, Kadri L, Bourdeau L, et al. Transcriptomics and lipidomics of the environmental strain Rhodococcus ruber point out consumption pathways and potential metabolic bottlenecks for polyethylene degradation. Environ Sci Technol ACS Publications. 2017;51:5172–81.
Gao R, Sun C. A marine bacterial community capable of degrading poly (ethylene terephthalate) and polyethylene. J Hazard Mater. Elsevier; 2021;416:125928.
Wang C, Wang Z, You Y, Xu W, Lv Z, Liu Z, et al. Response of Arthrobacter QD 15–4 to dimethyl phthalate by regulating energy metabolism and ABC transporters. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf Elsevier. 2019;174:146–52.
Liu T, Li J, Qiu L, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ, Zhong W. Combined genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the dibutyl phthalate metabolic pathway in Arthrobacter sp. ZJUTW Biotechnol Bioeng Wiley Online Library. 2020;117:3712–26.
Yang Y, Liu W, Zhang Z, Grossart H-P, Gadd GM. Microplastics provide new microbial niches in aquatic environments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol Springer. 2020;104:6501–11.
Medić A, Stojanović K, Izrael-Živković L, Beškoski V, Lončarević B, Kazazić S, et al. A comprehensive study of conditions of the biodegradation of a plastic additive 2, 6-di-tert-butylphenol and proteomic changes in the degrader Pseudomonas aeruginosa san ai. RSC Adv Royal Society of Chemistry. 2019;9:23696–710.
Wallace PW, Haernvall K, Ribitsch D, Zitzenbacher S, Schittmayer M, Steinkellner G, et al. PpEst is a novel PBAT degrading polyesterase identified by proteomic screening of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol Springer. 2017;101:2291–303.
Junghare M, Spiteller D, Schink B. Anaerobic degradation of xenobiotic isophthalate by the fermenting bacterium Syntrophorhabdus aromaticivorans. ISME J Nature Publishing Group. 2019;13:1252–68.
Li WJ, Wierckx N, Blank LM. Plastic monomer degradation—engineering Pseudomonas putida KT2440 for plastic monomer utilization. Fachgruppe Biologie; 2020.
Noguchi H, Taniguchi T, Itoh T. MetaGeneAnnotator: Detecting Species-Specific Patterns of Ribosomal Binding Site for Precise Gene Prediction in Anonymous Prokaryotic and Phage Genomes. DNA Research. 2008;15(6):387–96.
Alaimo S, Marceca GP, Giugno R, Ferro A, Pulvirenti A. Current Knowledge and Computational Techniques for Grapevine Meta-Omics Analysis. Front Plant Sci. 2018;8:2241.
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(23):7537–41.
Treangen TJ, Koren S, Sommer DD, Liu B, Astrovskaya I, Ondov B, Darling AE, Phillippy AM, Pop M. MetAMOS: a modular and open source metagenomic assembly and analysis pipeline. Genome Biol. 2013;14(1):1–20.
Franzosa EA, McIver LJ, Rahnavard G, Thompson LR, Schirmer M, Weingart G, Lipson KS, Knight R, Caporaso JG, Segata N, Huttenhower C. Species-level functional profiling of metagenomes and metatranscriptomes. Nat Methods. 2018;15(11):962–968.
Westreich ST, Treiber ML, Mills DA, Korf I, Lemay DG. SAMSA2: a standalone metatranscriptome analysis pipeline. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018;19(1):1–11.
Muth T, Behne A, Heyer R, Kohrs F, Benndorf D, Hoffmann M, Lehtevä M, Reichl U, Martens L, Rapp E. The MetaProteomeAnalyzer: A Powerful Open-Source Software Suite for Metaproteomics Data Analysis and Interpretation. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(3):1557–65.
Wright RJ, Bosch R, Langille MGI, Gibson MI, Christie-Oleza JA. A multi-OMIC characterisation of biodegradation and microbial community succession within the PET plastisphere. Microbiome Springer. 2021;9:1–22.
Arpia AA, Chen W-H, Ubando AT, Naqvi SR, Culaba AB. Microplastic degradation as a sustainable concurrent approach for producing biofuel and obliterating hazardous environmental effects: a state-of-the-art review. J Hazard Mater. Elsevier; 2021;126381.
Rodríguez-Narvaez OM, Goonetilleke A, Perez L, Bandala ER. Engineered technologies for the separation and degradation of microplastics in water: a review. Chem Eng J. Elsevier; 2021;128692.
Du H, Xie Y, Wang J. Microplastic degradation methods and corresponding degradation mechanism: research status and future perspectives. J Hazard Mater. Elsevier; 2021;126377.
Tarafdar A, Sirohi R, Gaur VK, Kumar S, Sharma P, Varjani S, et al. Engineering interventions in enzyme production: lab to industrial scale. Bioresour Technol. 2021;326.
Mishra B, Varjani S, Kumar G, Awasthi MK, Awasthi SK, Sindhu R, et al. Microbial approaches for remediation of pollutants: innovations, future outlook, and challenges. Energy Environ. SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, England; 2020;0958305X19896781.
Devda V, Chaudhary K, Varjani S, Pathak B, Patel AK, Singhania RR, et al. Recovery of resources from industrial wastewater employing electrochemical technologies: status, advancements and perspectives. Bioengineered Taylor & Francis. 2021;12:4697–718.
Perren W, Wojtasik A, Cai Q. Removal of microbeads from wastewater using electrocoagulation. ACS omega ACS Publications. 2018;3:3357–64.
Lu M-M, Gao F, Li C, Yang H-L. Response of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris to Cr stress and continuous Cr removal in a membrane photobioreactor. Chemosphere. Elsevier; 2021;262:128422.
Zurier HS, Goddard JM. Biodegradation of microplastics in food and agriculture. Curr Opin Food Sci Elsevier. 2021;37:37–44.
Tran KM, Lee H-M, Thai TD, Shen J, Eyun S, Na D. Synthetically engineered microbial scavengers for enhanced bioremediation. J Hazard Mater. Elsevier; 2021;126516.
Samak NA, Jia Y, Sharshar MM, Mu T, Yang M, Peh S, et al. Recent advances in biocatalysts engineering for polyethylene terephthalate plastic waste green recycling. Environ Int. Elsevier; 2020;145:106144.
PIB Delhi. Government notifies the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021, prohibiting identified single use plastic items by 2022 [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2021 Nov 20]. Available from: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1745433
Ministry of Jal Shakti G of I. National Mission for Clean Ganga. 2019.
Basak S, Das MK, Duttaroy AK. Plastics derived endocrine-disrupting compounds and their effects on early development. Birth defects Res Wiley Online Library. 2020;112:1308–25.
Ghosh K, Jones BH. Roadmap to biodegradable plastics—current state and research needs. ACS Sustain Chem Eng ACS Publications. 2021;9:6170–87.
Choe S, Kim Y, Won Y, Myung J. Bridging three gaps in biodegradable plastics: misconceptions and truths about biodegradation. Front Chem. Frontiers Media SA; 2021;9.
Amobonye A, Bhagwat P, Singh S, Pillai S. Plastic biodegradation: frontline microbes and their enzymes. Sci Total Environ. Elsevier; 2020;143536.
Sana SS, Dogiparthi LK, Gangadhar L, Chakravorty A, Abhishek N. Effects of microplastics and nanoplastics on marine environment and human health. Environ Sci Pollut Res. Springer; 2020;1–14.
Yong CQY, Valiyaveetill S, Tang BL. Toxicity of microplastics and nanoplastics in mammalian systems. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; 2020;17:1509.
Auta HS, Emenike CU, Fauziah SH. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ Int Elsevier. 2017;102:165–76.
Awasthi S, Srivastava P, Singh P, Tiwary D, Mishra PK. Biodegradation of thermally treated high-density polyethylene (HDPE) by Klebsiella pneumoniae CH001. 3 Biotech. Springer; 2017;7:1–10.
Habib S, Iruthayam A, Abd Shukor MY, Alias SA, Smykla J, Yasid NA. Biodeterioration of untreated polypropylene microplastic particles by Antarctic bacteria. Polymers (Basel). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute; 2020;12:2616.
Kim HR, Lee HM, Yu HC, Jeon E, Lee S, Li J, et al. Biodegradation of polystyrene by Pseudomonas sp. isolated from the gut of superworms (larvae of Zophobas atratus). Environ Sci Technol. ACS Publications; 2020;54:6987–96.
Magnin A, Hoornaert L, Pollet E, Laurichesse S, Phalip V, Avérous L. Isolation and characterization of different promising fungi for biological waste management of polyurethanes. Microb Biotechnol Wiley Online Library. 2019;12:544–55.
Kumar S, Teotia UVS, Singh Y. Screening of poly vinyl chloride degrading bacteria from plastic contaminated area of Baddi. J Appl Pharm Res. 2017;5:34–7.
Giacomucci L, Raddadi N, Soccio M, Lotti N, Fava F. Polyvinyl chloride biodegradation by Pseudomonas citronellolis and Bacillus flexus. N Biotechnol Elsevier. 2019;52:35–41.
Moyses DN, Teixeira DA, Waldow VA, Freire DMG, Castro AM. Fungal and enzymatic bio-depolymerization of waste post-consumer poly (ethylene terephthalate) (PET) bottles using Penicillium species. 3 Biotech. Springer; 2021;11:1–12.
Hu K, Tian W, Yang Y, Nie G, Zhou P, Wang Y, et al. Microplastics remediation in aqueous systems: strategies and technologies. Water Res. Elsevier; 2021;117144.
Khan MJ, Singh N, Mishra S, Ahirwar A, Bast F, Varjani S, Schoefs, B, Marchand, J, Rajendran, K, Banu, JR, Saratale, GD, Saratale RG, Vinayak, V. Impact of light on microalgal photosynthetic microbial fuel cells and removal of pollutants by nanoadsorbent biopolymers: updates, challenges and innovations. Chemosphere, 2022: 132589 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132589.
Khan MJ, Rai A, Ahirwar A, Sirotiya V, Mourya M, Mishra S, Schoefs B, Marchand J, Bhatia SK, Varjani S, Vinayak V. Diatom microalgae as smart nanocontainers for biosensing wastewater pollutants: recent trends and innovations. Bioengineered. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1996748.
Acknowledgements
SV is thankful to the management of Gujarat Pollution Control Board necessary facilities for their work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Water Pollution
Vivek K. Gaur, Shivangi Gupta, and Poonam Sharma are equal first authors
Highlights
• Escalating microplastic contamination is inevitable.
• Meta “omics” approaches offer better insights into microbial-aided degradation.
• Bioengineering approaches can serve as a better tool for plastic degradation.
• Plastic contamination increases the emergence of antibiotic-resistant genes.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaur, V.K., Gupta, S., Sharma, P. et al. Metabolic Cascade for Remediation of Plastic Waste: a Case Study on Microplastic Degradation. Curr Pollution Rep 8, 30–50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-021-00210-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-021-00210-7