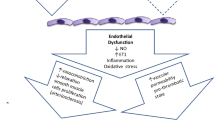
Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to show the effect of a new mechanism on endothelin (ET) receptors in the physiopathology of diabetes-related pulmonary injury. We tested the hypothesis that dual ET-1 receptor antagonism via bosentan can reverse diabetes-induced lung injury.
Methods
The rats (24 male) were separated into four groups: group 1 (HEALTHY): Control group; group 2 (DM): Streptozotocin 60 mg/kg (i.p.); group 3 (DM + BOS-1): Diabetes + bosentan 50 mg/kg per-os; group 4 (DM + BOS-2): Diabetes + bosentan 100 mg/kg per-os. The bosentan treatment was initiated immediately after the onset of STZ-induced diabetes and continued for 6 weeks.
Results
In the treatment group, SOD activity was significantly increased, although GSH and MDA levels and TNF-α and TGF-β gene expression were decreased. Bosentan 50 mg/kg and bosentan 100 mg/kg showed a significantly down-regulatory effect on ET-1, ET-A, and ET-B mRNA expression.
Conclusions
In conclusion, increased endothelin levels in the lung associated with diabetes may be one cause of endothelial dysfunction, cytokine increase, and oxidant/antioxidant imbalance in the pathogenesis of complications that may develop during diabetes. With its multiple effects, bosentan therapy may be an effective option against complications that may develop in association with diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karalliedde J, Gnudi L (2014) Diabetes mellitus, a complex and heterogeneous disease, and the role of insulin resistance as a determinant of diabetic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant Off Publ Eur Dial Transplant Assoc Eur Renal Assoc. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfu405
Dave S (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells derived in vitro transdifferentiated insulin-producing cells: a new approach to treat type 1 diabetes. Adv Biomed Res 3:266. doi:10.4103/2277-9175.148247
Rosenbloom AL, Silverstein JH, Amemiya S, Zeitler P, Klingensmith G (2009) Type 2 diabetes in the child and adolescent. Pediatr Diabetes 10(Suppl 12):17–32. doi:10.1111/j.1399-448.2009.00584.x
Simsek DG, Aycan Z, Ozen S, Cetinkaya S, Kara C, Abali S, Demir K, Tunc O, Ucakturk A, Asar G, Bas F, Cetinkaya E, Aydin M, Karaguzel G, Orbak Z, Siklar Z, Altincik A, Okten A, Ozkan B, Ocal G, Semiz S, Arslanoglu I, Evliyaoglu O, Bundak R, Darcan S (2013) Diabetes care, glycemic control, complications, and concomitant autoimmune diseases in children with type 1 diabetes in Turkey: a multicenter study. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 5(1):20–26. doi:10.4274/Jcrpe.893
Demirel F, Tepe D, Kara O, Esen I (2013) Microvascular complications in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 5(3):145–149. doi:10.4274/Jcrpe.994
Genuth S, Eastman R, Kahn R, Klein R, Lachin J, Lebovitz H, Nathan D, Vinicor F (2003) Implications of the United kingdom prospective diabetes study. Diabetes Care 26(Suppl 1):S28–S32
Gilbert RE (2013) Endothelial loss and repair in the vascular complications of diabetes: pathogenetic mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Circ J 77(4):849–856
Genuth S (2006) Insights from the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study on the use of intensive glycemic treatment to reduce the risk of complications of type 1 diabetes. Endocr Pract 12(Suppl 1):34–41. doi:10.4158/EP.12.S1.34
Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL (2009) Effect of glucose variability on the long-term risk of microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(10):1901–1903. doi:10.2337/dc09-0109
Popov D, Simionescu M (2001) Structural and transport property alterations of the lung capillary endothelium in diabetes. Ital J Anat Embryol 106(2 Suppl 1):405–412
Vojtkova J, Ciljakova M, Michnova Z, Turcan T (2012) Chronic complications of diabetes mellitus related to the respiratory system. Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab 18(3):112–115
Weynand B, Jonckheere A, Frans A, Rahier J (1999) Diabetes mellitus induces a thickening of the pulmonary basal lamina. Respiration 66(1):14–19. doi:10.1159/000029331
Hsia CC, Raskin P (2007) Lung function changes related to diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther 9(Suppl 1):S73–S82. doi:10.1089/dia.2007.0227
Kuziemski K, Specjalski K, Jassem E (2011) Diabetic pulmonary microangiopathy—fact or fiction? Endokrynol Pol 62(2):171–176
Pitocco D, Fuso L, Conte EG, Zaccardi F, Condoluci C, Scavone G, Incalzi RA, Ghirlanda G (2012) The diabetic lung–a new target organ? Rev Diabet Stud 9(1):23–35. doi:10.1900/RDS.2012.9.23
Scano G, Filippelli M, Romagnoli I, Mancini M, Misuri G, Duranti R, Rosi E (2000) Hypoxic and hypercapnic breathlessness in patients with type I diabetes mellitus. Chest 117(4):960–967
Galie N, Beghetti M, Gatzoulis MA, Granton J, Berger RMF, Lauer A, Chiossi E, Landzberg M, Invest B (2006) Bosentan therapy in patients with Eisenmenger syndrome—a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Circulation 114(1):48–54. doi:10.1161/Circulationaha.106.630715
Sitbon O, Gressin V, Speich R, Macdonald PS, Opravil M, Cooper DA, Fourme T, Humbert M, Delfraissy JF, Simonneau G (2004) Bosentan for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170(11):1212–1217. doi:10.1164/rccm.200404-445OC
Hoeper MM, Halank M, Marx C, Hoeffken G, Seyfarth HJ, Schauer J, Niedermeyer J, Winkler J (2005) Bosentan therapy for portopulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 25(3):502–508. doi:10.1183/09031936.05.00080804
Rafnsson A, Bohm F, Settergren M, Gonon A, Brismar K, Pernow J (2012) The endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan improves peripheral endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: a randomised trial. Diabetologia 55(3):600–607. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2415-y
Hauber HP, Blaukovitsch M (2010) Current and future treatment options in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 9(3):158–172
Cosentino F, Luscher TF (1998) Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 32(Suppl 3):S54–S61
Eleftheriadis T, Antoniadi G, Pissas G, Liakopoulos V, Stefanidis I (2013) The renal endothelium in diabetic nephropathy. Ren Fail 35(4):592–599. doi:10.3109/0886022X.2013.773836
Eringa EC, Serne EH, Meijer RI, Schalkwijk CG, Houben AJ, Stehouwer CD, Smulders YM, van Hinsbergh VW (2013) Endothelial dysfunction in (pre)diabetes: characteristics, causative mechanisms and pathogenic role in type 2 diabetes. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 14(1):39–48. doi:10.1007/s11154-013-9239-7
Feener EP, King GL (2001) Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: role in cardiovascular disease. Heart Fail Monit 1(3):74–82
Lee SH, Channick RN (2005) Endothelin antagonism in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 26(4):402–408. doi:10.1055/s-2005-916155
Shao D, Park JE, Wort SJ (2011) The role of endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pharmacol Res 63(6):504–511. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2011.03.003
Arison RN, Ciaccio EI, Glitzer MS, Cassaro JA, Pruss MP (1967) Light and electron microscopy of lesions in rats rendered diabetic with streptozotocin. Diabetes 16(1):51–56
Hasanein P, Shahidi S (2010) Effects of combined treatment with vitamins C and E on passive avoidance learning and memory in diabetic rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93(4):472–478. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2010.01.004
de Souza LF, Barreto F, da Silva EG, Andrades ME, Guimaraes EL, Behr GA, Moreira JC, Bernard EA (2007) Regulation of LPS stimulated ROS production in peritoneal macrophages from alloxan-induced diabetic rats: involvement of high glucose and PPARgamma. Life Sci 81(2):153–159. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2007.04.035
Ghorbani A, Omrani GR, Hadjzadeh MA, Varedi M (2013) Proinsulin C-peptide inhibits lipolysis in diabetic rat adipose tissue through phosphodiestrase-3B enzyme. Horm Metab Res 45(3):221–225. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1323764
Ghorbani A, Varedi M, Hadjzadeh MA, Omrani GH (2010) Type-1 diabetes induces depot-specific alterations in adipocyte diameter and mass of adipose tissues in the rat. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 118(7):442–448. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1247566
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25(1):192–205
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34(3):497–500
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Guerci B, Bohme P, Kearney-Schwartz A, Zannad F, Drouin P (2001) Endothelial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Part 2: altered endothelial function and the effects of treatments in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab 27(4 Pt 1):436–447
Sarman B, Toth M, Somogyi A (1998) Role of endothelin-1 in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Rev 14(2):171–175
Ergul A (2011) Endothelin-1 and diabetic complications: focus on the vasculature. Pharmacol Res 63(6):477–482. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2011.01.012
Comellas AP, Briva A (2009) Role of endothelin-1 in acute lung injury. Transl Res 153(6):263–271. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2009.02.007
Ross B, D’Orleans-Juste P, Giaid A (2010) Potential role of endothelin-1 in pulmonary fibrosis: from the bench to the clinic. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 42(1):16–20. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2009-0175TR
Schneider MP, Boesen EI, Pollock DM (2007) Contrasting actions of endothelin ET(A) and ET(B) receptors in cardiovascular disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:731–759. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.47.120505.105134
Cardillo C, Campia U, Bryant MB, Panza JA (2002) Increased activity of endogenous endothelin in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Circulation 106(14):1783–1787
McAuley DF, Nugent AG, McGurk C, Maguire S, Hayes JR, Johnston GD (2000) Vasoconstriction to endogenous endothelin-1 is impaired in patients with Type II diabetes mellitus. Clin Sci 99(3):175–179. doi:10.1042/Cs20000005
Zhou Y, Mitra S, Varadharaj S, Parinandi N, Zweier JL, Flavahan NA (2006) Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mediates enhanced contraction to endothelin ETA receptor stimulation in endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice. Circ Res 98(11):1439–1445. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000224120.52792.10
Climent B, Fernandez N, Sanz E, Sanchez A, Monge L, Garcia-Villalon AL, Dieguez G (2005) Enhanced response of pig coronary arteries to endothelin-1 after ischemia-reperfusion. Role of endothelin receptors, nitric oxide and prostanoids. Eur J Pharmacol 524(1–3):102–110. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.002
Fonseca C, Abraham D, Renzoni EA (2011) Endothelin in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 44(1):1–10. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2009-0388TR
Channick RN, Simonneau G, Sitbon O, Robbins IM, Frost A, Tapson VF, Badesch DB, Roux S, Rainisio M, Bodin F, Rubin LJ (2001) Effects of the dual endothelin-receptor antagonist bosentan in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a randomised placebo-controlled study. Lancet 358(9288):1119–1123. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)06250-X
Prakash A, Perry CM (2002) Bosentan. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 2(5):335–343 (discussion 343)
Araz O, Demirci E, Yilmazel Ucar E, Calik M, Pulur D, Karaman A, Yayla M, Altun E, Halici Z, Akgun M (2013) Comparison of reducing effect on lung injury of dexamethasone and bosentan in acute lung injury: an experimental study. Multidiscip Respir Med 8(1):74. doi:10.1186/2049-6958-8-74
Galie N, Rubin L, Hoeper M, Jansa P, Al-Hiti H, Meyer G, Chiossi E, Kusic-Pajic A, Simonneau G (2008) Treatment of patients with mildly symptomatic pulmonary arterial hypertension with bosentan (EARLY study): a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 371(9630):2093–2100. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60919-8
Elmarakby AA, Sullivan JC (2012) Relationship between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. Cardiovasc Ther 30(1):49–59. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00218.x
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Jarque A, Muros M, Mora C, Garcia J (2009) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha as a therapeutic target for diabetic nephropathy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20(2):165–173. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.02.005
Nishimura M, Obayashi H, Mizuta I, Hara H, Adachi T, Ohta M, Tegoshi H, Fukui M, Hasegawa G, Shigeta H, Kitagawa Y, Nakano K, Kaji R, Nakamura N (2003) TNF, TNF receptor type 1, and allograft inflammatory factor-1 gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes. Hum Immunol 64(2):302–309
Gonzalez-Clemente JM, Mauricio D, Richart C, Broch M, Caixas A, Megia A, Gimenez-Palop O, Simon I, Martinez-Riquelme A, Gimenez-Perez G, Vendrell J (2005) Diabetic neuropathy is associated with activation of the TNF-alpha system in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol 63(5):525–529. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02376.x
Yoshida A, Yoshida S, Khalil AK, Ishibashi T, Inomata H (1998) Role of NF-kappa B-mediated interleukin-8 expression in intraocular neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 39(7):1097–1106
Gupta S, Gambhir JK, Kalra O, Gautam A, Shukla K, Mehndiratta M, Agarwal S, Shukla R (2013) Association of biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress with the risk of chronic kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes mellitus in North Indian population. J Diabetes Complications 27(6):548–552. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2013.07.005
Tahara A, Kurosaki E, Yokono M, Yamajuku D, Kihara R, Hayashizaki Y, Takasu T, Imamura M, Li Q, Tomiyama H, Kobayashi Y, Noda A, Sasamata M, Shibasaki M (2013) Effects of SGLT2 selective inhibitor ipragliflozin on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, and obesity in type 2 diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol 715(1–3):246–255. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.05.014
Bowen T, Jenkins RH, Fraser DJ (2013) MicroRNAs, transforming growth factor beta-1, and tissue fibrosis. J Pathol 229(2):274–285. doi:10.1002/path.4119
Samarakoon R, Overstreet JM, Higgins PJ (2013) TGF-beta signaling in tissue fibrosis: redox controls, target genes and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Signal 25(1):264–268. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.10.003
Gao Y, Xu X, Ding K, Liang Y, Jiang D, Dai H (2013) Rapamycin inhibits transforming growth factor beta1-induced fibrogenesis in primary human lung fibroblasts. Yonsei Med J 54(2):437–444. doi:10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.437
Song X, Liu W, Xie S, Wang M, Cao G, Mao C, Lv C (2013) All-trans retinoic acid ameliorates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by downregulating the TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling pathway in rats. Lab Invest 93(11):1219–1231. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2013.108
El Gazaerly H, Elbardisey DM, Eltokhy HM, Teaama D (2013) Effect of transforming growth factor Beta 1 on wound healing in induced diabetic rats. Int J Health Sci (Qassim) 7(2):160–172
Sipal S, Halici Z, Kiki I, Polat B, Albayrak A, Albayrak F, Karakus E, Aksak S, Ozturk B, Gundogdu C (2012) Comparative study of three angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists in preventing liver fibrosis in diabetic rats: stereology, histopathology, and electron microscopy. J Mol Histol 43(6):723–735. doi:10.1007/s10735-012-9441-z
Halici Z, Bilen H, Albayrak F, Uyanik A, Cetinkaya R, Suleyman H, Keles ON, Unal B (2009) Does telmisartan prevent hepatic fibrosis in rats with alloxan-induced diabetes? Eur J Pharmacol 614(1–3):146–152. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.04.042
Miric G, Dallemagne C, Endre Z, Margolin S, Taylor SM, Brown L (2001) Reversal of cardiac and renal fibrosis by pirfenidone and spironolactone in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 133(5):687–694. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704131
Sharma K, Ix JH, Mathew AV, Cho M, Pflueger A, Dunn SR, Francos B, Sharma S, Falkner B, McGowan TA, Donohue M, Ramachandrarao S, Xu R, Fervenza FC, Kopp JB (2011) Pirfenidone for diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(6):1144–1151. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010101049
Shepler B, Nash C, Smith C, Dimarco A, Petty J, Szewciw S (2012) Update on potential drugs for the treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Clin Ther 34(6):1237–1246. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.04.026
Obrosova IG (2005) Increased sorbitol pathway activity generates oxidative stress in tissue sites for diabetic complications. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(11–12):1543–1552. doi:10.1089/ars.2005.7.1543
Vincent AM, Russell JW, Low P, Feldman EL (2004) Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Endocr Rev 25(4):612–628. doi:10.1210/Er.2003-0019
Ziegler D, Sohr CGH, Nourooz-Zadeh J (2004) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in relation to the severity of diabetic polyneuropathy and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 27(9):2178–2183. doi:10.2337/diacare.27.9.2178
Pennathur S, Heinecke JW (2007) Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in vascular disease. Curr Diab Rep 7(4):257–264
Wen Y, Skidmore JC, Porter-Turner MM, Rea CA, Khokher MA, Singh BM (2002) Relationship of glycation, antioxidant status and oxidative stress to vascular endothelial damage in diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 4(5):305–308
Uyanik A, Unal D, Uyanik MH, Halici Z, Odabasoglu F, Altunkaynak ZB, Cadirci E, Keles M, Gundogdu C, Suleyman H, Bayir Y, Albayrak M, Unal B (2010) The effects of polymicrobial sepsis with diabetes mellitus on kidney tissues in ovariectomized rats. Ren Fail 32(5):592–602. doi:10.3109/08860221003759478
Suys B, de Beeck LO, Rooman R, Kransfeld S, Heuten H, Goovaerts I, Vrints C, de Wolf D, Matthys D, Manuel-y-Keenoy B (2007) Impact of oxidative stress on the endothelial dysfunction of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus: protection by superoxide dismutase? Pediatr Res 62(4):456–461. doi:10.1203/PDR.0b013e318142581a
Goyal R, Singhai M, Faizy AF (2011) Glutathione peroxidase activity in obese and nonobese diabetic patients and role of hyperglycemia in oxidative stress. J Midlife Health 2(2):72–76. doi:10.4103/0976-7800.92529
Likidlilid A, Patchanans N, Poldee S, Peerapatdit T (2007) Glutathione and glutathione peroxidase in type 1 diabetic patients. J Med Assoc Thai 90(9):1759–1767
Yayla M, Halici Z, Unal B, Bayir Y, Akpinar E, Gocer F (2014) Protective effect of Et-1 receptor antagonist bosentan on paracetamol induced acute liver toxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 726C:87–95. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.022
Halici Z, Bilen H, Albayrak F, Uyanik A, Cetinkaya R, Suleyman H, Keles ON, Unal B (2009) Does telmisartan prevent hepatic fibrosis in rats with alloxan-induced diabetes? Eur J Pharmacol 614(1–3):146–152. doi:10.1016/J.Ejphar.04.042
Albayrak A, Uyanik MH, Odabasoglu F, Halici Z, Uyanik A, Bayir Y, Albayrak F, Albayrak Y, Polat B, Suleyman H (2011) The effects of diabetes and/or polymicrobial sepsis on the status of antioxidant enzymes and pro-inflammatory cytokines on heart, liver, and lung of ovariectomized rats. J Surg Res 169(1):67–75. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2009.09.055
Nakhjavani M, Esteghamati A, Nowroozi S, Asgarani F, Rashidi A, Khalilzadeh O (2010) Type 2 diabetes mellitus duration: an independent predictor of serum malondialdehyde levels. Singapore Med J 51(7):582–585
Reis JS, Veloso CA, Volpe CM, Fernandes JS, Borges EA, Isoni CA, Dos Anjos PM, Nogueira-Machado JA (2012) Soluble RAGE and malondialdehyde in type 1 diabetes patients without chronic complications during the course of the disease. Diab Vasc Dis Res 9(4):309–314. doi:10.1177/1479164111436316
Singh G, Sharma B, Jaggi AS, Singh N (2014) Efficacy of bosentan, a dual ETA and ETB endothelin receptor antagonist, in experimental diabetes induced vascular endothelial dysfunction and associated dementia in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:27–35. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2014.05.002
Jiang JH, Yuen V, Xiang H, McNeill JH (2006) Improvement in cardiac function of diabetic rats by bosentan is not associated with changes in the activation of PKC isoforms. Mol Cell Biochem 282(1–2):177–185. doi:10.1007/S11010-006-1926-1
Sachidanandam K, Portik-Dobos V, Kelly-Cobbs AI, Ergul A (2010) Dual endothelin receptor antagonism prevents remodeling of resistance arteries in diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharm 88(6):616–621. doi:10.1139/Y10-034
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Marc Iglarz and Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd., for providing us bosentan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
Animal experiments and procedures were performed in accordance with the national guidelines for the use and care of laboratory animals and were approved by Ataturk University’s local animal care committee.
Informed consent
All authors consent journal’s entire rule and confirm the publication of manuscript in the Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cayir, A., Ugan, R.A., Albayrak, A. et al. The lung endothelin system: a potent therapeutic target with bosentan for the amelioration of lung alterations in a rat model of diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol Invest 38, 987–998 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0282-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-015-0282-y