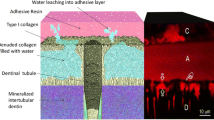
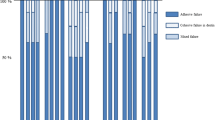
Abstract
One of the most important aspects in the field of dentistry is adhesion. Adhesion can be enhanced through different mechanisms, most commonly by chemical and mechanical modifications of dental material surfaces. One example of chemical adhesion utilizes primers or bonding agents containing coupling agents. Universal primers which are (mainly organophosphate-based monomers) and silane coupling agents are the most effective and most widely used for unifying dissimilar materials. Other than improving adhesion, Silanes have many other applications in dentistry. They have been found also to enhance the mechanical properties of materials either by adhesion or by becoming a constituent of dental materials itself. Universal primers, on the other hand, are utilized in bonding between different dental materials such as ceramics, metals, alloys, as well as to resin composites. Unfortunately, these primers, coupling agents, and bonding agents have, in general, poor hydrolytic stability. They are susceptible to humid oral environment, which invariably render them potentially unstable in the humid oral environment as saliva is always present. Improving their hydrolytic stability should therefore result in stronger adhesion for dental materials and dental prosthesis with a better clinical survival rate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
C.Y.K. Lung and J.P. Matinlinna, Silanes for adhesion promotion and surface modification, in Silane Chemistry, Applications and Performance, K. Moriguchi and S. Utagawa (Eds.), pg., 87–109. Nova Science Publisher, Hauppage, NY (2013). Gives basic understanding of primers.
Lung CYK, Matinlinna JP. Aspects of silane coupling agents and surface conditioning in dentistry: an overview. Dental Mater. 2012;28:467–77. Gives ample information of primers in dentistry.
Plueddemann EP. Silane coupling agents. 2nd ed. New York: Plenum Press; 1991.
Matinlinna JP, Tsoi JK-H, De Vries J, Busscher HJ. Characterization of novel silane coatings on titanium implant surfaces. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2013;24:688–97. Gives an understanding of the action of silane on titanium.
Lung CYK, Kukk E, Hägerth T, Matinlinna JP. Surface hydroxylation of silica-coated zirconia by various chemical treatments. Appl Surface Sci. 2010;257:1228–35. Gives an interesting take on the grit-blasting effect on zirconia followed by silanization.
Matinlinna JP, Lassila LVJ, Ozcan M, Yli-Urpo A, Vallittu PK. An introduction to silanes and their clinical applications in dentistry. Int J Prosthodont. 2004;17:155–64. A classical article which forms the basis of silanes and how they can be used in dentistry.
Ho GW, Matinlinna JP. Insights into ceramics as dental materials part I: ceramic material types in dentistry. Silicon. 2011;3:109–15. A good review article, giving a correlation between silanized fillers and good mechanical properties.
Ho GW, Matinlinna JP. Insights into ceramics as dental materials part II: chemical surface treatments. Silicon. 2011;3:117–23. A good review article, giving a correlation between silanized fillers and good mechanical properties.
Vallittu PK, Narva K. Impact strength of a modified continuous glass fiber—poly (methyl methacrylate). Int J Prosthodont. 1997;10(2):142–8.
Vallittu P. Curing of a silane coupling agent and its effect on the transverse strength of autopolymerizing polymethylmethacrylate—glass fibre composite. J Oral Rehabil. 1997;24(2):124–30.
Matinlinna JP, Ozcan M, Lassila LVJ, Vallittu PK. Applications of trialkoxysilanes in dental biomaterials: a review. In: Mittal KL, editor. Silanes and other coupling agents, Vol 4. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2007. p. 199–215. Another outstanding article which helps a great deal understanding what silanes are and their actions.
Marsden JG. In: Skeist I, editor. Handbook of adhesives. New York: Van Nostrand-Reinhold; 1990. p. 536–48.
Silane E. In: Othmer K, editor. Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology, B. Arkles. London: Wiley; 1997. p. 69–81.
McDonough WG, Antonucci JM, Dunkers JP. Interfacial shear strengths of dental resin-glass fibers by the microbond test. Dent Mater. 2001;17(6):492–8.
Ferracane JL. Resin composite—state of the art. Dent Mater. 2011;27(1):29–38.
Lin CT, Lee SY, Keh ES, Dong DR, Huang HM, Shih YH. Influence of silanization and filler fraction on aged dental composites. J Oral Rehabil. 2000;27(11):919–26.
García AH, Lozano MAM, Vila JC, Escribano AB, Galve PF. Composite resins. A review of the materials and clinical indications. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2006;11(2):E215–20.
Kitayama S, Nikaido T, Takahashi R, Zhu L, Ikeda M, Foxton RM. Effect of primer treatment on bonding of resin cements to zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 2010;26(5):426–32.
Vallittu PK. Comparison of two different silane compounds used for improving adhesion between fibres and acrylic denture base material. J Oral Rehabil. 1993;20:533–9.
Samimi P, Mortazavi V, Salamat F. Effects of heat treating silane and different etching techniques on glass fiber post push-out bond strength. Oper Dent. 2014;39(5):E217–24.
Debnath S, Ranade R, Wunder SL, Baran GR, Zhang J, Fisher ER. Chemical surface treatment of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene for improved adhesion to methacrylate resins. J Appl Polym Sci. 2005;96(5):1564–72.
Etcheverry M, Damiani DE, Ferreira ML, Barbosa SE, Capiati NJ. Chemical grafting of metallocene‐catalyzed functional polypropylene copolymer on glass substrates through surface modification. J Appl Polym Sci. 2008;109(5):2815–22.
Ramos Jr V, Runyan DA, Christensen LC. The effect of plasma-treated polyethylene fiber on the fracture strength of polymethyl methacrylate. J Prosthet Dent. 1996;76(1):94–6.
Mittal KL. Polymer surface modification: relevance to adhesion, 2004, vol 3. CRC Press.
Wang J, Liang G, Zhao W, Lü S, Zhang Z. Studies on surface modification of UHMWPE fibers via UV initiated grafting. Appl Surf Sci. 2006;253(2):668–73.
Cho EH, Lee SG, Kim JK. Surface modification of UHMWPE with γ-ray radiation for improving interfacial bonding strength with bone cement (II). Curr Appl Phys. 2005;5(5):475–9.
Bahramian N, Atai M, Naimi-Jamal MR. Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene fiber reinforced dental composites: effect of fiber surface treatment on mechanical properties of the composites. Dent Mater. 2015;31(9):1022–9.
Kim YK, Son JS, Kim K-H, Kwon T-Y. A simple 2-step silane treatment for improved bonding durability of resin cement to quartz fiber post. J Endod. 2013;39(10):1287–90.
Fonseca RB, Paula MSd, Favarão IN, Kasuya AVB, Almeida LNd, Mendes GAM, Carlo HL. Reinforcement of dental methacrylate with glass fiber after heated silane application. BioMed Research International 2014 (5):364398 May 2014.
Oliveira AS, Ramalho ES, Spazzin AO, Naves LZ, Moraes RR. Influence of silane and solvated bonding agents on the bond strength to glass‐fibre posts. Aust Endod J. 2013;39(3):122–5.
Yu B, Jiang Z, Tang X-Z, Yue CY, Yang J. Enhanced interphase between epoxy matrix and carbon fiber with carbon nanotube-modified silane coating. Compos Sci Technol. 2014;99:131–40.
Wang T, Tsoi JK-H, Matinlinna JP. A novel zirconia fiber-reinforced resin composite for dental use. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;53:151–60. Article shows an increase in fracture toughness due to the silanization of zirconia micro-fibers.
Ozcan M, Vallittu PK. Effect of surface conditioning methods on the bond strength of luting cement to ceramics. Dent Mater. 2003;19:725–31. This article indicates why surface modification is important before the silanization process.
Kern M, Thompson VP. Durability of resin bonds to a cobalt-chromium alloy. J Dent. 1995;23:47–54.
Cobb DS, Vargas MA, Fridrich TA, Bouschlicher MR. Metal surface treatment: characterization and effect on composite-to-metal bond strength. Oper Dent. 2000;25:427–33.
Foxton RM, Pereira PN, Masatoshi N, Tagami J, Miura H. Long-term durability of the dual-cure resin cement/silicon oxide ceramic bond. J Adhes Dent. 2002;4:125–35.
Nogami T, Tanoue N, Atsuta M, Matsumura H. Effectiveness of two-liquid silane primers on bonding sintered feldspathic porcelain with a dual-cured composite luting agent. J Oral Rehabil. 2004;31:770–4.
Matsumura H, Kato H, Atsuta M. Shear bond strength to feldspathic porcelain of two luting cements in combination with three surface treatments. J Prosthet Dent. 1997;78:511–7.
Sakai M, Taira Y, Sawase T. Silane primers rather than heat treatment contribute to adhesive bonding between tri-N-butylborane resin and a machinable leucite-reinforced ceramic. Dent Mater J. 2011;30:854–60.
Taira Y, Sakai M, Sawase T. Effects of primer containing silane and thiophosphate monomers on bonding resin to a leucite-reinforced ceramic. J Dent. 2012;40:353–8.
Li R. Development of a ceramic primer with higher bond durability for resin cement. J Oral Rehabil. 2010;37:560–8.
Matinlinna JP, Choi AH, Tsoi JK. Bonding promotion of resin composite to silica-coated zirconia implant surface using a novel silane system. Clin Oral Implants Res, 2012. This is a very good article showing why silanization would be more effective after silica coating the substrate first.
Meng X, Yoshida K, Taira Y, Kamada K, Luo X. Effect of siloxane quantity and ph of silane coupling agents and contact angle of resin bonding agent on bond durability of resin cements to machinable ceramic. J Adhes Dent. 2011;13:71–8.
Quiroz JR, Ozcan M, de Oliveria LF, Della Bona A, Takahashi FE, Bottino MA. Surface characterization of fedspathic ceramic using ATR FT-IR and ellipsometry after various silanization protocols. Dent Mater. 2012;28(2):189–96. Another spectacular article which shows us the importance of different silanization protocols by their chemical analysis.
Matinlinna JP, Vallittu PK. Silane based concepts on bonding resin composite to metals. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2007;8(2):1–8. A striking article which forms the basis of the bonding of resin cements to prostheis with silanization.
Matinlinna JP, Mittal KL, Adhesion aspects in dentistry. Leiden, 2009, The Netherlands: Koninklijke Brill NV. An important article showing how and why adhesion is important.
Hooshmand T, van Noort R, Keshvad A. Bond durability of the resin-bonded and silane treated ceramic surface. Dent Mater. 2002;18:179–88.
Fabianelli A, Pollington S, Papacchini F, Goracci C, Cantoro A, Ferrari M, et al. The effect of different surface treatments on bond strength between leucite reinforced feldspathic ceramic and composite resin. J Dent. 2010;38:39–43.
De Carvalho RF, Martins ME, de Queiroz JR, Leite FP, Ozcan M. Influence of silane heat treatment on bond strength of resin cement to a feldspathic ceramic. Dent Mater J. 2011;30:392–7.
Murrillo F, De Góes M. Effect of different silane-containing solutions on glass-ceramic/cement bonding interacting with dual-cure resin cements. -ODOVTOS-Int. J. Dental S.C. 2014;16:87–105.
Hooshmand T, van Noort R, Keshvad A. Storage effect of a pre-activated silane on the resin to ceramic bond. Dent Mater. 2004;20:635–42.
Guazzato M, Albakry M, Ringer SP, Swain MV. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part II. Zirconia-based dental ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004;20:449–56.
Denry I, Kelly JR. State of the art of zirconia for dental applications. Dent Mater. 2008;24:299–307.
Griggs JA. Recent advances in materials for all-ceramic restorations. Dent Clin N Am. 2007;51:713–27. viii.
Kelly JR, Denry I. Stabilized zirconia as a structural ceramic: an overview. Dent Mater. 2008;24:289–98.
Yilmaz H, Aydin C, Gul BE. Flexural strength and fracture toughness of dental core ceramics. J Prosthet Dent. 2007;98:120–8.
Thompson JY, Stoner BR, Piascik JR, Smith R. Adhesion/cementation to zirconia and other non-silicate ceramics: where are we now? Dent Mater. 2011;27:71–82.
Pagniano RP, Seghi RR, Rosenstiel SF, Wang RT, Katsube N. The effect of a layer of resin luting agent on the biaxial flexure strength of two all-ceramic systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2005;93:459–66.
Blatz MB, Sadan A, Kern M. Resin-ceramic bonding: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent. 2003;89:268–74.
Aida M, Hayakawa T, Mizukawa K. Adhesion of composite to porcelain with various surface conditions. J Prosthet Dent. 1995;73:464–70.
Kern M, Wegner SM. Bonding to zirconia ceramic: adhesion methods and their durability. Dent Mater. 1998;14:64–71.
Sun R, Suansuwan N, Kilpatrick N, Swain M. Characterisation of tribochemically assisted bonding of composite resin to porcelain and metal. J Dent. 2000;28:441–5.
Attia A, Lehmann F, Kern M. Influence of surface conditioning and cleaning methods on resin bonding to zirconia ceramic. Dent Mater. 2011;27:207–13.
Heikkinen TT, Lassila LVJ, Matinlinna JP, Vallittu PK. Thermocycling effects on resin bond to silicatized and silanized zirconia. J Adhes Sci Technol. 2009;23:1043–51.
Brentel AS, Özcan M, Valandro LF, Alarça LG, Amaral R, Bottino MA. Microtensile bond strength of a resin cement to feldpathic ceramic after different etching and silanization regimens in dry and aged conditions. Dent Mater. 2007;23:1323–31.
Derand T, Molin M, Kvam K. Bond strength of composite luting cement to zirconia ceramic surfaces. Dent Mater. 2005;21:1158–62.
Heikkinen TT, Lassila LV, Matinlinna JP, Vallittu PK. Effect of operating air pressure on tribochemical silica-coating. Acta Odontol Scand. 2007;65:241–8.
Kim BK, Bae HE, Shim JS, Lee KW. The influence of ceramic surface treatments on the tensile bond strength of composite resin to all-ceramic coping materials. J Prosthet Dent. 2005;94:357–62.
Ozcan M, Matinlinna JP. Surface conditioning protocol for the adhesion of resin-based cements to base and noble alloys: how to condition and why? J Adhes Dent. 2015;17(4):372–3. This article gives a very good understanding of grit-blasting and application of silane on the prosthesis.
Blatz MB, Sadan A, Martin J, Lang B. In vitro evaluation of shear bond strengths of resin to densely-sintered high-purity zirconium-oxide ceramic after long-term storage and thermal cycling. J Prosthet Dent. 2004;91:356–62.
Kitayama S, Nikaido T, Ikeda M, Alireza S, Miura H, Tagami J. Internal coating of zirconia restoration with silica-based ceramic improves bonding of resin cement to dental zirconia ceramic. Bio-Med Mater Eng. 2010;20:77–87.
Qeblawi DM, Munoz CA, Brewer JD, Monaco Jr EA. The effect of zirconia surface treatment on flexural strength and shear bond strength to a resin cement. J Prosthet Dent. 2010;103:210–20.
Chen L, Shen H, Suh BI. Effect of incorporating BisGMA resin on the bonding properties of silane and zirconia primers. J Prosthet Dent. 2013;110:402–7.
Aboushelib MN, Mirmohamadi H, Matinlinna JP, Kukk E, Ounsi HF, Salameh Z. Innovations in bonding to zirconia-based materials. Part II: focusing on chemical interactions. Dent Mater. 2009;25:989–93. An article giving new concepts of bonding dental materials to resin cements.
Matinlinna JP, Lassila LV. Enhanced resin-composite bonding to zirconia framework after pretreatment with selected silane monomers. Dent Mater. 2011;27:273–80.
Wang L, Liu YH, Si WJ, Feng HL, Tao YQ, Ma ZZ. Friction and wear behaviors of dental ceramics against natural tooth enamel. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2012;32(11):2599–606.
Zakir M, Tsoi JK-H, Chu CH, Lung CYK, Matinlinna JP. Bonding dissimilar materials in dentistry: a critical review. Rev Adhes Adhes. 2014; 2(4):413–32. A very important article which reviews the primers including silanes and many others for e.g., zirconates, phosphates, titanates etc .
Ozcan M, Matinlinna JP, Vallittu PK, Huysmans MC. Effect of drying time of 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane on the shear bond strength of a composite resin to silica-coated base/noble alloys. Dent Mater. 2004;20(6):586–90. This article gives an idea of how adhesion can be promoted by surface modification of noble and base metal alloys.
Shimizu H, Kurtz KS, Tachii Y, Takahashi Y. Use of metal conditioners to improve bond strengths of autopolymerizing denture base resin to cast Ti–6Al–7Nb and Co–Cr. J Dent. 2006;34(2):117–22.
Antoniadou M, Kern M, Strub JR. Effect of a new metal primer on the bond strength between a resin cement and two high-noble alloys. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;84(5):554–60.
Sirirungrojying S, Saito K, Hayakawa T, Kasai K. Efficacy of using self-etching primer with a 4-META/MMA-TBB resin cement in bonding orthodontic brackets to human enamel and effect of saliva contamination on shear bond strength. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(2):251–8.
Matinlinna JP, Lassila LV, Vallittu PK. The effect of a novel silane blend system on resin bond strength to silica-coated Ti substrate. J Dent. 2006;34(7):436–43.
Madhav GV, Raj S, Yadav N, Mudgal I, Mehta N, Tatwadiyan R. Shear bond strength of acrylic teeth to acrylic denture base after different surface conditioning methods. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013;14(5):892–7.
Shimizu H, Kawahuchi T, Yoshida K, Tsue F, Takahashi Y. Effect of surface preparation on the failure load of a highly filled composite resin bonded to a denture base resin. J Prosthodont. 2009;18(8):684–7.
Katsumata Y, Hojo S, Hamano N, Watanabe T, Yanaguchi H, Okada S, et al. Bonding strength of autopolymerizing resin to nylon denture base polymer. Dent Mater J. 2009;28(4):409–18.
Atsu S, Keskin Y. Effect of silica coating and silane surface treatment on the bond strength of soft denture liner to denture base material. J Appl Oral Sci. 2013;21(4):300–6.
Stawarczyk B, Beuer F, Wimmer T, Jahn D, Sener B, Roos M, et al. Polyetheretherketone-a suitable material for fixed dental prostheses? J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(7):1209–16.
Keul C, Liebermann A, Schmidlin PR, Roos M, Sener B, Stawarczyk B. Influence of PEEK surface modification on surface properties and bond strength to veneering resin composites. J Adhes Dent. 2014;16(4):383–92.
Najeeb S, Khurshid Z, Matinlinna JP, Siddique F, Mohammad ZN, Baroudi K. Nano-modified PEEK dental implants: bioactivecomposites and surface modification: A review. Int J Dentistry 2015, Artcle ID 381759, 7 pages
Schmidlin PR, Stawarczyk B, Wieland M, Attin T, Hämmerle CH, Fischer J. Effect of different surface pre-treatments and luting materials on shear bond strength to PEEK. Dent Mater. 2010;26(6):553–9.
Stawarczyk B, Jordan P, Schmidlin PR, Roos M, Eichberger M, Gernet W, et al. PEEK surface treatment effects on tensile bond strength to veneering resins. J Prosthet Dent. 2014;112(5):1278–88.
Stawarczyk B, Keul C, Beuer F, Roos M, Schmidlin PR. Tensile bond strength of veneering resins to PEEK: impact of different adhesives. Dent Mater J. 2013;32(3):441–8.
Kern M, Lehmann F. Influence of surface conditioning on bonding to polyetheretherketon (PEEK). Dent Mater. 2012;28(12):1280–3.
Wang C, Niu L-n, Wang Y-j, Jiao K, Liu Y, Zhou W, et al. Bonding of resin cement to zirconia with high pressure primer coating. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(7):e101174. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0101174.
Inokoshi M, Kameyama A, de Munck J, Minakuchi S, van Meerbeek B. Durable bonding to mechanically and/or chemically pre-treated dental zirconia. J Dent. 2013;41:170–9.
Acknowledements
The authors would like to acknowledge and thank Ms. Madeline Yon for proof reading the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All the authors of this review article declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subject performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Dental Restorative Materials
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakir, M., Ashraf, U., Tian, T. et al. The Role of Silane Coupling Agents and Universal Primers in Durable Adhesion to Dental Restorative Materials - a Review. Curr Oral Health Rep 3, 244–253 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40496-016-0108-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40496-016-0108-9