Abstract
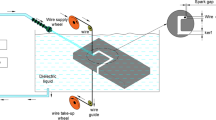
The current study investigates the behavior of wire electric discharge machining (WEDM) of the super alloy Udimet-L605 by employing sophisticated machine learning approaches. The experimental work was designed on the basis of the Taguchi orthogonal L27 array, considering six explanatory variables and evaluating their influences on the cutting speed, wire wear ratio (WWR), and dimensional deviation (DD). A support vector machine (SVM) algorithm using a normalized poly-kernel and a radial-basis flow kernel is recommended for modeling the wire electric discharge machining process. The grey relational analysis (GRA) approach was utilized to obtain the optimal combination of process variables simultaneously, providing the desirable outcome for the cutting speed, WWR, and DD. Scanning electron microscope and energy dispersive X-ray analyses of the samples were performed for the confirmation of the results. An SVM based on the radial-basis kernel model dominated the normalized poly-kernel model. The optimal combination of process variables for a mutually desirable outcome for the cutting speed, WWR, and DD was determined as T on1, T off2, I P1, WT3, SV1, and WF3. The pulse-on time is the significant variable influencing the cutting speed, WWR, and DD. The largest percentage of copper (8.66%) was observed at the highest cutting speed setting of the machine compared to 7.05% of copper at the low cutting speed setting of the machine.








































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf JS, Sandrock GD (1968) Some observations concerning the oxidation of the cobalt-base superalloy L-605 (HS-25). NASA TN D-4715, 1-37, Id. 20020916024
Hebsur MG, Noebe RD, Revilock DM (2003) Superior ballistic impact resistance achieved by the co-base alloy Haynes 25 (L605). Research and Technology, NASA/TM-211990
Tosun N, Cogun C (2003) An investigation on wire wears in WEDM. J Mater Process Technol 134(3):273–278
Puri AB, Bhattacharyya B (2003) An analysis and optimization of the geometrical inaccuracy due to wire lag phenomenon in WEDM. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(2):151–159
Sarkar S, Mitra S, Bhattacharyya B (2006) Parametric optimization of wire electrical discharge machining of γ titanium aluminide alloy through an artificial neural network model. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27(5–6):501–508
Ramakrishnan R, Karunamoorthy L (2006) Multi response optimization of wire EDM operations using robust design of experiments. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 29(1–2):105–112
Mahapatra SS, Patnaik A (2007) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(9–10):911–925
Gauri SK, Chakraborty S (2009) Optimisation of multiple responses for WEDM processes using weighted principal components. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 40(11–12):1102–1110
Kumar S, Singh R (2010) Investigating surface properties of OHNS die steel after electrical discharge machining with manganese powder mixed in the dielectric. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50(5–8):625–633
Kumar K, Agarwal S (2012) Multi-objective parametric optimization on machining with wire electric discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(5–8):617–633
Azhiri RB, Teimouri R, Baboly MG et al (2014) Application of Taguchi, ANFIS and grey relational analysis for studying, modeling and optimization of wire EDM process while using gaseous media. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(1–4):279–295
Rao TB, Krishna AG (2013) Simultaneous optimization of multiple performance characteristics in WEDM for machining ZC63/SiCp MMC. Adv Manuf 1(3):265–275
Kosaraju S, Anne VG (2013) Optimal machining conditions for turning Ti-6Al-4V using response surface methodology. Adv Manuf 1(4):329–339
Das AK, Saha P (2013) Machining of circular micro holes by electrochemical micro-machining process. Adv Manuf 1(4):314–319
Khan ZA, Siddiquee AN, Khan NZ et al (2014) Multi response optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters using Taguchi based grey relational analysis. Procedia Mater Sci 6:1683–1695
Prasad DVSSSV, Krishna AG (2015) Empirical modeling and optimization of kerf and wire wear ratio in wire electrical discharge machining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 77(1–4):427–441
Tripathy S, Tripathy DK (2016) Multi-attribute optimization of machining process parameters in powder mixed electro-discharge machining using TOPSIS and grey relational analysis. Int J Eng Sci Technol 19(1):62–70
Nain SS, Garg D, Kumar S (2017) Modeling and optimization of process variables of wire-cut electric discharge machining of super alloy Udimet-L605. Eng Sci Technol Int J 20:247–264
Liu H, Wang X, Tan D et al (2006) Study on traffic information fusion algorithm based on support vector machines. In: Proceeding of the sixth international conference on intelligent systems design and applications, IEEE, vol 6, pp 183–187
Pal M, Singh NK, Tiwari NK (2010) Support vector regression based modelling of pier scour using field data. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24(5):911–916
Lu WC, Ji XB, Li MJ et al (2013) Using support vector machine for materials design. Adv Manuf 1(2):151–159
Laha D, Ren Y, Suganthan PN (2015) Modeling of steel making process with effective machine learning techniques. Expert Syst Appl 42:4687–4696
Zhang L, Jia Z, Wang F et al (2010) A hybrid model using supporting vector machine and multi-objective genetic algorithm for processing parameters optimization in micro-EDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51:575–586
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Smola AJ (1996) Regression estimation with support vector learning machines. Dissertation, Technical University of Munich
Cortes C, Vapnik VN (1995) Support vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Luenberger DG (1984) Linear and nonlinear programming. Addison-Wesley, New Jersey
Witten IH, Frank E (2005) Data mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, p 2
Roy RK (1990) A primer on Taguchi method. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Ross PJ (1996) Taguchi techniques for quality engineering. McGraw Hill, New York
Deng J (1989) Introduction to grey system. J Grey Syst 1:1–24
Deng J (1982) Control problems of grey systems. Syst Control Lett 5:288–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nain, S.S., Garg, D. & Kumar, S. Evaluation and analysis of cutting speed, wire wear ratio, and dimensional deviation of wire electric discharge machining of super alloy Udimet-L605 using support vector machine and grey relational analysis. Adv. Manuf. 6, 225–246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-017-0192-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-017-0192-7