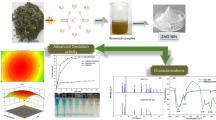
Abstract
Nanomaterials hold great potential to reduce pollution load from industrial wastewater. The silica nanoparticles (SNPs) were synthesized by sol–gel method and characterized by FTIR spectroscopy, XRD analysis and UV–visible spectroscopy. These SNPs were applied on industrial wastewater for reduction of pollution load, collected from Blund Dyestuff industry. To calculate treatment efficacy all parameters like color, total dissolve solids and conductivity were measured before and after treatment. Response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to design reaction layout for five groups of synthesized SNPs to evaluate the best among all. SNPs were also used in combination with natural coagulant; Potassium Aluminum Sulfate (alum) which boosted the activity of synthesized SNPs. It was observed that silica nanoparticles (SN-3) calcinated at 700 °C showed better results among the five types of SNPs. It reduced color up to 75%, conductivity 25% and TDS up to 35% at dose 0.16 g/100 ml of wastewater, 4 h contact time and 8 pH of original solution along with 8 mL of 10% alum solution. Other groups of SNPs showed reductions as well but lesser, as compared to SN-3.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
15 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04064-4
References
Ahmad R, Ansari K (2021) Enhanced sequestration of methylene blue and crystal violet dye onto green synthesis of pectin modified hybrid (Pect/AILP-Kal) nanocomposite. Process Biochem 111:132–143
Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S (2016) A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: a green expertise. J Adv Res 7(1):17–28
Ali A, Zafar MZH, Haq I, Phull AR, Ali JS, Hussain A (2016) Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 9:49–49
Atta AM (2020) Novel magnetic silica-ionic liquid nanocomposites for wastewater treatment. Nanomaterials 10(1):71–71
Attinti R, Sarkar D, Barrett KR, Datta R (2015) Adsorption of arsenic (V) from aqueous solutions by goethite/silica nanocomposite. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12(12):3905–3914
Baetke SC, Lammers T, Kiessling F (2015) Applications of nanoparticles for diagnosis and therapy of cancer. Br J Radiol 88(1054):20150207
Baş D, Boyacı IH (2007) Modeling and optimization I: usability of response surface methodology. J Food Eng 78(3):836–845
Basu H, Singhal RK, Pimple MV, Reddy AVR (2015) Arsenic removal from groundwater by goethite impregnated calcium alginate beads. Water Air Soil Pollution 226(2):1–11
Bettermann P, Liebau F (1975) The transformation of amorphous silica to crystalline silica under hydrothermal conditions. Contrib Miner Petrol 53(1):25–36
Ealias AM, Saravanakumar M (2017) A review on the classification, charac- terisation, synthesis of nanoparticles and their application. Mater Sci Eng 263:32019–32019
Gita S, Hussan A, Choudhury TG (2017) Impact of textile dyes waste on aquatic environments and its treatment. Environ Ecol 35(3C):2349–2353
Heidi Lynn R, Priscilla BLG, Emmanuel I (2012) Metal nanoparticle modified polysulfone membranes for use in wastewater treatment: a critical review. Journal of surface engineered materials and advanced technology
Irfan M, Siddiqui M, Bashir F, Butt M, Abbas N (2020) Efficient removal of hydrogen sulfide from wastewater using waste-tire-derived rubber particles. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17(7):3515–3524
Kandpal D, Kalele S, Kulkarni S (2007) Synthesis and characterization of silica-gold core-shell (SiO 2@ Au) nanoparticles. Pramana 69(2):277–283
Khan NA, Khan SU, Ahmed S, Farooqi IH, Dhingra A, Hussain A, Changani F (2019) Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment: a review. Asian J Water Environ Pollut 16(4):81–86
Li X, Iocozzia J, Chen Y, Zhao S, Cui X, Wang W, Lin Z (2018) From precision synthesis of block copolymers to properties and applications of nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(8):2046–2070
Merci S (2020) Investigation of photocatalytic chlorpyrifos degradation by a new silica mesoporous material immobilized by WS2 and Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Application of response surface methodology. Appl Organomet Chem 34(3):e5343–e5343
Mittala J, Ahmadb R, Mittalc A (2021) Kahwa tea (Camellia sinensis) carbon—a novel and green low-cost adsorbent for the sequestration of Titan yellow dye from its aqueous solutions. Desalinat Water Treat 227:404–411
Mohammadi M, Khorrami MK, Ghasemzadeh H (2019) ATR-FTIR spec- troscopy and chemometric techniques for determination of polymer solution viscosity in the presence of SiO2 nanoparticle and salinity. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 220:117049–117049
Mohammed L, Gomaa HG, Ragab D, Zhu J (2017) Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: A review. Particuology 30:1–14
Morin-Crini N (2019) Synthesis of silica materials containing cyclodextrin and their applications in wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 17(2):683–696
Mourdikoudis S, Pallares RM, Thanh NT (2018) Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 10(27):12871–12934
Nandanwar R, Singh P, Haque FZ (2015) Synthesis and characterization of SiO2 nanoparticles by sol-gel process and its degradation of methylene blue. Am Chem Sci J 5(1):1–10
Naseem T, Durrani T (2021) The role of some important metal oxide nanoparticles for wastewater and antibacterial applications: a review. Environ Chem Ecotoxicol 3:59–75
Olawale O, Oyawale FA (2012) Characterization of rice husk via atomic absorption spectrophotometer for optimal silica production. Int J Sci Technol 2(4):210–213
Ong CB, Ng LY, Mohammad AW (2018) A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:536–551
Prasad T, Halder S, Dhar S (2020) Process parameter effects on particle size reduction of sol-gel synthesized silica nanoparticles. Materials Today: Proceed 22:1669–1675
Ramimoghadam D, Bagheri S, Hamid SB (2014) Biotemplated synthesis of anatase titanium dioxide nanoparticles via lignocellulosic waste material. BioMed Res Int 2014:1–7
Rovani S, Santos JJ, Corio P, Fungaro DA (2018) Highly pure silica nanoparti- cles with high adsorption capacity obtained from sugarcane waste ash. ACS Omega 3(3):2618–2627
Sharma P, Singh L, Dilbaghi N (2009) Response surface methodological approach for the decolorization of simulated dye effluent using Aspergillus fumigatus fresenius. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):1081–1086
Singh S (2019) Applications of nanoparticles in wastewater treatment. Nanobiotechnol Bioformulat, 395–418
Soni G, Yadav KS (2015) Applications of nanoparticles in treatment and diagnosis of leukemia. Mater Sci Eng, C 47:156–164
Stanley R, Nesaraj AS (2014) Effect of surfactants on the wet chemical synthesis of silica nanoparticles. Int J Appl Sci Eng 12(1):9–21
Stark WJ, Stoessel PR, Wohlleben W, Hafner A (2015) Industrial applications of nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 44(16):5793–5805
Wyckoff RW (1925) Crystal structure of high temperature cristobalite. Am J Sci 5(54):448–459
Xu HY, Qi SY, Li Y, Zhao Y, Li JW (2013) Heterogeneous Fenton-like discoloration of Rhodamine B using natural schorl as catalyst: optimization by response surface methodology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(8):5764–5772
Xue SH, Xie H, Ping H, Li QC, Su BL, Fu ZY (2015) Induced transformation of amorphous silica to cristobalite on bacterial surfaces. RSC Adv 5(88):71844–71848
Zazo H, Colino CI, Lanao JM (2016) Current applications of nanoparticles in infectious diseases. J Control Release 224:86–102
Zhang Y (2011) Synthesis of mesoporous carbon capsules encapsulated with magnetite nanoparticles and their application in wastewater treatment. J Mater Chem 21(11):3664–3671
Zhu Y, Liao L (2015) Applications of nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery: a review. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15(7):4753–4773
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Funding
Author has received no fund from any funding body.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M Shabani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaman, K.U., Abbas, N., Irshad, M. et al. Treatability study of synthesized silica nanoparticles to reduce pollution load of industrial wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 6183–6200 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03972-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03972-9