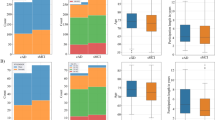
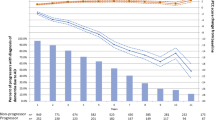
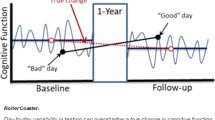
Abstract
The process of diagnosing dementia conditions, especially Alzheimer’s disease, and the cognitive tests that are involved in this process, are important areas of study. Everyday Cognition (ECog) is one test that can be used as part of Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis to measure cognitive decline in different areas. In this study, we investigate two versions of the ECog test: the study partner reported version (ECogSP), and the patient reported version (ECogPT). We compare these, using statistical analysis and machine learning techniques, to create classification models to demonstrate the progression in ECog scores over time by using the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative longitudinal data repository (ADNI); participants are classed with having normal cognition, mild cognitive impairment, or Alzheimer’s disease. We found that participants who are diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease at baseline, or during a subsequent visit, tend to self-report consistent ECogPT scores over time indicating no change in cognitive ability. However, study partners tend to report higher and increasing ECogSP scores on behalf of participants in the same diagnosis category; this would indicate a degradation in the participant’s cognitive ability over time, consistent with the progress of Alzheimer’s disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADNI. Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. 2017. https://adni.loni.usc.edu/about/#core-container. Accessed 22 Oct 2019.
Bakkour A, Morris JC, Wolk DA, Dickerson BC. The cortical signature of prodromal AD: regional thinning predicts mild AD dementia. Neurology. 2009;72:1048–55.
Balsis S, Benge JF, Lowe DA, Geraci L, Doody RS. How do scores on the ADAS-Cog, MMSE, and CDR-SOB correspond? Clin Neuropsychol. 2015;29(7):1002–9.
Bates DM, Pinheiro JC. Linear and nonlinear mixed-effects models. Appl Stat Agric. 1998. https://doi.org/10.4148/2475-7772.1273.
Bergeron D, Flynn K, Verret L, Poulin S, Bouchard RW, Bocti C, Fülöp T, Lacombe G, Gauthier S, Nasreddine Z, Laforce RJ. Multicenter validation of an MMSE-Mo CA conversion table. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2017;65(5):1067–72.
Breiman L. Random forests. Machine Learning. 2001;45(1):5–32.
Carr DB, Gray S, Baty J, Morris JC. The value of study partner versus individual’s complaints of memory impairment in early dementia. Neurology. 2000;55(11):1724–7.
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res. 2002;16:321–57.
Cohen W. Fast effective rule induction. In: Prieditis A, Russell S, editors. Proceedings of the 12th international conference on machine learning, ICML. Tahoe City: Morgan Kaufmann; 1995. p. 115–23.
Davatzikos C, Bhatt P, Shaw LM, Batmanghelich KN, Trojanowski JQ. Prediction of MCI to AD conversion, via MRI, CSF biomarkers, and pattern classification. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32(12):2322–e19.
Davatzikos C, Xu F, An Y, Fan Y, Resnick SM. Longitudinal progression of Alzheimer’s-like patterns of atrophy in normal older adults: The SPARE-AD index. Brain. 2009;132(8):2026–35.
Desikan RS, Cabral HJ, Settecase F, Hess CP, Dillon WP, Glastonbury CM, Weiner MW, Schmansky NJ, Salat DH, Fischl B, The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Automated MRI measures predict progression to Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31(8):1364–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.04.023.
Evans MC, Barnes J, Nielsen C, Kim LG, Clegg SL, Blair M, Leung KK, Douiri A, Boyes RG, Ourselin S, Fox NC. Volume changes in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: cognitive associations. Eur Radiol. 2010;20(3):674–82.
Farias ST, Mungas D, Reed BR, Cahn-Weiner D, Jagust W, Baynes K, DeCarli C. The measurement of everyday cognition (ECog): scale development and psychometric properties. Neuropsychology. 2008;22(4):531.
Folstein M, Folstein SE, McHugh P. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12(3):189–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6.
Frank E, Witten I. Generating accurate rule sets without global optimisation. In: Proceedings of the fifteenth international conference on machine learning, Madison, WI; 1998. p. 144–51.
Geuze E, Vermetten E, Bremner JD. MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 2. Findings in neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10(2):160–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001579.
Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten IH. The WEKA data mining software: An update. ACM SIGKDD Explor Newsl. 2009;11(1):10–8.
Ito K, Hutmacher MM, Corrigan BW. Modeling of functional assessment questionnaire (FAQ) as continuous bounded data from the ADNI database. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2012;39(6):601–18.
Jack CR Jr, Knopman DS, Jagust WJ, Shaw LM, Aisen PS, Weiner MW, Petersen RC, Trojanowski JQ. Hypothetical model of dynamic biomarkers of the Alzheimer's pathological cascade. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9(1):119–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70299-6.
Jack CR, Lowe VJ, Weigand SD, Wiste HJ, Senjem ML, Knopman DS, Shiung MM, Gunter JL, Boeve BF, Kemp BJ, Weiner M, Petersen RC, The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Serial PIB and MRI in normal, mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: implications for sequence of pathological events in Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 2009;132(5):1355–65. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp062.
Killiany RJ, Hyman BT, Gomez-Isla T, Moss MB, Kikinis R, Jolesz F, Tanzi R, Jones K, Albert MS. MRI measures of entorhinal cortex vs hippocampus in preclinical AD. Neurology. 2002;58(8):1188–96. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.58.8.1188.
Ministry of Health NZ. Dementia, treatment. 2018. Retrieved from https://www.health.govt.nz/your-health/conditions-and-treatments/diseases-and-illnesses/dementia. Accessed 4 Jan 2020.
Moradi E, Hallikainen I, Hänninen T, Tohka J, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Rey's auditory verbal learning test scores can be predicted from whole brain MRI in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage Clinical. 2017;13:415–27.
Mueller SG, Weiner MW, Thal LJ, Petersen RC, Jack C, Jagust W, Trojanowski JQ, Toga AW, Beckett L. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2005;15(4):869–xii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2005.09.008.
Pfeffer RI, Kurosaki TT, Harrah HC, Chance JM, Filos S. Measurement of functional activities in older adults in the community. J Gerontol. 1982;37(3):323–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronj/37.3.323.
Picard RR, Cook RD. Cross-validation of regression models. J Am Stat Assoc. 1984;79(387):575–83.
Quinlan JR. C4. 5: programs for machine learning. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2014.
Rabin LA, Wang C, Katz MJ, Derby CA, Buschke H, Lipton RB. Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease: Neuropsychological tests, self-reports, and study partner reports of cognitive difficulties. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(6):1128–34.
Rey A. L’examen psychologique dans les cas d’encéphalopathie traumatique. Arch Psychol. 1941;28:286–340.
Rosen W, Mohs R, Davis K. A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry. 1984;141(11):1356–64. https://doi.org/10.1176/ajp.141.11.1356.
Schmidt M. Rey Auditory verbal learning test: a handbook. Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services; 1996.
Schuff N, Woerner N, Boreta L, Kornfield T, Shaw LM, Trojanowski JQ, Thompson PM, Jack CR Jr, The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. MRI of hippocampal volume loss in early Alzheimer’s disease in relation to ApoE genotype and biomarkers. Brain. 2009;132(4):1067–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp007.
The Alzheimer’s Disease Prediction of Longitudinal Evolution (TADPOLE). TADPOLE-Home. 2019. https://tadpole.grand-challenge.org/. Accessed 5 Dec 2019.
Varon D, Barker W, Loewenstein D, Greig M, Bohorquez A, Santos I, Shen Q, Harper M, Vallejo-Luces D, R. Visual rating and volumetric measurement of medial temporal atrophy in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) cohort: baseline diagnosis and the prediction of MCI outcome. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2015;30(2):192–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.4126.
Vemuri P, Wiste H, Weigand S, Knopman D, Trojanowski J, Shaw L, Bernstein MA, Aisen PS, Weiner M, Petersen RC, Jack CR Jr, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Serial MRI and CSF biomarkers in normal aging, MCI, and AD. Neurology. 2010;75(2):143–51. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e7ca82.
Weiner MW, Veitch DP, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Cairns NJ, Green RC, Harvey D, Jack CR, Jagust W, Liu E, Morris JC, Petersen RC, Saykin AJ, Schmidt ME, Shaw L, Siuciak JA, Soares H, Toga AW, Trojanowski JQ, Si JA. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: a review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012;8(10):S1–S68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nic.2005.09.008.
World Health Organization. (2019). Dementia. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia. Accessed 11 Oct 2019.
Zou H, Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol). 2005;67(2):301–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thabtah, F., Spencer, R. & Ye, Y. The correlation of everyday cognition test scores and the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: a data analytics study. Health Inf Sci Syst 8, 24 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-020-00114-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-020-00114-8