Abstract
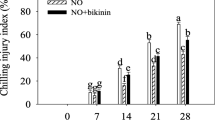
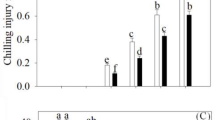
The effects of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) on promotion of chilling tolerance and the methionine sulfoxide reductase (MSR)-thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) system in peach (Prunus persica) fruit were investigated. The peaches were immersed in distilled water (as a control) and GABA solution followed by chilling treatment for 35 days. GABA treatment suppressed the augmentation of chilling injury (CI) index and weight loss rate, and the decline of firmness and total soluble solids content in peaches caused by chilling. The superoxide anion (O2·−) production rate, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content and reactive oxygen species accumulation were also retarded following GABA application. GABA treatment elevated the activity and gene expression of methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MSRA) and MSRB. Moreover, the activity and gene expression of TrxR were enhanced by GABA application. Additionally, GABA treatment increased the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) content and decreased the oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) content, consequently boosting the NADPH/NADP ratio. Also, the activity and gene expression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6GPDH) were promoted following GABA application. Thus, GABA treatment induced the MSR-TrxR system, consequently reducing CI in peaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data in this paper are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
Chumyama A, Faiyueb B, Saengnil K (2019) Reduction of enzymatic browning of fresh-cut guava fruit by exogenous hydrogen peroxide-activated peroxiredoxin/thioredoxin system. Sci Hortic 255:260–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.05.042
Diaz M, Nikkanen L, Himanen K, Toivola J, Rintamki E (2020) Two chloroplast thioredoxin systems differentially modulate photosynthesis in Arabidopsis depending on light intensity and leaf age. Plant J 104:718–734. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14959
Ding P, Fang L, Wang G, Li X, Huang S, Gao Y, Zhu J, Xiao L, Tong J, Chen F, Xia G (2019) Wheat methionine sulfoxide reductase A4.1 interacts with heme oxygenase 1 to enhance seedling tolerance to salinity or drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 101:200–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-019-00901-2
Habibi F, Ramezanian A, Guillén F, Serrano M, Valero D (2020) Effect of various postharvest treatment on aroma volatile compounds of blood orange fruit exposed to chilling temperature after long-term storage. Food Bioprocess Technol 13:2054–2064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-020-02547-1
Huang D, Tian W, Feng J, Zhu H (2020) Interaction between nitric oxide and storage temperature on sphingolipid metabolism of postharvest peach fruit. Plant Physiol Biochem 151:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.03.012
Jannatizadeh A, Aghdam M, Luo Z, Razavi F (2019) Impact of exogenous melatonin application on chilling injury in tomato fruits during cold storage. Food Bioprocess Technol 12:741–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-2247-1
Jiao C, Duan Y (2019) The role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in gibberellic acid-induced chilling tolerance and defense response in postharvest fruit. Food Bioprocess Technol 12:1733–1740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-019-02338-3
Jiao C, Chai Y, Duan Y (2019) Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mediates nitric-oxide-induced chilling tolerance and defense response in postharvest peach fruit. J Agric Food Chem 67:4764–4773. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00153
Jing G, Zhou J, Zhu S (2016) Effects of nitric oxide on mitochondrial oxidative defence in postharvest peach fruits. J Sci Food Agric 96:1997–2003. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7310
Kim H, Kim J (2008) Thioredoxin as a reducing agent for mammalian methionine sulfoxide reductases b lacking resolving cysteine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 371:490–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.101
Kinnersley A, Turano F (2000) Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and plant responses to stress. Crit Rev Plant Sci 19:479–509. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680091139277
Lepistö A, Pakula E, Toivola J, Krieger-Liszkay A, Vignols F, Rintamäki E (2013) Deletion of chloroplast NADPH-dependent thioredoxin reductase results in inability to regulate starch synthesis and causes stunted growth under short-day photoperiods. J Exp Bot 64:3843–3854. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert216
Li W, Lee S, Chieh P, Lin C, Wang Y, Chan M (2012) Arabidopsis root-abundant cytosolic methionine sulfoxide reductase B genes MsrB7 and MsrB8 are involved in tolerance to oxidative stress. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1707–1719. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcs114
Ma Y, Wang P, Gu Z, Tao Y, Shen C, Zhou Y, Han Y, Yang R (2019) Ca2+ involved in GABA signal transduction for phenolics accumulation in germinated hulless barley under NaCl stress. Food Chem X 2:10023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2019.100023
Mihara S, Yoshida K, Higo A, Hisabori T (2016) Functional significance of NADPH-thioredoxin reductase C in the antioxidant defense system of Cyanobacterium anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Plant Cell Physiol 58:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcw182
Romero M (2004) Investigations into the role of the plastidial peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase in response to oxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136:3784–3794. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.046656
Roy S, Nandi A (2017) Arabidopsis thaliana methionine sulfoxide reductase B8 influences stress-induced cell death and effector-triggered immunity. Plant Mol Biol 93:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0550-z
Sadanandom A, Poghosyan Z, Fairbairn D, Murphy D (2019) Differential regulation of plastidial and cytosolic isoforms of peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 123:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.123.1.255
Sang T, Shan X, Li B, Shu S, Sun J, Guo S (2016) Comparative proteomic analysis reveals the positive effect of exogenous spermidine on photosynthesis and salinity tolerance in cucumber seedlings. Plant Cell Rep 35:1769–1782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1995-x
Shang H, Cao S, Yang Z, Cai Y, Zheng Y (2011) Effect of exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid treatment on proline accumulation and chilling injury in peach fruit after long-term cold storage. J Agric Food Chem 59:1264–1268. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf104424z
Sun X, Sun M, Jia B, Qin Z, Zhu Y (2016) A Glycine soja methionine sulfoxide reductase B5a interacts with the Ca2+/CAM-binding kinase GsCBRLK and activates ROS signaling under carbonate alkaline stress. Plant J 86:514–529. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13187
Tian Y, Peng K, Bao Y, Zhang D, Jing C (2021) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase genes of winter wheat enhance the cold tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 161:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.02.005
Wang Y, Luo Z, Huang X, Yang K, Du R (2014) Effect of exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) treatment on chilling injury and antioxidant capacity in banana peel. Sci Hortic 168:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.01.022
Wang Y, Yang Q, Jiang H, Wang B, Bi Y, Li Y, Prusky D (2020) Reactive oxygen species-mediated the accumulation of suberin polyphenolics and lignin at wound sites on muskmelons elicited by benzo (1, 2, 3)-thiadiazole-7-carbothioic acid S-methyl ester. Postharvest Biol Technol 170:111325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111325
Yang A, Cao S, Yang Z, Cai Y, Zheng Y (2011) γ-aminobutyric acid treatment reduces chilling injury and activates the defence response of peach fruit. Food Chem 129:1619–1622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.06.018
Yang Q, Wang F, Rao J (2016) Effect of putrescine treatment on chilling injury, fatty acid composition and antioxidant system in kiwifruit. PLoS ONE 11:e0162159. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162159
Yao W, Xu T, Farooq S, Jin P, Zheng Y (2019) Glycine betaine treatment alleviates chilling injury in zucchini fruit (Cucurbita pepo L.) by modulating antioxidant enzymes and membrane fatty acid metabolism. Postharvest Biol Technol 144:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.05.007
Yu G, Zou J, Feng J, Peng X, Wu J, Wu Y, Palanivelu R, Sun M (2014) Exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) affects pollen tube growth via modulating putative Ca2+-permeable membrane channels and is coupled to negative regulation on glutamate decarboxylase. J Exp Bot 65:3235–3248. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru171
Zhu Y, Wang K, Wu C, Zhao Y, Yin X, Zhang B, Grierson D, Cheng K, Xu C (2019) Effect of ethylene on cell wall and lipid metabolism during alleviation of postharvest chilling injury in peach. Cells 8:1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121612
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by research start-up funds for high-level talents of Anhui Agricultural University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CJ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Data curation, Writing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Heakeun Yun.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, C. γ-Aminobutyric acid boosts chilling tolerance by promoting the methionine sulfoxide reductase-thioredoxin reductase system in peach fruit. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 63, 353–361 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00408-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-021-00408-0