Abstract
Purpose
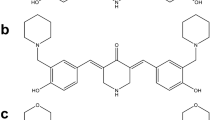
Previously, compounds containing a piperidone structure have been shown to be highly cytotoxic to cancer cells. Recently, we found that the piperidone compound P2 exhibits a potent anti-neoplastic activity against human breast cancer-derived cells. Here, we aimed to evaluate two piperidone compounds, P1 and P2, for their potential anti-neoplastic activity against human leukemia/lymphoma-derived cells.
Methods
Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction were evaluated using MTS, annexin V-FITC/PI and mitochondrial membrane potential polychromatic assays to confirm the mode of action of the piperidone compounds. The effects of compound P1 and P2 treatment on gene expression were assessed using AmpliSeq analysis and, subsequently, confirmed by RT-qPCR and Western blotting.
Results
We found that the two related piperidone compounds P1 and P2 selectively killed the leukemia/lymphoma cells tested at nanomolar concentrations through induction of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, as demonstrated by mitochondrial depolarization and caspase-3 activation. AmpliSeq-based transcriptome analyses of the effects of compounds P1 and P2 on HL-60 acute leukemia cells revealed a differential expression of hundreds of genes, 358 of which were found to be affected by both. Additional pathway analyses revealed that a significant number of the common genes were related to the unfolded protein response, implying a possible role of the two compounds in the induction of proteotoxic stress. Subsequent analyses of the transcriptome data revealed that P1 and P2 induced similar gene expression alterations as other well-known proteasome inhibitors. Finally, we found that Noxa, an important mediator of the activity of proteasome inhibitors, was significantly upregulated at both the mRNA and protein levels, indicating a possible role in the cytotoxic mechanism induced by P1 and P2.
Conclusions
Our data indicate that the cytotoxic activity of P1 and P2 on leukemia/lymphoma cells is mediated by proteasome inhibition, leading to activation of pro-apoptotic pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO | Cancer WHO Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/. (Accessed: 7th November 2017)
WHO Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014. WHO Available at: http://www.who.int/nmh/publications/ncd-status-report-2014/en/. (Accessed: 9th November 2017)
American Cancer Society Cancer Facts & Figures 2016. (American Cancer Society, 2016)
X. Ma, H. Yu, Global burden of Cancer. Yale J Biol Med 79, 85–94 (2006)
D. Hanahan, R.A. Weinberg, Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011)
G. M. Cooper, The development and causes of Cancer. in The Cell: A Molecular Approach (Sinauer Associates, 2000)
G. S. Markopoulos, E. Roupakia, M. Tokamani, E. Chavdoula, M. Hatziapostolou, C, Polytarchou, K. B. Marcu, A. G. Papavassiliou, R. Sandaltzopoulos, E. Kolettas, a step-by-step microRNA guide to cancer development and metastasis. Cell Oncol 40, 303–339 (2017)
G. M. Cooper, Applications of molecular biology to Cancer prevention and treatment. In The Cell: A Molecular Approach (Sinauer Associates, 2000)
K.L. Nastiuk, J.J. Krolewski, Opportunities and challenges in combination gene cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 98, 35–40 (2016)
S. Kummar, H.X. Chen, J. Wright, S. Holbeck, M.D. Millin, J. Tomaszewski, J. Zweibel, J. Collins, J.H. Doroshow, Utilizing targeted cancer therapeutic agents in combination: Novel approaches and urgent requirements. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9, 843–856 (2010)
C. Holohan, S.V. Schaeybroeck, D.B. Longley, P.G. Johnston, Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nature Rev Cancer 13, 714–726 (2013)
A. Chavez-Gonzalez, B. Bakhshinejad, K. Pakravan, M.L. Guzman, S. Babashah, Novel strategies for targeting leukemia stem cells: Sounding the death knell for blood cancer. Cell Oncol 40, 1–20 (2017)
Z. Mousavian, A. Nowzari-Dalini, R.W. Stam, Y. Rahmatallah, A. Masoudi-Nejad, Network-based expression analysis reveals key genes related to glucocorticoid resistance in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell Oncol 40, 33–45 (2017)
Z. Liu, B. Delavan, R. Roberts, W. Tong, Lessons learned from two decades of anticancer drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sciences 38, 852–872 (2017)
P. D’Arcy, S. Brnjic, M.H. Olofsson, M. Fryknäs, K. Lindsten, M. De Cesare, P. Perego, B. Sadeghi, M. Hassan, R. Larsson, S. Linder, Inhibition of proteasome deubiquitinating activity as a new cancer therapy. Nat Med 17, 1636–1640 (2011)
T. Mujtaba, Q.P. Dou, Advances in the understanding of mechanisms and therapeutic use of Bortezomib. Discov Med 12, 471–480 (2011)
P. Moreau, P.G. Richardson, M. Cavo, R.Z. Orlowski, J.F.S. Miguel, A. Palumbo, J.-L. Harousseau, Proteasome inhibitors in multiple myeloma: 10 years later. Blood 120, 947–959 (2012)
C. Dai, S. Dai, J. Cao, Proteotoxic stress of cancer: Implication of the heat-shock response in oncogenesis. J Cell Physiol 227, 2982–2987 (2012)
J. Adams, The proteasome: Structure, function, and role in the cell. Cancer Treatment Rev 29. Supplement 1, 3–9 (2003)
T. Hideshima, P.G. Richardson, K.C. Anderson, Mechanism of action of proteasome inhibitors and deacetylase inhibitors and the biological basis of synergy in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther 10, 2034–2042 (2011)
H.-W. Chiu, Y.-C. Tseng, Y.-H. Hsu, Y.-F. Lin, N.-P. Foo, H.-R. Guo, Y.-J. Wang, Arsenic trioxide induces programmed cell death through stimulation of ER stress and inhibition of the ubiquitin–proteasome system in human sarcoma cells. Cancer Lett 356, 762–772 (2015)
E.A. Obeng, L.M. Carlson, D.M. Gutman, W.J. Harrington, K.P. Lee, L.H. Boise, Proteasome inhibitors induce a terminal unfolded protein response in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 107, 4907–4916 (2006)
J.-Z. Qin, J. Ziffra, L. Stennett, B. Bodner, B.K. Bonish, V. Chaturvedi, F. Bennett, P.M. Pollock, J.M. Trent, M.J.C. Hendrix, P. Rizzo, L. Miele, B.J. Nickoloff, Proteasome inhibitors trigger NOXA-mediated apoptosis in melanoma and myeloma cells. Cancer Res 65, 6282–6293 (2005)
M. Baou, S.L. Kohlhaas, M. Butterworth, M. Vogler, D. Dinsdale, R. Walewska, A. Majid, E. Eldering, M.J.S. Dyer, G.M. Cohen, Role of NOXA and its ubiquitination in proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Haematologica 95, 1510–1518 (2010)
D.C.S. Huang, A. Strasser, BH3-only proteins -essential initiators of apoptotic cell death. Cell 103, 839–842 (2000)
J.E. Guikema, M. Amiot, E. Eldering, Exploiting the pro-apoptotic function of NOXA as a therapeutic modality in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 21, 767–779 (2017)
A.M. Fribley, B. Evenchik, Q. Zeng, B.K. Park, J.Y. Guan, H. Zhang, T.J. Hale, M.S. Soengas, R.J. Kaufman, C.-Y. Wang, Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 induces apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant squamous cell carcinoma cells by induction of Noxa. J Biol Chem 281, 31440–31447 (2006)
A. Craxton, M. Butterworth, N. Harper, L. Fairall, J. Schwabe, A. Ciechanover, G.M. Cohen, NOXA, a sensor of proteasome integrity, is degraded by 26S proteasomes by an ubiquitin-independent pathway that is blocked by MCL-1. Cell Death Differ 19, 1424–1434 (2012)
L.M. Nunes, M. Hossain, A. Varela-Ramirez, U. Das, Y.M. Ayala-Marin, J.R. Dimmock, R.J. Aguilera, A novel class of piperidones exhibit potent, selective and pro-apoptotic anti-leukemia properties. Oncol Lett 11, 3842–3848 (2016)
E. Robles-Escajeda, U. Das, N.M. Ortega, K. Parra, G. Francia, J.R. Dimmock, A. Varela-Ramirez, R.J. Aguilera, A novel curcumin-like dienone induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol 39, 265–277 (2016)
U. Das, J. Alcorn, A. Shrivastav, R.K. Sharma, E. De Clercq, J. Balzarini, J.R. Dimmock, Design, synthesis and cytotoxic properties of novel 1-[4-(2-alkylaminoethoxy)phenylcarbonyl]-3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidones and related compounds. Eur J Med Chem 42, 71–80 (2007)
E. Robles-Escajeda, D. Lerma, A.M. Nyakeriga, J.A. Ross, R.A. Kirken, R.J. Aguilera, A. Varela-Ramirez, Searching in mother nature for anti-cancer activity: Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effect elicited by green barley on leukemia/lymphoma cells. PLoS One 8, e73508 (2013)
Y. Quan, B. Li, Y.-M. Sun, H.-Y. Zhang, Elucidating pharmacological mechanisms of natural medicines by biclustering analysis of the gene expression profile: A case study on curcumin and si-wu-tang. Int J Mol Sci 16, 510–520 (2014)
K. Segawa, S. Nagata, An apoptotic ‘eat me’ signal: Phosphatidylserine exposure. Trends Cell Biol 25, 639–650 (2015)
S.W.G. Tait, D.R. Green, Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11, 621–632 (2010)
A.L. Davis, S. Qiao, J.L. Lesson, M. Rojo de la Vega, S.L. Park, C.M. Seanez, V. Gokhale, C.M. Cabello, G.T. Wondrak, The quinone methide Aurin is a heat shock response inducer that causes proteotoxic stress and Noxa-dependent apoptosis in malignant melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 290, 1623–1638 (2015)
X.H. Lowman, M.A. McDonnell, A. Kosloske, O.A. Odumade, C. Jenness, C.B. Karim, R. Jemmerson, A. Kelekar, The proapoptotic function of Noxa in human leukemia cells is regulated by the kinase Cdk5 and by glucose. Mol Cell 40, 823–833 (2010)
I.N. Mungrue, J. Pagnon, O. Kohannim, P.S. Gargalovic, A.J. Lusis, CHAC1/MGC4504 is a novel proapoptotic component of the unfolded protein response, downstream of the ATF4-ATF3-CHOP cascade. J Immunol 182, 466–476 (2009)
C.V. Dang, C-Myc target genes involved in cell growth, apoptosis. and metabolism Mol Cell Biol 19, 1–11 (1999)
J. Wang, L.Y. Xie, S. Allan, D. Beach, G.J. Hannon, Myc activates telomerase. Genes Dev 12, 1769–1774 (1998)
B.-J. Chen, Y.-L. Wu, Y. Tanaka, W. Zhang, Small molecules targeting c-Myc oncogene: Promising anti-cancer therapeutics. Int J Biol Sci 10, 1084–1096 (2014)
J. Lamb, E.D. Crawford, D. Peck, J.W. Modell, I.C. Blat, M.J. Wrobel, J. Lerner, J.-P. Brunet, A. Subramanian, K.N. Ross, M. Reich, H. Hieronymus, G. Wei, S.A. Armstrong, P.A. Clemons, R. Wei, S.A. Carr, E.S. Lander, T.R. Golub, The connectivity map: Using gene-expression signatures to connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science 313, 1929–1935 (2006)
G. de Bettignies, O. Coux, Proteasome inhibitors: Dozens of molecules and still counting. Biochimie 92, 1530–1545 (2010)
H. Mi, X. Huang, A. Muruganujan, H. Tang, C. Mills, D. Kang, P.D. Thomas, PANTHER version 11: Expanded annotation data from gene ontology and Reactome pathways, and data analysis tool enhancements. Nucleic Acids Res 45, D183–D189 (2017)
C. Ploner, R. Kofler, A. Villunger, Noxa: At the tip of the balance between life and death. Oncogene 27, S84–S92 (2009)
N. Guo, Z. Peng, MG132, a proteasome inhibitor, induces apoptosis in tumor cells. Asia-Pacific J Clin Oncol 9, 6–11 (2013)
L. Galluzzi, M.C. Maiuri, I. Vitale, H. Zischka, M. Castedo, L. Zitvogel, G. Kroemer, Cell death modalities: Classification and pathophysiological implications. Cell Death Differ 14, 1237–1243 (2007)
N. Mohana-Kumaran, D.S. Hill, J.D. Allen, N.K. Haass, Targeting the intrinsic apoptosis pathway as a strategy for melanoma therapy. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 27, 525–539 (2014)
S. Elmore, Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35, 495–516 (2007)
W. Li, A. Turner, P. Aggarwal, A. Matter, E. Storvick, D.K. Arnett, U. Broeckel, Comprehensive evaluation of AmpliSeq transcriptome, a novel targeted whole transcriptome RNA sequencing methodology for global gene expression analysis. BMC Genomics 16, 1069 (2015)
S.L. Downey, B.I. Florea, H.S. Overkleeft, A.F. Kisselev, Use of proteasome inhibitors. Curr Protoc Immunol 109, 9.10.1–9.10.8 (2015)
M.A. Nikiforov, M. Riblett, W.-H. Tang, V. Gratchouck, D. Zhuang, Y. Fernandez, M. Verhaegen, S. Varambally, A.M. Chinnaiyan, A.J. Jakubowiak, M.S. Soengas, Tumor cell-selective regulation of NOXA by c-MYC in response to proteasome inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104, 19488–19493 (2007)
C. Hetz, E. Chevet, H.P. Harding, Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12, 703–719 (2013)
M. Edagawa, J. Kawauchi, M. Hirata, H. Goshima, M. Inoue, T. Okamoto, A. Murakami, Y. Maehara, S. Kitajima, Role of activating transcription factor 3 (atf3) in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced sensitization of p53-deficient human colon cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis through up-regulation of death receptor 5 (DR5) by zerumbone and celecoxib. J Biol Chem 289, 21544–21561 (2014)
I.B. Roninson, Oncogenic functions of tumour suppressor p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1: Association with cell senescence and tumour-promoting activities of stromal fibroblasts. Cancer Lett 179, 1–14 (2002)
X.E. Guo, B. Ngo, A.S. Modrek, W.-H. Lee, Targeting tumor suppressor networks for Cancer therapeutics. Curr Drug Targets 15, 2–16 (2014)
X. Wang, M. Mazurkiewicz, E.-K. Hillert, M.H. Olofsson, S. Pierrou, P. Hillertz, J. Gullbo, K. Selvaraju, A. Paulus, S. Akhtar, F. Bossler, A.C. Khan, S. Linder, P.D. Arcy, The proteasome deubiquitinase inhibitor VLX1570 shows selectivity for ubiquitin-specific protease-14 and induces apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells. Sci Rep 6, srep26979 (2016)
P. D’Arcy, X. Wang, S. Linder, Deubiquitinase inhibition as a cancer therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol Ther 147, 32–54 (2015)
A. Varela-Ramirez, Female versus male cells in anti-Cancer drug discovery: The winner is …. AAPS Blog (2014) Available at: https://aapsblog.aaps.org/2014/06/18/female-versus-male-cells-in-anti-cancer-drug-discovery-the-winner-is/
L.M. Nunes, E. Robles-Escajeda, Y. Santiago-Vazquez, N.M. Ortega, C. Lema, A. Muro, G. Almodovar, U. Das, S. Das, J.R. Dimmock, R.J. Aguilera, A. Varela-Ramirez, The gender of cell lines matters when screening for novel anti-cancer drugs. AAPS J 16, 872–874 (2014)
Y. Santiago-Vázquez, U. Das, A. Varela-Ramirez, S.T. Baca, Y. Ayala-Marin, C. Lema, S. Das, A. Baryyan, J.R. Dimmock, R.J. Aguilera, Tumor-selective cytotoxicity of a novel pentadiene analogue on human leukemia/ lymphoma cells. Clin Cancer Drugs 3, 138–146 (2016)
J.A. Clayton, F.S. Collins, NIH to balance sex in cell and animal studies. Nature 509, 282–283 (2014)
E. Pollitzer, Cell sex matters. Nature 500, 23–24 (2013)
Acknowledgments
Funding for this work was provided by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences-Support of Competitive Research (SCORE) grant 1SC3GM103713 to RJA, as well as a Canadian Institutes of Health Research-Regional Partnerships Program Saskatchewan grant to JRD. We thank Madan Balal for the compound docking experiments presented in the supplementary material. The synthesis and docking work performed by the Dr. Rachid Skouta research laboratory was partially supported by Lung Cancer Research Foundation and Green Fund grants. The authors also thank the Genomic Analysis and Cytometry, Screening and Imaging Core Facilities at the University of Texas at El Paso (UTEP), which were supported by a Research Centers in Minority Institutions (RCMI) program grant 5G12MD007592 to the Border Biomedical Research Center (BBRC) in UTEP from the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, a component of the National Institutes of Health. The authors thank Gladys Almodovar (with UTEP) for cell culture expertise. LC was supported by NIGMS RISE training grant R25 GM069621-15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 6709 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contreras, L., Calderon, R.I., Varela-Ramirez, A. et al. Induction of apoptosis via proteasome inhibition in leukemia/lymphoma cells by two potent piperidones. Cell Oncol. 41, 623–636 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0397-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-018-0397-1