Abstract
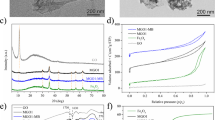
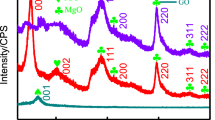
In this study, reduced graphene oxide (RGO) with good water dispersibility and excellent adsorption performance was successfully prepared using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as reductant, and their characterization and adsorption performance for Basic Red13 (BR13) and Cu2+ were analyzed. The results showed that RGO had an obvious graphene-like structure with the C/O ratio of 3.19, while the C/O ratio of graphene oxide (GO) was only 1.81. The reason for the good water dispersibility of RGO was the retention of partial oxygen-containing groups, especially carboxyl groups. The adsorption of RGO for BR13 and Cu2+ was typical monolayer physisorption, which could be well-described by pseudo-first-order and Langmuir isotherm models. The maximum adsorption capacities of RGO were 1674.01 mg/g for BR13 at pH = 13 and 164.72 mg/g for Cu2+ at pH = 6, which much higher than the corresponding values of 1258.65 mg/g and 123.14 mg/g for GO. In particular, the adsorption capacity of RGO for BR13 was the highest value reported so far. Moreover, no significant loss of adsorption performance was observed even after five cycles. This work suggested that reduced graphene oxide was an efficient adsorbent for the removal of organic dyes and heavy metal ions from water, which had great potential in pollution control applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siyal, A.A.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Khan, M.I.; Rabat, N.E.; Zulfiqar, M.; Man, Z.; Siame, J.; Azizli, K.A.: A review on geopolymers as emerging materials for the adsorption of heavy metals and dyes. J. Environ. Manage. 224, 327–339 (2018)
Ye, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Lin, J.; Lin, X.; Bruggen, B.V.; Zhao, S.: Loose nanofiltration-based electrodialysis for highly efficient textile wastewater treatment. J. Membrane Sci. 608, 118182 (2020)
Mbamba, C.K.; Lindblom, E.; Flores-Alsina, X.; Tait, S.; Anderson, S.; Saagi, R.; Batstone, D.J.; Gernaey, K.V.; Jeppsson, U.: Plant-wide model-based analysis of iron dosage strategies for chemical phosphorus removal in wastewater treatment systems. Water Res. 155, 12–25 (2019)
Liang, J.; Mai, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Su, M.; Du, J.; Wu, Y.; Dai, J.; Tang, Q.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Wei, Y.: Performance and microbial communities of a novel integrated industrial-scale pulp and paper wastewater treatment plant. J. Clean. Prod. 278, 123896 (2020)
Dotto, G.L.; McKay, G.: Current scenario and challenges in adsorption for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8, 103988 (2020)
Da’na, E.: Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: a review. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 247, 145–157 (2017)
Cheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Ma, A.; Xia, H.; Peng, J.; Li, C.; Shu, J.: Comparison of activated carbon and iron/cerium modified activated carbon to remove methylene blue from wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 65, 92–102 (2018)
Lan, J.; Dong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fen, L.; Zhou, M.; Hou, H.; Du, D.: A novel method for solidification/stabilization of Cd(II), Hg(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) by activated electrolytic manganese slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 409, 124933 (2021)
Chen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.: Comparison of heavy metal removals from aqueous solutions by chemical precipitation and characteristics of precipitates. J. Water Process Eng. 26, 289–300 (2018)
Ramezanalizadeh, H.; Manteghi, F.: Synthesis of a novel MOF/CuWO4 heterostructure for efficient photocatalytic degradation and removal of water pollutants. J. Clean. Prod. 172, 2655–2666 (2018)
Chauhan, M.; Saini, V.K.; Suthar, S.: Enhancement in selective adsorption and removal efficiency of natural clay by intercalation of Zr-pillars into its layered nanostructure. J. Clean. Prod. 258, 120686 (2020)
Ma, Y.; Zheng, D.; Mo, Z.; Dong, R.; Qiu, X.: Magnetic lignin-based carbon nanoparticles and the adsorption for removal of methyl orange. Colloid. Surface. A. 559, 226–234 (2018)
Satayeva, A.R.; Howell, C.A.; Korobeinyk, A.V.; Jandosov, J.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Mansurov, Z.A.; Mikhalovsky, S.V.: Investigation of rice husk derived activated carbon for removal of nitrate contamination from water. Sci. Total Environ. 630, 1237–1245 (2018)
Ren, Y.; Han, Y.; Lei, X.; Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q.: A magnetic ion exchange resin with high efficiency of removing Cr (VI). Colloid. Surface. A. 604, 125279 (2020)
Li, H.; Zheng, F.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, L.; Hu, P.; Gao, G.; Zhen, Q.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J.L.: Facile preparation of zeolite-activated carbon composite from coal gangue with enhanced adsorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 390, 124513 (2020)
Peng, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, S.: A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J. Mol. Liq. 230, 496–504 (2017)
Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Xing, B.: Adsorption of phenanthrene on multilayer graphene as affected by surfactant and exfoliation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 331–339 (2014)
Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.; Joanni, E.; Singh, R.K.; Maegawa, K.; Tan, W.K.; Kawamura, G.; Kar, K.K.; Matsuda, A.: Heteroatom doped graphene engineering for energy storage and conversion. Mater Today 39, 47–65 (2020)
Song, D.; Mahajan, A.; Secor, E.B.; Hersam, M.C.; Francis, L.F.; Frisbie, C.D.: High-resolution transfer printing of graphene lines for fully printed, flexible electronics. ACS Nano 11, 7431–7439 (2017)
Reina, G.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Criado, A.; Vázquez, E.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M.: Promises, facts and challenges for graphene in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 46, 4400–4416 (2017)
Wu, W.; Shi, Y.; Liu, G.; Fan, X.; Yu, Y.: Recent development of graphene oxide based forward osmosis membrane for water treatment: a critical review. Desalination 491, 114452 (2020)
Thakur, K.; Kandasubramanian, B.: Graphene and graphene oxide-based composites for removal of organic pollutants: a review. J. Chem. Eng. Data 64, 833–867 (2019)
Wei, M.; Chai, H.; Cao, Y.; Jia, D.: Sulfonated graphene oxide as an adsorbent for removal of Pb2+ and methylene blue. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 524, 297–305 (2018)
Wang, X.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Ding, F.: The transition metal surface dependent methane decomposition in graphene chemical vapor deposition growth. Nanoscale 9, 11584–11589 (2018)
Martinez, A.; Fuse, K.; Yamashita, S.: Mechanical exfoliation of graphene for the passive mode-locking of fiber lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 121107 (2011)
De Silva, K.K.H.; Huang, H.; Joshi, R.K.; Yoshimura, M.: Chemical reduction of graphene oxide using green reductants. Carbon 119, 190–199 (2017)
De Silva, K.K.H.; Huang, H.; Yoshimura, M.: Progress of reduction of graphene oxide by ascorbic acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 447, 338–346 (2018)
Yousefi, N.; Wong, K.K.W.; Hosseinidoust, Z.; Sørensen, H.O.; Bruns, S.; Zheng, Y.; Tufenkji, N.: Hierarchically porous, ultra-strong reduced graphene oxide-cellulose nanocrystal sponges for exceptional adsorption of water contaminants. Nanoscale 10, 7171–7184 (2018)
Erickson, K.; Erni, R.; Lee, Z.; Alem, N.; Gannett, W.; Zettl, A.: Determination of the local chemical structure of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 22, 4467–4472 (2010)
Gupta, K.; Khatri, O.P.: Reduced graphene oxide as an effective adsorbent for removal of malachite green dye: plausible adsorption pathways. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 501, 11–21 (2017)
Chang, C.F.; Truong, Q.D.; Chen, J.R.: Graphene sheets synthesized by ionic-liquid-assisted electrolysis for application in water purification. Appl. Surf. Sci. 264, 329–334 (2013)
Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M.; Sinitskii, A.; Sun, Z.; Slesarev, A.; Alemany, L.B.; Lu, W.; Tour, J.M.: Tour, Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4, 4806–4814 (2010)
Tang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Cui, F.; Xing, B.: Wrinkle-and edge-adsorption of aromatic compounds on graphene oxide as revealed by atomic force microscopy, molecular dynamics simulation, and density functional theory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 7689–7697 (2018)
Talyzin, A.V.; Hausmaninger, T.; You, S.; Szabo, T.: The structure of graphene oxide membranes in liquid water, ethanol and water-ethanol mixtures. Nanoscale 6, 272–281 (2014)
Saleem, H.; Haneef, M.; Abbasi, H.Y.: Synthesis route of reduced graphene oxide via thermal reduction of chemically exfoliated graphene oxide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 204, 1–7 (2018)
Jeong, H.K.; Lee, Y.P.; Lahaye, R.J.W.E.; Park, M.H.; An, K.H.; Kim, I.J.; Yang, C.; Park, C.Y.; Ruoff, R.S.; Lee, Y.H.: Evidence of graphitic AB stacking order of graphite oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 30, 1362–1366 (2008)
Sun, L.; Yu, H.; Fugetsu, B.: Graphene oxide adsorption enhanced by in situ reduction with sodium hydrosulfite to remove acridine orange from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 203–204, 101–110 (2012)
Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, B.: Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 4817–4825 (2014)
Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Q.; Yin, R.; Liu, F.; Chen, H.: Characterization of graphite oxide after heat treatment. New J. Chem. 36, 1373 (2012)
Shen, Y.; Boffa, V.; Corazzari, I.; Qiao, A.; Tao, H.; Yue, Y.: Revealing hidden endotherm of Hummers’ graphene oxide during low-temperature thermal reduction. Carbon 138, 337–347 (2018)
Chaabane, L.; Beyou, E.; El Ghali, A.; Baouab, M.H.V.: Comparative studies on the adsorption of metal ions from aqueous solutions using various functionalized graphene oxide sheets as supported adsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 389, 121839 (2019)
Li, D.; Müller, M.B.; Gilje, S.; Kaner, R.B.; Wallace, G.G.: Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 101–105 (2008)
Gao, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Ma, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.: Environment-friendly method to produce graphene that employs vitamin c and amino acid. Chem. Mater. 22, 2213–2218 (2010)
Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S.: Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 45, 1558–1565 (2007)
Konios, D.; Stylianakis, M.M.; Stratakis, E.; Kymakis, E.: Dispersion behaviour of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 430, 108–112 (2014)
Hu, J.; Kong, G.; Zhu, Y.; Che, C.: Ultrafast room-temperature reduction of graphene oxide by sodium borohydride, sodium molybdate and hydrochloric acid. Chin. Chem. Lett. 32, 543–547 (2021)
Luo, S.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.: Amino siloxane oligomer-linked graphene oxide as an efficient adsorbent for removal of Pb (II) from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 274, 145–155 (2014)
Mishra, S.; Yadav, A.; Verma, N.: Carbon gel-supported Fe-graphene disks: synthesis, adsorption of aqueous Cr(VI) and Pb(II) and the removal mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 326, 987–999 (2017)
Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.: Few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45, 10454–10462 (2011)
He, K.; Chen, G.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; Huang, Z.; Shi, J.; Peng, M.; Huang, T.; Hu, L.: Enhanced removal performance for methylene blue by kaolin with grapheme oxide modification. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 89, 77–85 (2018)
Zhao, G.; Zhu, H.: Cation-π interactions in graphene-containing systems for water treatment and beyond. Adv. Mater. 32, 1905756 (2020)
Liu, Y.; Men, B.; Hu, A.; You, Q.; Liao, G.; Wang, D.: Facile synthesis of graphene-based hyper-cross-linked porous carbon composite with superior adsorption capability for chlorophenols. J. Environ. Sci. 90, 395–407 (2020)
Xiao, J.; Lv, W.; Xie, Z.; Tan, Y.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q.: Environmentally friendly reduced graphene oxide as a broad-spectrum adsorbent for anionic and cationic dyes via π-π interactions. J. Mater. Chem. A. 4, 12126–12135 (2016)
Lagergren, S.: About the theory of so-called sorption of soluble substances. Kung. Sven. Veten. Hand. 24, 1–39 (1898)
Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G.: Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Van, T.T.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Le, H.T.N.; Vo, D.N.; Nanda, S.; Nguyen, T.D.: Optimization, equilibrium, adsorption behavior and role of surface functional groups on graphene oxide-based nanocomposite towards diclofenac drug. J. Environ. Sci. 93, 137–150 (2020)
Yan, H.; Wu, H.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Tao, X.; Yang, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R.: Influence of the surface structure of graphene oxide on the adsorption of aromatic organic compounds from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 7, 6690–6697 (2015)
Wang, J.; Chen, B.: Adsorption and coadsorption of organic pollutants and a heavy metal by graphene oxide and reduced graphene materials. Chem. Eng. J. 281, 379–388 (2015)
Cheung, W.H.; Szeto, Y.S.; McKay, G.: Intraparticle diffusion processes during acid dye adsorption onto chitosan. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 2897–2904 (2007)
Zhang, C.; Luan, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, W.: Characterization and adsorption performance of graphene oxide-montmorillonite nanocomposite for the simultaneous removal of Pb2+ and p-nitrophenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 378, 120739 (2019)
Robati, D.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Najafi, F.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K.: Kinetics and thermodynamics of malachite green dye adsorption from aqueous solutions on graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. J. Mol. Liq. 214, 259–263 (2016)
Bulut, Y.; Aydın, H.: A kinetics and thermodynamics study of methylene blue adsorption on wheat shells. Desalination 194, 259–267 (2006)
Payne, K.; Abdel-Fattah, T.: Adsorption of arsenate and arsenite by iron-treated activated carbon and zeolites: effects of pH, temperature, and ionic strength. J. Environ. Sci. Heal. A 40, 723–749 (2005)
Yao, Q.F.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, C.; Sun, Q.F.: MnO2 nanoflakes/cellulose nanofibre aerogel fabricated via ultrasonication for high-performance water desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 9580–9590 (2017)
Rauf, M.; Bukallah, S.; Hamour, F.; Nasir, A.: Adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions onto sand and their kinetic behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 137, 238–243 (2008)
Vijayaraghavan, K.; Padmesh, T.V.N.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M.: Biosorption of nickel (II) ions onto Sargassum wightii: application of two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models. J. Hazard. Mater. 133, 304–308 (2006)
Yang, S.T.; Chang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, A.: Folding/aggregation of graphene oxide and its application in Cu2+ removal. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 351, 22–127 (2010)
Chen, X.; Chen, B.: Macroscopic and spectroscopic investigations of the adsorption of nitroaromatic compounds on graphene oxide, reduced graphene oxide, and graphene nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 6181–6189 (2015)
Cui, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Hu, L.; Yan, L.; Wei, Q.; Du, B.: EDTA functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for removal of Pb(II), Hg(II) and Cu(II) in water treatment: adsorption mechanism and separation property. Chem. Eng. J. 281, 1–10 (2015)
Kumar, S.; Nair, R.R.; Pillai, P.B.; Gupta, S.N.; Iyengar, M.A.; Sood, A.K.: Graphene oxide-MnFe2O4 magnetic nanohybrids for efficient removal of lead and arsenic from water. ACS appl. Mater. Interf. 6, 17426–17436 (2014)
Zhao, G.; Li, J.; Wang, X.: Kinetic and thermodynamic study of 1-naphthol adsorption from aqueous solution to sulfonated graphene nanosheets. Chem. Eng. J. 173, 185–190 (2011)
Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.: Fabrication of a graphene–cuprous oxide composite. J. Solid State Chem. 182, 2486–2490 (2009)
Boudechiche, N.; Fares, M.; Ouyahia, S.; Yazid, H.; Trari, M.; Sadaoui, Z.: Comparative study on removal of two basic dyes in aqueous medium by adsorption using activated carbon from Ziziphus lotus stones. Microchemical J. 146, 1010–1018 (2019)
Dil, E.A.; Asfaram, M.A.; Mehrabi, F.; Bazrafshan, A.A.; Tayebi, L.: Synthesis and application of Ce-doped TiO2 nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon for ultrasound-assisted adsorption of Basic Red 46 dye. Ultrason. Sonochem. 58, 104702 (2019)
Safari, M.; Khataee, A.; Soltani, R.D.C.; Rezaee, R.: Ultrasonically facilitated adsorption of an azo dye onto nanostructures obtained from cellulosic wastes of broom and cooler straw. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 522, 228–241 (2018)
Bayram, T.; Bucak, S.; Ozturk, D.: BR13 dye removal using Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate modified montmorillonite: equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetic and reusability studies. Chem. Eng. Process. 158, 108186 (2020)
Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Xu, F.; Jiang, H.: Chen, L,: Hydroxyapatite modified sludge-based biochar for the adsorption of Cu2+ and Cd2+: Adsorption behavior and mechanisms. Bioresource Technol. 321, 124413 (2021)
Liu, J.; Hu, C.; Huang, Q.: Adsorption of Cu2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+ onto oiltea shell from water. Bioresource Technol. 271, 487–491 (2019)
Mi, X.; Huang, G.; Xie, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.: Preparation of graphene oxide aerogel and its adsorption for Cu2+ ions. Carbon 50, 4856–4864 (2012)
Li, Y.H.; Ding, J.; Luan, Z.; Di, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, D.; Wei, B.: Competitive adsorption of Pb2+, Cu2+ and Cd2+ ions from aqueous solutions by multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 41, 2787–2792 (2003)
Tan, P.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Bi, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.: Adsorption of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous single metal solutions on graphene oxide membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 297, 251–260 (2015)
Peng, M.; Chen, G.; Zeng, G.; Chen, A.; He, K.; Huang, Z.; Hu, L.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Yuan, L.; Hang, T.: Superhydrophobic kaolinite modified graphene oxide-melamine sponge with excellent properties for oil-water separation. Appl. Clay Sci. 163, 63–71 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by TIANGONG UNIVERSITY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Wang, J., Guo, J. et al. Reduction in Graphene Oxide by Sodium Borohydride for Enhanced BR13 Dye and Cu2+ Adsorption. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 8387–8399 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06708-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06708-6