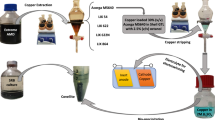
Abstract
Copper and cobalt usually coexist in the leachate of waste lithium ion batteries, sea nodules and other copper ore or by-product. Conventional methods for the separation of copper and cobalt hardly avoid some defects, such as longer extraction time, co-extraction and too many stages. In this paper, a microfluidic extraction procedure for simultaneously separating copper \((\hbox {Cu}^{2+})\) and cobalt \((\hbox {Co}^{2+})\) ions in a microchannel was investigated. In addition, some key operation parameters, such as initial pH, volume flow rate and extractant concentration, were optimized by a method of response surface methodology (RSM). The result showed that under the optimized operation parameters of initial pH of 2.5, volume flow rate of \(0.035~\hbox {mL}~\hbox {min}^{-1}\) and extractant concentration of 17.36%, the extraction rate of copper could be as high as 96.73%, with a low cobalt extraction rate, which was only 2.41%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, F.; He, F.; Zhao, J.; et al.: Extraction and separation of cobalt(II), copper(II) and manganese(II) by Cyanex272, PC-88A and their mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 93(3), 8–14 (2012)
Sridhar, V.; Verma, J.K.: Extraction of copper, nickel and cobalt from the leach liquor of manganese-bearing sea nodules using LIX 984N and ACORGA M5640. Miner. Eng. 24(8), 959–962 (2011)
Sahu, S.K.; Agrawal, A.; Pandey, B.D.; et al.: Recovery of copper, nickel and cobalt from the leach liquor of a sulphide concentrate by solvent extraction. Miner. Eng. 17(7–8), 949–951 (2004)
Zhang, W.; Cui, C.; Yang, Y.: Mass transfer of copper(II) in hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane with different carriers. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 18(2), 346–350 (2010)
Lu, J.; Dreisinger, D.: Solvent extraction of copper from chloride solution I: extraction isotherms. Hydrometallurgy 137(5), 13–17 (2013)
Liu, X.R.; Qiu, G.Z.; Hu, Y.H.: Degradation of Lix984N and its effect on interfacial emulsion. J. Cent. South Univ. 13(6), 668–672 (2006)
Lu, J.; Dreisinger, D.: Two-stage countercurrent solvent extraction of copper from cuprous chloride solution: Cu(II) loading coupled with Cu(I) oxidation by oxygen and iron scrubbing. Hydrometallurgy 150, 41–46 (2014)
Balesini, A.A.; Zakeri, A.; Razavizadeh, H.; et al.: Nickel solvent extraction from cold purification filter cakes of Angouran mine concentrate using LIX984N. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 20(11), 1029–1034 (2013)
Liqing, L.I.; Hong, Z.; Cao, Z.; et al.: Recovery of copper(II) and nickel(II) from plating wastewater by solvent extraction. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 19(6), 926–930 (2011)
Zhang, W.; Cui, C.; Ren, Z.; et al.: Simultaneous removal and recovery of copper(II) from acidic wastewater by hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane with LIX984N as carrier. Chem. Eng. J. 157(1), 230–237 (2010)
Yang, B.; Wang, C.; Li, D. et al.: Selective separation of copper and cadmium from zinc solutions by low current density electrolysis. Trans. Nonferrous. Met. Soc. China. 20(3), 533–536 (2010)
Gharehbagh, F.S.; Mousavian, S.M.A.: Hydrodynamic characterization of mixer-settlers. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 40(3), 302–312 (2009)
Javanshir, S.; Abdollahy, M.; Abolghasemi, H.: Drop size distribution in a mixer-settler reactor for the gold chloride/DBC system. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 90(10), 1680–1686 (2012)
Moreno, C.M.; Pérez-Correa, J.R.; Otero, A.: Dynamic modelling of copper solvent extraction mixer-settler units. Miner. Eng. 22(15), 1350–1358 (2009)
Agrawal, A.; Manoj, M.K.; Kumari, S.; et al.: Extractive separation of copper and nickel from copper bleed stream by solvent extraction route. Miner. Eng. 21(15), 1126–1130 (2008)
Sridhar, V.; Verma, J.K.; Kumar, S.A.: Selective separation of copper and nickel by solvent extraction using LIX984N. Hydrometallurgy 99(1), 124–126 (2009)
Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; et al.: Separation of copper, iron(III), zinc and nickel from nitrate solution by solvent extraction using LK-C2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 70(3), 306–313 (2010)
Korchinsky, W.J.; Ismail, A.M.: Mass-transfer parameters in rotating-disc contactors: influence of column diameter. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 43(43), 147–158 (1988)
Kadam, B.D.; Joshi, J.B.; Koganti, S.B.; et al.: Hydrodynamic and mass transfer characteristics of annular centrifugal extractors. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 86(3), 233–244 (2008)
Tamhane, T.V.; Joshi, J.B.; Mudali, U.K.; et al.: Axial mixing in annular centrifugal extractors. Chem. Eng. J. 207–208, 462–472 (2012)
Liu, J.S.; Lan, Z.Y.; Qiu, G.Z.; et al.: Mechanism of crud formation in copper solvent extraction. J. Cent. South Univ. 9(3), 169–172 (2002)
Priest, C.; Zhou, J.; Sedev, R.; et al.: Microfluidic extraction of copper from particle-laden solutions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 98(3–4), 168–173 (2011)
Zhang, L.H.; Peng, J.H.; Ju, S.H.; et al.: Microfluidic solvent extraction and separation of cobalt and nickel. RSC Adv. 4(31), 16081–16086 (2014)
Ciceri, D.; Mason, L.R.; Harvie, D.J.E.; et al.: Extraction kinetics of Fe(III) by di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid using a Y–Y shaped microfluidic device. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 92(3), 571–580 (2014)
Rahimi, M.; Aghel, B.; Hatamifar, B.; et al.: CFD modeling of mixing intensification assisted with ultrasound wave in a T-type microreactor. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 86, 36–46 (2014)
Yin, S.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; et al.: Microfluidic solvent extraction of La(III) with 2-ethylhexyl phosphoric acid-2-ethylhexyl ester (P507) by a microreactor. Chem. Eng. Process. 91, 1–6 (2015)
Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Su, Y.; et al.: An experimental study of copper extraction characteristics in a T-junction microchannel. Chem. Eng. Technol. 36(6), 985–992 (2013)
Li, C.; Jiang, F.; Ju, S.; et al.: Separation of \(\text{ In }^{3+}\) and \(\text{ Fe }^{3+}\) from sulfate solutions using D2EHPA in a laminar microreactor. Can. Metall. Q. 54(4), 432–438 (2015)
Kalil, S.J.; Maugeri, F.; Rodrigues, M.I.: Response surface analysis and simulation as a tool for bioprocess design and optimization. Process Biochem. 35(6), 539–550 (2000)
Wang, Y.X.; Lu, Z.X.: Optimization of processing parameters for the mycelial growth and extracellular polysaccharide production by Boletus, spp. ACCC 50328. Process Biochem. 40(3–4), 1043–1051 (2005)
Zhang, W.; Cui, C.; Yang, Y.: Mass transfer of copper(II) in hollow fiber renewal liquid membrane with different carriers. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 18(2), 346–350 (2010)
Miguel, E.R.D.S.; Aguilar, J.C.; Bernal, J.P.; et al.: Extraction of Cu(II), Fe(III), Ga(III), Ni(II), In(III), Co(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) with LIX984 dissolved in n-heptane. Hydrometallurgy 47(1), 19–30 (1997)
Panigrahi, S.; Parhi, P.K.; Sarangi, K.; et al.: A study on extraction of copper using LIX 84-I and LIX 622N. Sep. Purif. Technol. 70(1), 58–62 (2009)
Kongolo, K.; Mwema, M.D.; Banza, A.N.; et al.: Cobalt and zinc recovery from copper sulfuric solution by solvent extraction. Miner. Eng. 16(12), 1371–1374 (2003)
Huang, K.; Li, Q.W.; Chen, J.: Recovery of copper, nickel and cobalt from acidic pressure leaching solutions of low-grade sulfide flotation concentrates. Miner. Eng. 20(7), 722–728 (2007)
Pradhan, S.; Devi, N.; Mishra, S.: Separation of copper and iron from chloride media using Cyanex 921 in kerosene. J. Cent. South Univ. 21(5), 1752–1755 (2014)
Alguacil, F.J.; Cobo, A.: Solvent extraction with LIX 973N for the selective separation of copper and nickel. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 74(5), 467–471 (1999)
Chakravarti, A.K.; Chowdhury, S.B.; Mukherjee, D.C.: Liquid membrane multiple emulsion process of separation of copper(II) from waste waters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 166(1–3), 7–25 (2000)
Sengupta, B.; Sengupta, R.; Subrahmanyam, N.: Copper extraction into emulsion liquid membranes using LIX 984N-C. Hydrometallurgy 81(1), 67–73 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Bq., Jiang, F., Peng, Jh. et al. Optimization Study of Operation Parameters for Extracting \(\hbox {Cu}^{2+}\) from Sulfuric Solution Containing \(\hbox {Co}^{2+}\) with LIX984N in a Laminar Microchip. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 2145–2153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2495-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2495-1