Abstract
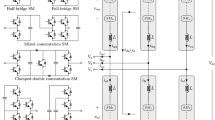
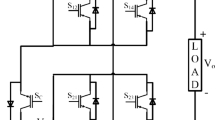
This paper proposes a new topology for multilevel inverters based on series and parallel {R1–7} connection’s of the dc voltage sources. Series and parallel {R1–7} connections ability of the proposed topology make it capable of increasing the number of voltage levels and the output current, respectively. The proposed topology is optimized from the viewpoint of number of switches, number of dc voltage sources, and maximum blocked voltage by switches. The optimal topologies with minimum number of switches and dc voltage sources are computed to produce the maximum number of output voltage levels with minimum blocked voltage by switches. In addition, a new algorithm for the determination of magnitudes of dc voltage sources is presented. Furthermore, to verify the theoretical aspects, the proposed topology is compared with some of the new presented multilevel inverters. The performance of the proposed multilevel inverter is verified by the simulation and experimental results of a single-phase 25-level inverter.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- V dc :
-
Isolated dc voltage source
- m :
-
Number of dc voltage sources connected in parallel
- n :
-
Number of dc voltage sources for the extended unit
- n j :
-
Number of dc voltage sources for the jth unit
- N step,j :
-
Number of voltage levels for the jth unit
- V j :
-
Magnitude of dc voltage source used in jth unit
- v o :
-
Output voltage
- v o,j :
-
Output voltage of the jth unit
- V o, max :
-
Maximum output voltage
- I j :
-
Nominal current of the dc voltage source used in jth unit
- I o, j :
-
Nominal output current of jth unit
- k :
-
Number of units
- N IGBT :
-
Number of IGBTs
- N step :
-
Number of voltage levels
- N dc :
-
Number of dc voltage sources
- V switch :
-
Standing voltage
- V switch,j :
-
Standing voltage of jth unit
- c :
-
Constant value
- \({C_{k}^{m}}\) :
-
Number of mcombinations from k numbers
- R :
-
Load resistance
- L :
-
Load inductance
References
Baker, R.H.; Bannister, L.H.: Electric Power Converter. U.S. Patent 3 867 643 (1975)
Nabae A., Takahashi I., Akagi H.: A new neutral-point clamped PWM inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. IA-17(5), 518–523 (1981)
Sato, Y.; Ito, T.: Experimental verification of loss reduction in diode clamped multilevel inverters. In: Proceedings of ECCE, pp. 190–196 (2011)
Hagiwara M., Nishimura K., Akagi H.: A medium voltage motor drive with a modular multilevel PWM inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 25(7), 1786–1799 (2010)
De, S.; Banerjee, D.; Siva kumar, K.; Gopakumar, K.; Ramchand, R.; Patel, C.: Multilevel inverters for low power application. IET Power Electron. 4(4), 384–392 (2011)
Zhang, L.; Watkins, S.J.: Capacitor voltage balancing in multilevel flying capacitor inverters by rule-based switching pattern selection. In: Proceedings of IET Electric Power Applications, pp. 339–347 (2007)
Du Z., Ozpineci B., Tolbert L.M., Chiasson J.N.: dc-ac cascaded H-bridge multilevel boost inverter with no inductors for electric/hybrid electric vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 45(3), 963–970 (2009)
Ruiz-Caballero D.A., Ramos-Astudillo R.M., Mussa S.A., Heldwein M.L.: Symmetrical hybrid multilevel dc-ac converters with reduced number of insulated dc supplies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(7), 2307–2314 (2010)
Suresh, Y.; Panda, A.K.: Performance of cascade multilevel H-bridge inverter with single dc source by employing low frequency three-phase transformers. In: Proceedings of IECON, pp. 1981–1986 (2010)
Perez M.A., Cortes P., Rodriguez J.: Predictive control algorithm technique for multilevel asymmetric cascaded H-bridge inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55(12), 4354–4361 (2008)
Leon J.I., Vazquez S., Watson A.J., Franquelo L.G., Wheeler P.W., Carrasco J.M.: Feed forward space vector modulation for single-phase multilevel cascaded converters with any dc voltage ratio. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(2), 315–325 (2009)
Babaei E.: A cascade multilevel converter topology with reduced number of switches. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23(6), 2657–2664 (2008)
Babaei E.: Optimal topologies for cascaded sub-multilevel converters. J. Power Electron. 10(3), 251–261 (2010)
Babaei E., Hosseini S.H.: New cascaded multilevel inverter topology with minimum number of switches. Elsevier J. Energy Convers. Manag. 50(11), 2761–2767 (2009)
Ebrahimi, J.; Babaei, E.; Gharehpetian, G.B.: A new topology of cascaded multilevel converters with reduced number of components for high-voltage applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26(11), 3109–3118 (2011)
Ebrahimi J., Babaei E., Gharehpetian G.B.: A new multilevel converter topology with reduced number of power electronic components. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 59(2), 655–667 (2012)
Hinago Y., Koizumi H.: A single-phase multilevel inverter using switched series/parallel dc voltage sources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(8), 2643–2650 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babaei, E., Sheermohammadzadeh, S. & Sabahi, M. Improvement of Multilevel Inverters Topology Using Series and Parallel Connections of DC Voltage Sources. Arab J Sci Eng 39, 1117–1127 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0696-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-013-0696-9