Abstract
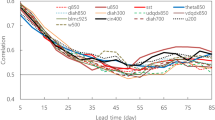
Despite significant progress having been made in recent years, the forecast skill for seasonal precipitation over China remains limited. In this study, a deep-learning-based statistical prediction model for seasonal precipitation over China was developed. The model was trained to learn the distribution of the seasonal precipitation using simultaneous general circulation data. First, it was pre-trained with the hindcasts of several general circulation models (GCMs), and evaluation of the test set suggested that the pre-trained model could basically reproduce the GCM-predicted precipitation, with the anomaly pattern correlation coefficients (PCCs) greater than 0.80. Then, transfer learning was applied by using ECMWF Reanalysis v5 (ERA5) data and gridded precipitation observational data over China, to further correct the systemic errors in the model. As a result, using general circulation fields from reanalysis as the input, this hybrid model performed reasonably well in simulating the seasonal precipitation over China, with the PCC reaching 0.71. In addition, the results using the circulation fields predicted by GCMs as the input were also assessed. In general, the proposed model improves the PCC over China by 0.10–0.13, as compared to the raw GCM outputs, for lead times of 1–4 months. This deep learning model has been used at the National Climate Center of China Meteorological Administration for the past two years to provide guidance for summer precipitation prediction over China and has performed extremely well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ba, J. L., J. R. Kiros, and G. E. Hinton, 2016: Layer normalization. arXiv preprint. Available online at https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Chen, H. P., J. Q. Sun, and H. J. Wang, 2012: A statistical downscaling model for forecasting summer rainfall in China from DEMETER hindcast datasets. Wea. Forecasting, 27, 608–628, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/WAF-D-11-00079.1.
Chu, J. L., H. W. Kang, C. Y. Tam, et al., 2008: Seasonal forecast for local precipitation over northern Taiwan using statistical downscaling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 113 doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009424.
Dai, H. X., and K. Fan, 2021: An effective downscaling model for operational prediction of summer precipitation over China. Atmos. Res., 257, 105621, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105621.
Fan, K., H. J. Wang, and Y. J. Choi, 2008: A physically-based statistical forecast model for the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River Valley summer rainfall. Chinese Sci. Bull., 53, 602–609, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0083-1.
Gagne, D. J., H. M. Christensen, A. C. Subramanian, et al., 2020: Machine learning for stochastic parameterization: Generative adversarial networks in the Lorenz’ 96 model. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst., 12, e2019MS001896, doi: https://doi.org/10.1299/0019MS001896.
Grönquist, P., C. Y. Yao, T. Ben-Nun, et al., 2021: Deep learning for post-processing ensemble weather forecasts. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. A, 379, 20200092, doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2020.0092.
Ham, Y. G., J. H. Kim, and J. J. Luo, 2019: Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature, 573, 568–572, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1559-7.
He, K. M., X. Y. Zhang, S. Q. Ren, et al., 2016: Deep residual learning for image recognition. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 770–778, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
Hersbach, H., B. Bell, P. Berrisford, et al., 2019a: ERA5 monthly averaged data on single levels from 1979 to present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS), doi: https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.f17050d7.
Hersbach, H., B. Bell, P. Berrisford, et al., 2019b: ERA5 monthly averaged data on pressure levels from 1979 to present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS), doi: https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.6860a573.
Johnson, S. J., T. N. Stockdale, L. Ferranti, et al., 2019: SEAS5: The new ECMWF seasonal forecast system. Geosci. Model Dev., 12, 1087–1117, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-12-1087-2019.
Kadow, C., D. M. Hall, and U. Ulbrich, 2020: Artificial intelligence reconstructs missing climate information. Nature Geosci., 13, 408–413, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-020-0582-5.
Kämäräinen, M., P. Uotila, A. Y. Karpechko, et al., 2019: Statistical learning methods as a basis for skillful seasonal temperature forecasts in Europe. J. Climate, 32, 5363–5379, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0765.1.
Klein, W. H., 1982: Statistical weather forecasting on different time scales. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 170–177. Available online at https://www.jstor.org/stable/26222740. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
LeCun, Y., Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, 2015: Deep learning. Nature, 521, 436–444, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539.
Liang, P., Z. Z. Hu, Y. Y. Liu, et al., 2019: Challenges in predicting and simulating summer rainfall in the eastern China. Climate Dyn., 52, 2217–2233, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4256-6.
Liu, Y., and K. Fan., 2014: An application of hybrid downscaling model to forecast summer precipitation at stations in China. Atmos. Res., 143, 17–30, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.01.024.
Liu, Y. J., E. Racah, J. Correa, et al., 2016: Application of deep convolutional neural networks for detecting extreme weather in climate datasets. arXiv preprint. Available online at https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.01156. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Loshchilov, I., and F. Hutter, 2019: Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv preprint. Available online at https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Luo, L. F., W. Tang, Z. H. Lin, et al., 2013: Evaluation of summer temperature and precipitation predictions from NCEP CFSv2 retrospective forecast over China. Climate Dyn., 41, 2213–2230, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1927-1.
Marzban, C., S. Sandgathe, and E. Kalnay, 2006: MOS, perfect prog, and reanalysis. Mon. Wea. Rev., 134, 657–663, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR3088.1.
Mishra, N., C. Prodhomme, and V. Guemas, 2019: Multi-model skill assessment of seasonal temperature and precipitation forecasts over Europe. Climate Dyn., 52, 4207–4225, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4404-z.
Pan, B. X., K. Hsu, A. AghaKouchak, et al., 2019: Improving precipitation estimation using convolutional neural network. Water Resour. Res., 55, 2301–2321, doi: https://doi.org/10.1229/0018WR024090.
Peng, P. T., A. G. Barnston, and A. Kumar, 2013: A comparison of skill between two versions of the NCEP Climate Forecast System (CFS) and CPC’s operational short-lead seasonal outlooks. Wea. Forecasting, 28, 445–462, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/WAF-D-12-00057.1.
Racah, E., C. Beckham, T. Maharaj, et al., 2017: Extreme weather: A large-scale climate dataset for semi-supervised detection, localization, and understanding of extreme weather events. arXiv preprint. Available online at https://arxiv.org/abs/1612.02095. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Rasp, S., and S. Lerch, 2018: Neural networks for postprocessing ensemble weather forecasts. Mon. Wea. Rev., 146, 3885–3900, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-18-0187.1.
Rasp, S., M. S. Pritchard, and P. Gentine, 2018: Deep learning to represent subgrid processes in climate models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 115, 9684–9689, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1810286115.
Reichstein, M., G. Camps-Valls, B. Stevens, et al., 2019: Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature, 566, 195–204, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0912-1.
Rumelhart, D. E., G. E. Hinton, and R. J. Williams, 1986: Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature, 323, 533–536, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/323533a0.
Saha, S., S. Moorthi, X. R. Wu, et al., 2014: The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. Climate, 27, 2185–2208, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00823.1.
Selvaraju, R. R., M. Cogswell, A. Das, et al., 2017: Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, Venice, Italy, 618–626, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.74.
Shi, X. J., Z. H. Gao, L. Lausen, et al., 2017: Deep learning for precipitation nowcasting: A benchmark and a new model. arXiv preprint. Available online at https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03458. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Sønderby, C. K., L. Espeholt, J. Heek, et al., 2020: MetNet: A neural weather model for precipitation forecasting. arXiv preprint. Available online at https://axxiv.org/abs/2003.12140. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Srivastava, N., G. Hinton, A. Krizhevsky, et al., 2014: Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 15, 1929–1958. Available online at https://jmlr.org/papers/v15/srivastava14a.html. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Toms, B. A., E. A. Barnes, and I. Ebert-Uphoff, 2020: Physically interpretable neural networks for the geosciences: Applications to earth system variability. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst., 12, e2019MS002002, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS002002.
Trebing, K., T. Staǹczyk, and S. Mehrkanoon, 2021: SmaAt-UNet: Precipitation nowcasting using a small attention-UNet architecture. Pattern Recogn. Lett., 145, 178–186, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2021.01.036.
Wang, B., J. Y. Lee, I. S. Kang, et al., 2009: Advance and prospectus of seasonal prediction: Assessment of the APCC/Cli-PAS 14-model ensemble retrospective seasonal prediction (1980–2004). Climate Dyn., 33, 93–117, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0460-0.
Wang, B., J. Y. Lee, and B. Q. Xiang, 2015: Asian summer monsoon rainfall predictability: A predictable mode analysis. Climate Dyn., 44, 61–74, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2218-1.
Wang, X. Q., G. H. Huang, Q. G. Lin, et al., 2015: High-resolution temperature and precipitation projections over Ontario, Canada: A coupled dynamical-statistical approach. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 141, 1137–1146, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.2421.
Wen, N., Z. Y. Liu, and L. Li, 2019: Direct ENSO impact on East Asian summer precipitation in the developing summer. Climate Dyn., 52, 6799–6815, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4545-0.
Woo, S., J. Park, J. Y. Lee, et al., 2018: CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Munich, Germany, 3–19, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1.
Wu, R. G., Z. Z. Hu, and B. P. Kirtman, 2003: Evolution of ENSO-related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J. Climate, 16, 3742–3758. Available online at https://jmlr.org/papers/v15/srivastava14a.html. Accessed on 23 March 2022.
Xiao, M. Z., Q. Zhang, and V. P. Singh, 2015: Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD, and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Int. J. Climatol., 35, 3556–3567, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4228.
Zeiler, M. D., and R. Fergus, 2014: Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, Zurich, Switzerland, 818–833, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53.
Zhao, Y. F., J. Zhu, and Y. Xu, 2014: Establishment and assessment of the grid precipitation datasets in China for recent 50 years. J. Meteor. Sci., 34, 414–420, doi: https://doi.org/10.3969/2013jms.0008. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the insights offered by Bin Wang and Haohuan Fu from Tsinghua University, and Xiaolong Jia and Xiangwen Liu from the Beijing Climate Center. All the hindcast and ERA5 reanalysis data were generated by using Copernicus Climate Change Service information (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFA0602103), National Climate Center’s Project on Precipitation Prediction Method in Flood Season in China based on CMA—CPS (Climate Prediction System) and Machine Learning, and GEIGC (Global Energy Interconnection Group Co., Ltd.) Science and Technology Project (SGGEIG00JYJS2000053).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, W., Luo, Y., Wu, T. et al. Deep Learning for Seasonal Precipitation Prediction over China. J Meteorol Res 36, 271–281 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-022-1174-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-022-1174-7