Abstract
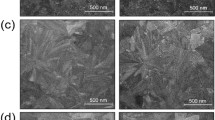
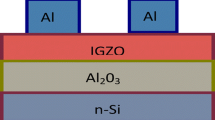
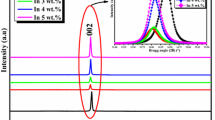
The effect of Ti doping in an indium oxide (InOx)-based semiconductor is investigated for the thin-film transistor (TFT) property and crystal structure of the film. InOx and Ti-doped InOx (InTiOx) films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering under the same O2 partial pressure conditions were systematically compared. The TFT behavior of the InOx showed higher conductivity than that of the InTiOx and was drastically changed to metallic conduction after annealing at 150 °C. Under the annealing conditions when the electrical transition to the metallic behavior occurred, the InOx film was crystallized. The X-ray diffraction analysis revealed that the shrinkage of the In2O3 unit cell is pronounced in the case of InOx films. Thus, Ti dopants may play the role as a suppressor for shrinkage of the unit cell, i.e. maintaining neighboring In–In distances, in addition to suppression of oxygen vacancies. The In–In distance, which is related to the overlapping of In 5s orbitals, is considered to be one of the key factor for which InOx-based materials are utilized as conducting films or semiconducting channels.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adurodija, F. O., Semple, L., & Brüning, R. (2006). Crystallization process and electro-optical properties of In2O3 and ITO thin films. Journal Materials Science, 41, 7096–7102.
Aikawa, S., Darmawan, P., Yanagisawa, K., Nabatame, T., Abe, Y., & Tsukagoshi, K. (2013). Thin-film transistors fabricated by low-temperature process based on Ga- and Zn-free amorphous oxide semiconductor. Applied Physics Letters, 102, 102101–102104. doi:10.1063/1.4794903.
Aikawa, S., Nabatame, T., & Tsukagoshi, K. (2013). Effects of dopants in InOx-based amorphous oxide semiconductors for thin-film transistor applications. Applied Physics Letters, 103, 172105. doi:10.1063/1.4822175.
Aikawa, S., Mitoma, N., Kizu, T., Nabatame, T., & Tsukagoshi, K. (2015). Suppression of excess oxygen for environmentally stable amorphous In–Si–O thin-film transistors. Applied Physics Letters, 106, 192103. doi:10.1063/1.4921054.
Barquinha, P., Pereira, L., Gonçalves, G., Martins, R., & Fortunato, E. (2009). Toward high-performance amorphous GIZO TFTs. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 156, H161. doi:10.1149/1.3049819.
Brese, N., & O’keeffe, M. (1991). Bond-valence parameters for solids. Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Science, 47, 192–197.
Buchholz, D. B., et al. (2014). The structure and properties of amorphous indium oxide. Chemistry of Materials, 26, 5401–5411.
Dhananjay, & Chu, C. W. (2007). Realization of In2O3 thin film transistors through reactive evaporation process. Applied Physics Letters, 91, 132111–132113.
Fakhri, M., Johann, H., Görrn, P., & Riedl, T. (2012). Water as origin of hysteresis in zinc tin oxide thin-film transistors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4, 4453–4456. doi:10.1021/am301308y.
Fortunato, E., Barquinha, P., Pimentel, A., Pereira, L., Goncalves, G., & Martins, R. (2007). Amorphous IZO TTFTs with saturation mobilities exceeding 100 cm2/Vs physica status solidi. (RRL)-Rapid Research Letters, 1, R34–R36.
Fuchs, F., & Bechstedt, F. (2008). Indium-oxide polymorphs from first principles: Quasiparticle electronic states. Physical Review B, 77, 155107.
Gonçalves, G., Barquinha, P., Pereira, L., Franco, N., Alves, E., Martins, R., et al. (2010). High mobility a-IGO films produced at room temperature and their application in TFTs. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 13, H20–H22.
Hennek, J. W., et al. (2013). Oxygen “Getter” effects on microstructure and carrier transport in low temperature combustion-processed a-InXZnO (X = Ga, Sc, Y, La) transistors. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135, 10729–10741. doi:10.1021/ja403586x.
Hosono, H., Kikuchi, N., Ueda, N., & Kawazoe, H. (1996). Working hypothesis to explore novel wide band gap electrically conducting amorphous oxides and examples. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 198–200, 165–169. doi:10.1016/0022-3093(96)80019-6.
Hsu, H.-H., Chang, C.-Y., Cheng, C.-H., Chiou, S.-H., & Huang, C.-H. (2014). High mobility bilayer metal–oxide thin film transistors using titanium-doped InGaZnO. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 35, 87–89.
Jeong, H., Jeong, H. S., Kim, D. H., Jeong, C. Y., & Kwon, H. I. (2016). Effects of post-deposition thermal annealing temperature on electrical properties of ZnON thin-film transistors. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 37, 747–750. doi:10.1109/led.2016.2559523.
Kamiya, T., Nomura, K., & Hosono, H. (2010). Present status of amorphous In–Ga–Zn–O thin-film transistors. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 11, 044305. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/11/4/044305.
Kerkache, L., Layadi, A., Dogheche, E., & Remiens, D. (2005). Physical properties of RF sputtered ITO thin films and annealing effect. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 39, 184.
Kim, J.-I., Ji, K. H., Jang, M., Yang, H., Choi, R., & Jeong, J. K. (2011). Ti-doped indium tin oxide thin films for transparent field-effect transistors: Control of charge-carrier density and crystalline structure. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 3, 2522–2528.
Kim, J.-H., et al. (2012). Effects of Ti addition on sol-gel derived InO and InZnO thin film transistors. Current Applied Physics, 12(Supplement 1), e24–e28. doi:10.1016/j.cap.2011.07.043.
Kim, W. J., Min, B.-K., Pradhan, D., & Sohn, Y. (2015). Crystal phase transformation and doping-induced blue emission of Eu-doped InOOH and cubic/corundum-type rhombohedral In2O3 nanowires. CrystEngComm, 17, 1189–1200. doi:10.1039/c4ce02111h.
Kizu, T., et al. (2014). Low-temperature processable amorphous In–W–O thin-film transistors with high mobility and stability. Applied Physics Letters, 104, 152103. doi:10.1063/1.4871511.
Kurishima, K., et al. (2016). Prospectively of carbon-doped indium-tungsten-oxide channel TFT for bias stress instability. ECS Transactions, 75, 149–156. doi:10.1149/07510.0149ecst.
Lee, S., et al. (2011). Trap-limited and percolation conduction mechanisms in amorphous oxide semiconductor thin film transistors. Applied Physics Letters, 98, 203503–203508.
Lin, M.-F., et al. (2015). Reduction of the interfacial trap density of indium-oxide thin film transistors by incorporation of hafnium and annealing process. AIP Advances. doi:10.1063/1.4905903.
Luo, Y.-R. (2007). BDEs of B(B ±)–, Al(Al ±)–, Ga(Ga ±)–,In(In ±)–, and Tl(Tl ±)–X bonds. In Comprehensive handbook of chemical bond energies. CRC Press, pp 1041–1086. doi:10.1201/9781420007282.ch23.
Mitoma, N., et al. (2014). Stable amorphous In2O3-based thin-film transistors by incorporating SiO2 to suppress oxygen vacancies. Applied Physics Letters, 104, 102103. doi:10.1063/1.4868303.
Mitoma, N., et al. (2015). Dopant selection for control of charge carrier density and mobility in amorphous indium oxide thin-film transistors: Comparison between Si- and W-dopants. Applied Physics Letters, 106, 042106. doi:10.1063/1.4907285.
Mitoma, N., et al. (2016). Phase transitions from semiconductive amorphous to conductive polycrystalline in indium silicon oxide thin films. Applied Physics Letters, 109, 221903.
Nayak, P. K., Hedhili, M. N., Cha, D., & Alshareef, H. N. (2013). High performance In2O3 thin film transistors using chemically derived aluminum oxide dielectric. Applied Physics Letters, 103, 033514–033518.
Nomura, K., Ohta, H., Takagi, A., Kamiya, T., Hirano, M., & Hosono, H. (2004). Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature, 432, 488–492. doi:10.1038/Nature03090.
Orui, T., et al. (2015). Charge compensation by excess oxygen in amorphous In–Ga–Zn–O films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Journal of Display Technology, 11, 518–522. doi:10.1109/jdt.2014.2358251.
Park, J.-S., Kim, K., Park, Y.-G., Mo, Y.-G., Kim, H. D., & Jeong, J. K. (2009). Novel ZrInZnO Thin-film transistor with excellent stability. Advanced Materials, 21, 329–333. doi:10.1002/adma.200802246.
Park, S., et al. (2013). Effects of operational and geometrical conditions upon photosensitivity of amorphous InZnO thin film transistors. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, 31, 050605.
Park, W.-T., Son, I., Park, H.-W., Chung, K.-B., Xu, Y., Lee, T., et al. (2015). Facile routes to improve performance of solution-processed amorphous metal oxide thin film transistors by water vapor annealing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7, 13289–13294. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b04374.
Qu, M., Chang, C.-H., Meng, T., Zhang, Q., Liu, P.-T., Shieh, H.-P.D. (2017). Stability study of indium tungsten oxide thin-film transistors annealed under various ambient conditions. Physica Status Solidi A. doi:10.1002/pssa.201600465.
Shigesato, Y., Takaki, S., & Haranoh, T. (1992). Electrical and structural properties of low resistivity tin-doped indium oxide films. Journal of Applied Physics, 71, 3356–3364.
Song, P. K., Akao, H., Kamei, M., Shigesato, Y., & Yasui, I. (1999). Preparation and crystallization of tin-doped and undoped amorphous indium oxide films deposited by sputtering. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 38, 5224.
Tang, H., et al. (2015). Effects of residual hydrogen in sputtering atmosphere on structures and properties of amorphous In–Ga–Zn–O thin films. Journal of Applied Physics, 118, 205703. doi:10.1063/1.4936552.
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Dr. K. Tsukagoshi and Dr. T. Kizu (National Institute for Materials Science, Japan), and Prof. T. Yamaguchi (Kogakuin University) for their fruitful discussions. SA acknowledges the Murata Science Foundation. A part of this work was financially supported by the Strategic Research Foundation Grant-aided Project for Private Universities matching fund subsidy from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. The TFTs were fabricated at the Functional Microstructured Surface Research Center at Kogakuin University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aikawa, S. Effect of Ti Doping to Maintain Structural Disorder in InOx-Based Thin-Film Transistors Fabricated by RF Magnetron Sputtering. 3D Res 8, 35 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13319-017-0147-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13319-017-0147-6