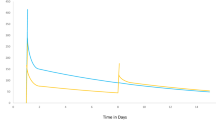
Abstract
Delafloxacin has recently received approval by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections. This article provides a balanced and comprehensive systematic critique of the literature in order to provide an up-to-date summary of its clinical pharmacology. Oral delafloxacin is rapidly absorbed and exhibits comparable exposure characteristics (300 mg intravenous versus 450 mg oral) between the two formulations, allowing easy transition from intravenous to oral therapy. The bioavailability is high (60–70%) and absorption is not affected by food intake, although further studies are required under clinically relevant conditions. Delafloxacin is primarily excreted renally (thus requiring renal dose adjustment in the setting of renal dysfunction), but also undergoes metabolism by uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes in the formation of a conjugated metabolite. Few drug-drug interaction studies have been identified, although more systematic characterizations in vitro and in vivo are warranted. Delafloxacin is a concentration-dependent bactericidal agent that has in vitro susceptibility for gram-positive (notably potent activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), gram-negative, and anaerobic organisms. In addition to acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections, the clinical utility of delafloxacin has also been studied in community-acquired pneumonia, acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, and gonorrhea, with potentially promising findings. Given its mild side effect profile, including an apparent lack of association with clinically important QTc prolongation, delafloxacin is generally well tolerated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Markham A. Delafloxacin: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77(13):1481–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0790-5.
Bassetti M, Pecori D, Cojutti P, Righi E, Pea F. Clinical and pharmacokinetic drug evaluation of delafloxacin for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017;13(11):1193–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2017.1386654.
Saravolatz LD, Stein GE. Delafloxacin: a new anti-MRSA fluoroquinolone. Clin Infect Dis. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciy600.
Wu K, Yan Z. FDA: center for drug evaluation and research- 208610Orig1s000. 2016. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2017/208610Orig1s000,208611Orig1s000ClinPharmR.pdf. Accessed July 2 2018.
Hoover R, Hunt T, Benedict M, Paulson SK, Lawrence L, Cammarata S, Sun E. Single and multiple ascending-dose studies of oral delafloxacin: effects of food, sex, and age. Clin Ther. 2016;38(1):39–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.10.016.
Hoover R, Hunt T, Benedict M, Paulson SK, Lawrence L, Cammarata S, Sun E. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic properties of intravenous delafloxacin after single and multiple doses in healthy volunteers. Clin Ther. 2016;38(1):53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.11.019.
McEwen A, Lawrence L, Hoover R, Stevens L, Mair S, Ford G, Williams D, Wood S. Disposition, metabolism and mass balance of delafloxacin in healthy human volunteers following intravenous administration. Xenobiotica. 2015;45(12):1054–62. https://doi.org/10.3109/00498254.2015.1042946.
Hoover RK, Alcorn H, Lawrence L, Paulson SK, Quintas M, Cammarata SK. Delafloxacin pharmacokinetics in subjects with varying degrees of renal function. J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;58(4):514–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.1041.
Hoover R, Alcorn H, Lawrence L, Paulson SK, Quintas M, Cammarata SK. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous delafloxacin in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;58(7):913–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.1099.
Hoover RK, Alcorn H, Lawrence L, Paulson SK, Quintas M, Luke DR, Cammarata SK. Clinical pharmacokinetics of sulfobutylether-beta-cyclodextrin in patients with varying degrees of renal impairment. J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;58(6):814–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.1077.
Hoover R, Marbury TC, Preston RA, Quintas M, Lawrence LE, Paulson SK, Luke DR, Cammarata SK. Clinical pharmacology of delafloxacin in patients with hepatic impairment. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;57(3):328–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.817.
Paulson SK, Wood-Horrall RN, Hoover R, Quintas M, Lawrence LE, Cammarata SK. The pharmacokinetics of the cyp3a substrate midazolam after steady-state dosing of delafloxacin. Clin Ther. 2017;39(6):1182–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.04.009.
Zinner SH, Vostrov SN, Alferova IV, Lubenko IY, Portnoy YA, Firsov AA. Comparative pharmacodynamics of the new fluoroquinolone ABT492 and ciprofloxacin with Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vitro dynamic model. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2004;24(2):173–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.02.026.
Almer LS, Hoffrage JB, Keller EL, Flamm RK, Shortridge VD. In vitro and bactericidal activities of ABT-492, a novel fluoroquinolone, against gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(7):2771–7. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.48.7.2771-2777.2004.
Gunderson SM, Hayes RA, Quinn JP, Danziger LH. In vitro pharmacodynamic activities of ABT-492, a novel quinolone, compared to those of levofloxacin against Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48(1):203–8. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.48.1.203-208.2004.
Firsov AA, Alferova IV, Smirnova MV, Lubenko IY, Portnoy YA, Zinner SH. Comparative pharmacodynamics of the new fluoroquinolone ABT492 and levofloxacin with Streptococcus pneumoniae in an in vitro dynamic model. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2005;25(5):409–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2005.02.004.
Thabit AK, Crandon JL, Nicolau DP. Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiling of delafloxacin in a murine lung model against community-acquired respiratory tract pathogens. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016;48(5):535–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2016.08.012.
Harnett SJ, Fraise AP, Andrews JM, Jevons G, Brenwald NP, Wise R. Comparative study of the in vitro activity of a new fluoroquinolone, ABT-492. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;53(5):783–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkh180.
Flamm RK, Rhomberg PR, Huband MD, Farrell DJ. In vitro activity of delafloxacin tested against isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(10):6381–5.
Soge OO, Salipante SJ, No D, Duffy E, Roberts MC. In vitro activity of delafloxacin against clinical Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates and selection of gonococcal delafloxacin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(5):3106–11.
Pfaller MA, Sader HS, Rhomberg PR, Flamm RK. In vitro activity of delafloxacin against contemporary bacterial pathogens from the United States and Europe, 2014. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(4):2609–16. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02609-16.
McCurdy S, Lawrence L, Quintas M, Woosley L, Flamm R, Tseng C, Cammarata S. In vitro activity of delafloxacin and microbiological response against fluoroquinolone-susceptible and nonsusceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates from two phase 3 studies of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(9):e00772–17. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00772-17.
Remy JM, Tow-Keogh CA, McConnell TS, Dalton JM, DeVito JA. Activity of delafloxacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: resistance selection and characterization. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67(12):2814–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dks307.
Hammerschlag MR, Roblin PM. The in vitro activity of a new fluoroquinolone, ABT-492, against recent clinical isolates of chlamydia pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;54(1):281–2. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkh304.
Waites KB, Crabb DM, Duffy LB. Comparative in Vitro susceptibilities and bactericidal activities of investigational fluoroquinolone ABT-492 and other antimicrobial agents against human mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47(12):3973–5. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.47.12.3973-3975.2003.
Lemaire S, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F. Contrasting effects of acidic pH on the extracellular and intracellular activities of the anti-gram-positive fluoroquinolones moxifloxacin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55(2):649–58. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01201-10.
Siala W, Mingeot-Leclercq M, Tulkens PM, Hallin M, Denis O, Van Bambeke F. Comparison of the antibiotic activities of daptomycin, vancomycin, and the investigational fluoroquinolone delafloxacin against biofilms from Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(11):6385–97. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03482-14.
Bauer J, Siala W, Tulkens PM, Van Bambeke F. A combined pharmacodynamic quantitative and qualitative model reveals the potent activity of daptomycin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(6):2726–37. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00181-13.
Firsov AA, Vostrov SN, Lubenko IY, Arzamastsev AP, Portnoy YA, Zinner SH. ABT492 and levofloxacin: comparison of their pharmacodynamics and their abilities to prevent the selection of resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro dynamic model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;54(1):178–86. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkh242.
O’Riordan W, Mehra P, Manos P, Kingsley J, Lawrence L, Cammarata S. A randomized phase 2 study comparing two doses of delafloxacin with tigecycline in adults with complicated skin and skin-structure infections. Int J Infect Dis. 2015;30:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2014.10.009.
Kingsley J, Mehra P, Lawrence LE, Henry E, Duffy E, Cammarata SK, Pullman J. A randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study to evaluate subjective and objective outcomes in patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections treated with delafloxacin, linezolid or vancomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(3):821–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkv411.
Pullman J, Gardovskis J, Farley B, Sun E, Quintas M, Lawrence L, Ling R, Cammarata S. Efficacy and safety of delafloxacin compared with vancomycin plus aztreonam for acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections: a phase 3, double-blind, randomized study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(12):3471–80. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkx329.
O’Riordan W, McManus A, Teras J, Poromanski I, Cruz-Saldariagga M, Quintas M, Lawrence L, Liang S, Cammarata S. A comparison of the efficacy and safety of intravenous followed by oral delafloxacin with vancomycin plus aztreonam for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections: a phase 3, multinational, double-blind, randomized study. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67:657–66. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciy165.
Longcor J, Hopkins S, Wikler M, Lawrence L. Phase 2 study of the safety and efficacy of oral delafloxacin (DLX) in subjects with acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (ABECB) [poster 1071]. Presented at ID week 2012; san Diego, CA, USA, October 17–21, 2012. https://idsa.confex.com/idsa/2012/webprogram/Paper37662.html. Accessed 20 July 2018.
Longcor J, Hopkins S, Wikler M, Lawrence L. Phase 2 study of the safety and efficacy of oral delafloxacin (DLX) in community acquired pneumonia (CAP) [poster 1069]. Presented at ID week 2012; San Diego, CA, USA, October 17–21, 2012. https://idsa.confex.com/idsa/2012/webprogram/Paper37764.html. Accessed 20 July 2018.
Melinta Therapeutics Inc. A phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, comparator-controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of intravenous to oral delafloxacin in adult subjects with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. 2018.https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02679573.Accessed July 21, 2018.
Melinta Therapeutics Inc. A comparative evaluation of the single-dose efficacy of oral delafloxacin versus the single-dose efficacy of an intramuscular injection of ceftriaxone in subjects with uncomplicated urogenital gonorrhea. 2018. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02015637.Accessed July 21 2018.
Litwin JS, Benedict MS, Thorn MD, Lawrence LE, Cammarata SK, Sun E. A thorough QT study to evaluate the effects of therapeutic and supratherapeutic doses of delafloxacin on cardiac repolarization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(6):3469–73. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.04813-14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding or any editorial assistance was received for the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
Jennifer Shiu, Grace Ting, and Tony KL Kiang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiu, J., Ting, G. & Kiang, T.K. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Delafloxacin. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 44, 305–317 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-018-0520-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-018-0520-8