Abstract
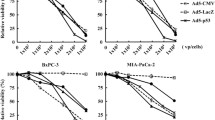
Type 5 adenoviruses expressing mda-7 gene (Ad-mda-7) induced cell death in various kinds of human tumors, but pancreatic carcinoma cells were relatively resistant to Ad-mda-7-mediated cytotoxicity. We then examined whether infection of Ad-mda-7 together with replication-competent Ad produced combinatory cytotoxic effects. We prepared replication-competent Ad, defective of the E1B55kDa gene or activated by a transcriptional regulatory region of the midkine or the survivin gene of which the expression was up-regulated in human tumors. Type 5 Ad bearing the exogenous regulatory region were further modified by replacing the fiber-knob region with that of type 35 Ad. Pancreatic carcinoma cells were infected with replication-incompetent Ad-mda-7 and the replication-competent Ad. Combinatory effects were examined with the CalcuSyn software and cell cycle analyses. Ad-mda-7 and the replication-competent Ad achieved cytotoxicity to pancreatic carcinoma. A combinatory use of Ad-mda-7 and either Ad defective of the E1B55kDa gene or Ad activated by the regulatory region produced synergistic cytotoxic effects. Cell cycle analyses demonstrated that the combination increased sub-G1 populations. These data collectively suggest that expression of MDA-7 augments cytotoxicity of replication-competent Ad and achieves adjuvant effects on Ad-mediated cell death.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ad:
-
Adenoviruses
- Ad-delE1B55:
-
Ad defective of E1B55kDa molecules
- Ad-mda-7:
-
Ad expressing the mda-7 gene
- Ad-LacZ:
-
Ad expressing the β-galactosidase gene
- AdF:
-
Type 5 Ad bearing type 35-derived fiber-knob region
- AdF-MK:
-
AdF in which E1 gene is activated by MK regulatory region
- AdF-Sur:
-
AdF in which E1 gene is activated by Sur regulatory region
- AdF-LacZ:
-
AdF expressing the β-galactosidase gene
- CAR:
-
Coxsakie adenovirus receptor
- CI:
-
Combination index
- Fa:
-
Fractions affected
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- MDA-7:
-
Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7
- MK:
-
Midkine
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Sur:
-
Survivin
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66.
Emdad L, Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, Gupta P, Sauane M, Dash R, et al. Historical perspective and recent insights into our understanding of the molecular and biochemical basis of the antitumor properties of mda-7/IL-24. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8:391–400.
Dash R, Bhutia SK, Azab B, Su ZZ, Quinn BA, Kegelmen TP, et al. mda-7/IL-24: a unique member of the IL-10 gene family promoting cancer-targeted toxicity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010;21:381–91.
Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, Sarkar D, Gopalkrishnan RV, Waxman S, Yacoub A, et al. Induction of reactive oxygen species renders mutant and wild-type K-ras pancreatic carcinoma cells susceptible to Ad.mda-7-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 2005;24:585–96.
Jounaidi Y, Doloff JC, Waxman DJ. Conditionally replicating adenoviruses for cancer treatment. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007;7:285–301.
Tomizawa M, Saisho H, Tagawa M. Regulatory regions of growth-related genes can activate an exogenous gene of the α-fetoprotein promoter to a comparable degree in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:3273–7.
Miyauchi M, Yoshida Y, Tada Y, Narita M, Maeda T, Bahar R, et al. Expression of herpes simplex virus-thymidine kinase gene controlled by a promoter region of the midkine gene confers selective cytotoxicity to ganciclovir in human carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2001;91:723–7.
Liu BB, Wang WH. Survivin and pancreatic cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 2011;2:164–8.
Maeda S, Shinchi H, Kurahara H, Mataki Y, Noma H, Maemura K, et al. Clinical significance of midkine expression in pancreatic head carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2007;97:405–11.
Bischoff JR, Kirn DH, Williams A, Heise C, Horn S, Muna M, et al. An adenovirus mutant that replicates selectively in p53-deficient human tumor cells. Science. 1996;274:373–6.
Yamanaka M, Tada Y, Kawamura K, Li Q, Okamoto S, Chai K, et al. E1B-55kD-defective adenoviruses activate p53 in mesothelioma and enhance cytotoxicity of anti-cancer agents. J Thorac Oncol. 2012;7:1850–7.
Yu L, Takenobu H, Shimozato O, Kawamura K, Nimura Y, Seki N, et al. Increased infectivity of adenovirus type 5 bearing type 11 or type 35 fibers to human esophageal and oral carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2005;14:831–5.
Yu L, Shimozato O, Li Q, Kawamura K, Ma G, Namba M, et al. Adenovirus type 5 substituted with type 11 or type 35 fiber structure increases its infectivity to human cells and enables dual gene transfer in CD46-dependent and -independent manners. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:2311–6.
Su Z, Lebedeva IV, Gopalkrishnan RV, Goldstein NI, Stein CA, Reed JC, et al. A combinatorial approach for selectively inducing programmed cell death in human pancreatic cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:10332–7.
Chada S, Mhashilkar AM, Liu Y, Nishikawa T, Bocangel D, Zheng M, et al. mda-7 gene transfer sensitizes breast carcinoma cells to chemotherapy, biologic therapies and radiotherapy: correlation with expression of bcl-2 family members. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006;13:490–502.
Zhang Z, Kawamura K, Jiang Y, Shingyoji M, Ma G, Li Q, et al. Heat-shock protein 90 inhibitors synergistically enhance melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7-mediated cell killing of human pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013;20:663–70.
Zhao L, Gu J, Dong A, Zhang Y, Zhong L, He L, et al. Potent antitumor activity of oncolytic adenovirus expressing mda-7/IL-24 for colorectal cancer. Hum Gene Ther. 2005;16:845–58.
Luo J, Xia Q, Zhang R, Lv C, Zhang W, Wang Y, et al. Treatment of cancer with a novel dual-targeted conditionally replicative adenovirus armed with mda-7/IL-24 gene. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2450–7.
Zhang KJ, Zhang J, Wu YM, Qian J, Liu XJ, Yan LC, et al. Complete eradication of hepatomas using an oncolytic adenovirus containing AFP promoter controlling E1A and an E1B deletion to drive IL-24 expression. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012;19:619–29.
Lebedeva IV, Washington I, Sarkar D, Clark JA, Fine RL, Dent P, et al. Strategy for reversing resistance to a single anticancer agent in human prostate and pancreatic carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:3484–9.
Cherubini G, Petouchoff T, Grossi M, Piersanti S, Cundari E, Saggio I. E1B55K-deleted adenovirus (ONYX-015) overrides G1/S and G2/M checkpoints and causes mitotic catastrophe and endoreduplication in p53-proficient normal cells. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:2244–52.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, the Grant-in-Aid for Research on seeds for Publicly Essential Drugs and Medical Devices from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan, and a Grant-in-Aid from the Nichias Corporation.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests in this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guangyu Ma and Boya Zhong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, G., Zhong, B., Okamoto, S. et al. A combinatory use of adenoviruses expressing melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 and replication-competent adenoviruses produces synergistic effects on pancreatic carcinoma cells. Tumor Biol. 36, 8137–8145 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3555-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3555-3