Abstract
Background
In genetic analyses, the term ‘batch effect’ refers to systematic differences caused by batch heterogeneity. Controlling this unintended effect is the most important step in quality control (QC) processes that precede analyses. Currently, batch effects are not appropriately controlled by statistics, and newer approaches are required.
Methods
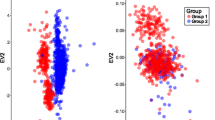
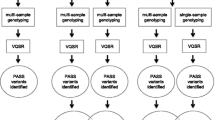
In this report, we propose a new method to detect the heterogeneity of probe intensities among different batches and a procedure for calling genotypes and QC in the presence of a batch effect. First, we conducted a multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) to test the differences in probe intensities among batches. If heterogeneity is detected, subjects should be clustered using a K-medoid algorithm using the averages of the probe intensity measurements for each batch and the genotypes of subjects in different clusters should be called separately.
Results
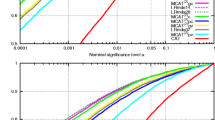
The proposed method was used to assess genotyping data of 3619 subjects consisting of 1074 patients with Alzheimer’s disease, 296 with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and 1153 controls. The proposed method improves the accuracy of called genotypes without the need to filter a lot of subjects and SNPs, and therefore is a reasonable approach for controlling batch effects.
Conclusions
We proposed a new strategy that detects batch effects with probe intensity measurement and calls genotypes in the presence of batch effects. The application of the proposed method to real data shows that it produces a balanced approach. Furthermore, the proposed method can be extended to various scenarios with a simple modification.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affymetrix I (2013) Axiom® genotyping solution data analysis guide. URL http://media.affymetrix.com/support/downloads/manuals/axiom_genotyping_solution_analysis_guide.pdf. Accessed 29 Mar 2016
Affymetrix I (2015) SNPolisher User Guide (Version 1.5.2), pp 1–104. https://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/manuals/SNPolisher_User_Guide.pdf. Accessed 24 April 2017
Anderson CA, Pettersson FH, Clarke GM, Cardon LR, Morris AP, Zondervan KT (2010) Data quality control in genetic case-control association studies. Nat Protoc 5(9):1564–1573
Browning BL, Yu Z (2009) Simultaneous genotype calling and haplotype phasing improves genotype accuracy and reduces false-positive associations for genome-wide association studies. Am J Hum Genet 85(6):847–861
Cariaso M, Lennon G (2012) SNPedia: a wiki supporting personal genome annotation, interpretation and analysis. Nucl Acids Res 40(D1):D1308–D1312
Chai HS, Therneau TM, Bailey KR, Kocher J-PA (2010) Spatial normalization improves the quality of genotype calling for Affymetrix SNP 6.0 arrays. BMC Bioinf 11(1):356
Dodge Y (2012) Statistical data analysis based on the L1-norm and related methods: Birkhäuser, Basel
Hao K, Li C, Rosenow C, Wong WH (2004) Estimation of genotype error rate using samples with pedigree information—an application on the GeneChip Mapping 10 K array. Genomics 84(4):623–630
Hong H, Su Z, Ge W, Shi L, Perkins R, Fang H, Xu J, Chen JJ, Han T, Kaput J (2008) Assessing batch effects of genotype calling algorithm BRLMM for the Affymetrix GeneChip Human Mapping 500 K array set using 270 HapMap samples. BMC Bioinf 9(9):S17
James G (1954) Tests of linear hypotheses in univariate and multivariate analysis when the ratios of the population variances are unknown. Biometrika 41(1/2):19–43
Kruskal WH, Wallis WA (1952) Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 47(260):583–621
Leek JT, Scharpf RB, Bravo HC, Simcha D, Langmead B, Johnson WE, Geman D, Baggerly K, Irizarry RA (2010) Tackling the widespread and critical impact of batch effects in high-throughput data. Nat Rev Genet 11(10):733–739
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984a) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group* under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34(7):939
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984b) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34(7):939–944
Miclaus K, Wolfinger R, Vega S, Chierici M, Furlanello C, Lambert C, Hong H, Zhang L, Yin S, Goodsaid F (2010) Batch effects in the BRLMM genotype calling algorithm influence GWAS results for the Affymetrix 500 K array. Pharmacogenom J 10(4):336–346
Moskvina V, Craddock N, Holmans P, Owen MJ, O’Donovan MC (2006) Effects of differential genotyping error rate on the type I error probability of case-control studies. Hum Hered 61(1):55–64
Nishida N, Koike A, Tajima A, Ogasawara Y, Ishibashi Y, Uehara Y, Inoue I, Tokunaga K (2008) Evaluating the performance of Affymetrix SNP Array 6.0 platform with 400 Japanese individuals. BMC Genom 9(1):431
Pillai K (1985) Multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA). Encyclop Stat Sci
Ritchie ME, Liu R, Carvalho BS, Irizarry RA (2011) Comparing genotyping algorithms for Illumina's Infinium whole-genome SNP BeadChips. BMC Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-68
Scherer A (2009) Batch effects and noise in microarray experiments: sources and solutions, vol 868. Wiley
Spencer CC, Su Z, Donnelly P, Marchini J (2009) Designing genome-wide association studies: sample size, power, imputation, and the choice of genotyping chip. PLoS Genet 5(5):e1000477
Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, Nordberg A, Bäckman L, Albert M, Almkvist O (2004) Mild cognitive impairment–beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Intern Med 256(3):240–246
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Brain Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2014M3C7A1046041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Sungho Won, Sujin Seo, Kyungtaek Park, Jang Jae Lee, Kyu Yeong Choi and Kun Ho Lee declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study had been approved by IRB of Chosun university hospital. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participant included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, S., Park, K., Lee, J.J. et al. SNP genotype calling and quality control for multi-batch-based studies. Genes Genom 41, 927–939 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00827-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00827-5