Abstract
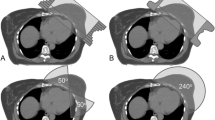
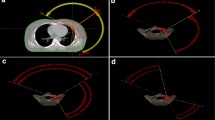
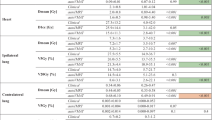
Volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) is modern rotational intensity modulated therapy used for treatment of several sites. The study aimed to analyze partial tangential arc VMAT treatment planning and delivery, including analyzing the cardiac and contralateral breast doses resulting from this technique. A total of 153 consecutively treated breast cancer (conservation as well as mastectomy) patients were taken for this dosimetric study. All patients were planned using partial arc VMAT in the Monaco treatment planning system using two partial arc beams. All patients were divided into seven different categories: (1) all the patients in the study, (2) left sided whole breast and chest wall patients, (3) left Chest wall patients, (4) left whole breast patients, (5) right sided whole breast and chest wall patients, (6) right chest wall patients, and (7) right whole breast patients. We evaluated each treatment plan for PTV coverage and doses to OARs. SPSS version 16.0 software was used for statistical analysis. There were 91 left sided and 62 right sided breast cancer patients in the overall analysis. The percentage of PTV volume receiving 95% of the prescription dose (PTV V95%, mean ± SD) varied in the range of 91.2 ± 5.2–94.8 ± 2.1% with mean dose of 92.4 ± 5.2% for all cases. The (mean ± SD) cardiac dose for all the patients was 289 ± 23 cGy. The (mean ± SD) cardiac doses were higher for left sided patients (424 ± 33.8 cGy) as compared to right sided patients (123.9 ± 80 cGy) (p < 0.001). Cardiac mean doses were higher with arc angles >30° versus 30° (324.5 ± 247.1 vs. 234.4 ± 188.4 cGy) (p = 0.001). Similarly contralateral breast mean dose was higher with arc angles >30° versus 30° (126 ± 115 vs. 88.6 ± 76.1 cGy) (p = 0.001). However cardiac V20, V30 and V40 Gy did not exhibit any statistical difference between the two groups (p = 0.26, 0.057 and 0.054 respectively). This is the first large study of its kind that assesses the dosimetric outcome of tangential partial arc VMAT treatments in a large group of mastectomy and breast conservation patients. Our study demonstrates the efficacy of this technique in dose coverage of PTV as well as in minimizing dose to OARs. Further, based on our results, we conclude that the arc length for the bi-tangential arcs should be 30° since it helps to achieve the most optimal balance between target coverage and acceptable OAR doses.


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 June 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
Cross P, Joseph DJ, Cant J et al (1992) Tangential breast irradiation: simple improvements. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23:433–442
Das IJ, Cheng CW, Fein DA et al (1997) Patterns of dose variability in radiation prescription of breast cancer. Radiother Oncol 44:83–89
Munshi A, Pai RH, Phurailatpam R, Budrukkar A, Jalali R, Sarin R, Deshpande DD, Shrivastava SK, Dinshaw KA (2009) Do all patients of breast carcinoma need 3-dimensional CT-based planning? A dosimetric study comparing different breast sizes. Med Dosim 34:140–144
Kantorowitz DA (2000) The impact of dose-specification policies upon nominal radiation dose received by breast tissue in the conservation treatment of breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:841–848
Donovan E, Bleakley N, Denholm E et al (2007) Randomised trial of standard 2D radiotherapy [RT] versus intensity modulated radiotherapy [IMRT] in patients prescribed breast radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 82:254–264
Jin GH, Chen LX, Deng XW, Liu XW, Huang Y, Huang XB (2013) A comparative dosimetric study for treating left-sided breast cancer for small breast size using five different radiotherapy techniques: conventional tangential field, filed-in-filed, tangential-IMRT, multi-beam IMRT and VMAT. Radiat Oncol 8:89
Coles CE, Moody AM, Wilson CB, Burnet NG (2005) Reduction of radiotherapy-induced late complications in early breast cancer: the role of intensity-modulated radiation therapy and partial breast irradiation. Part II—radiotherapy strategies to reduce radiation-induced late effects. Clin Oncol 17:98–110
Darby SC, Ewertz M, McGale P, Bennet AM, Blom-Goldman U, Brønnum D, Correa C, Cutter D, Gagliardi G, Gigante B, Jensen MB, Nisbet A, Peto R, Rahimi K, Taylor C, Hall P (2013) Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med 368:987–998
Teoh M, Clark CH, Wood K, Whitaker S, Nisbet A (2011) Volumetric modulated arc therapy: a review of current literature and clinical use in practice. Br J Radiol 84:967–996
Morganti AG, Cilla S, de Gaetano A, Panunzi S, Digesù C, Macchia G, Massaccesi M, Deodato F, Ferrandina G, Cellini N, Scambia G, Piermattei A, Valentini V (2011) Forward planned intensity modulated radiotherapy [IMRT] for whole breast postoperative radiotherapy. Is it useful? When? J Appl Clin Med Phys 12:3451
Wu S, Lai Y, He Z, Zhou Y, Chen S, Dai M, Zhou J, Lin Q, Chi F (2015) Dosimetric comparison of the simultaneous integrated boost in whole-breast irradiation after breast-conserving surgery: IMRT, IMRT plus an electron boost and VMAT. PLoS ONE 17:10
Paddick I (2000) A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans: technical note. J Neurosurg 93(Supplement 3):219–222
Early Breast Cancer Trialists Collaborative Group [EBCTCG] (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15 year survival: an overview of randomised trials. Lancet 365:1687–1717
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (1995) Effects of radiotherapy and surgery in early breast cancer: an overview of randomized trials. N Engl J Med 333:1444–1455
Overgaard M, Jensen MB, Overgaard J, Hansen PS, Rose C, Andersson M et al (1999) Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk postmenopausal breast-cancer patients given adjuvant tamoxifen: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group DBCG 82c randomised trial. Lancet 353:1641–1648
Ragaz J, Jackson SM, Le N, Plenderleith IH, Spinelli JJ et al (1997) Adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy in node-positive premenopausal women with breast cancer. N Engl J Med 337:956–962
Wollschläger D, Karle H, Stockinger M, Bartkowiak D, Bührdel S, Merzenich H, Wiegel T, Blettner M, Schmidberger H (2016) Radiation dose distribution in functional heart regions from tangential breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 119:65–70
Zurl B, Stranzl H, Winkler P, Kapp KS (2013) Quantification of contralateral breast dose and risk estimate of radiation-induced contralateral breast cancer among young women using tangential fields and different modes of breathing. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:500–505
Virén T, Heikkilä J, Myllyoja K, Koskela K, Lahtinen T, Seppälä J (2015) Tangential volumetric modulated arc therapy technique for left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol 10:79
Hongfu Zhao, Mingyuan He, Guanghui Cheng, Dongmei Han, Ning Wu, Dan Shi, Zhipeng Zhao, Jin J (2015) A comparative dosimetric study of left sided breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery treated with VMAT and IMRT. Radiat Oncol 10:231
Yu J, Hu T, Chen Y (2016) Small-arc volumetric-modulated arc therapy: a new approach that is superior to fixed-field IMRT in optimizing dosimetric and treatment-relevant parameters for patients undergoing whole-breast irradiation following breast-conserving surgery. Medicine 95(34):e4609
Liu H, Chen X, He Z, Li J (2016) Evaluation of 3D-CRT, IMRT and VMAT radiotherapy plans for left breast cancer based on clinical dosimetric study. Comput Med Imaging Graph 54:1–5
Giri UK, Sarkar B, Jassal K, Munshi A, Ganesh T, Mohanti B, Pradhan A (2017) Left-sided breast radiotherapy after conservative surgery: comparison of techniques between volumetric modulated arc therapy, forward-planning intensity-modulated radiotherapy and conventional technique. J Radiother Pract 16(1):101–108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: the name of the third author was corrected to Satheeshkumar Anbazhagan.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-017-0562-2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munshi, A., Sarkar, B., Anbazhagan, S. et al. Short tangential arcs in VMAT based breast and chest wall radiotherapy lead to conformity of the breast dose with lesser cardiac and lung doses: a prospective study of breast conservation and mastectomy patients. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 40, 729–736 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-017-0558-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-017-0558-y