Abstract
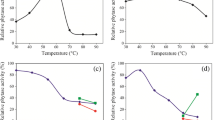
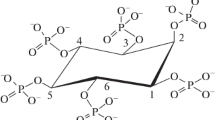
Microbial degradation of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) is crucial to deal with nutritional problems in monogastric animals as well as to prevent environmental phosphate pollution. The present study deals with the degradation of IP6 by microorganisms such as Sporosarcina spp. pasteurii, globiospora, psychrophila, Streptococcus thermophilus and Saccharomyces boulardii. These microbes were screened for phytase production under laboratory conditions. The specificity of the enzyme was tested for various phosphorylated substrates such as sodium phytate (IP6), sodium hexametaphosphate, phenyl phosphate, α-d-glucose-6 phosphate, inosine 5′ monophosphate and pyridoxal 5′ phosphate. These enzymes were highly specific to IP6. The influence of modulators such as phytochemicals and metal ions on the enzymatic activity was assessed. These modulators in different concentrations had varying effect on microbial phytases. Calcium (in optimal concentration of 0.5 M) played an important role in enzyme activation. The enzymes were then characterized based on their molecular weight 41~43 kDa. The phytase-producing microbes were assessed for IP6 degradation in a simulated intestinal setup. Among the selected microbes, Sporosarcina globiospora hydrolyzed IP6 effectively, as confirmed by colorimetric time-based analysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre M, Venema K (2017) Challenges in simulating the human gut for understanding the role of the microbiota in obesity. Benef Microbes 8(1):31–53. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2016.0113
Askelson TE, Campasino A, Lee JT, Duong T (2014) Evaluation of phytate-degrading Lactobacillus culture administration to broiler chickens. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(3):943–950. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03155-13
Bae HD, Yanke LJ, Cheng KJ, Selinger LB (1999) A novel staining method for detecting phytase activity. J Microbiol Methods 39:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00096-2
Bohn L, Meyer AS, Rasmussen SK (2008) Phytate: impact on environment and human nutrition. A challenge for molecular breeding. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9(3):165–191. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0710640
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Bryden WL, Li X (2010) Amino acid digestibility and poultry feed formulation: expression, limitations and application. R Bras Zootec 39:279–287. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-35982010001300031
Card RM, Cawthraw SA, Nunez-Garcia J, Ellis RJ, Gemma K, Pallen MJ, Woodward MJ, Anjum MF (2017) An in vitro chicken gut model demonstrates transfer of a multidrug resistance plasmid from Salmonella to commensal Escherichia coli. mBio 8:e00777-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00777-1
Chen CC, Cheng KJ, Ko TP, Guo RT (2015) Current progresses in phytase research: three-dimensional structure and protein engineering. ChemBioEng Rev 2(2):76–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201400026
Cowieson AJ, Ruckebusch JP, Knap I, Guggenbuhl P, Fru-Nji F (2016) Phytate-free nutrition: a new paradigm in monogastric animal production. Anim Feed Sci Tech 222:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.10.016
Demirkan E, Baygin E, Usta A (2014) Screening of phytate hydrolysis Bacillus sp. isolated from soil and optimization of the certain nutritional and physical parameters on the production of phytase. Turk J Biochem 39(2):206–214. https://doi.org/10.5505/tjb.2014.26817
Gontia-Mishra I, Tiwari S (2013) Molecular characterization and comparative phylogenetic analysis of phytases from fungi with their prospective applications. Food Technol Biotechnol 51(3):313–326
Greiner R, Farouk AE (2007) Purification and characterization of a bacterial phytase whose properties make it exceptionally useful as a feed supplement. Protein J 26(7):467–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-007-9086-z
Hellstrom A, Qvirist L, Svanberg U, Vilg JV, Andlid T (2015) Secretion of non-cell-bound phytase by the yeast Pichia kudriavzevii TY13. J Appl Microbiol 118(5):1126–1136. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12767
Heravi RM, Sankian M, Kermanshahi H, Nassiri MR, Moussavi AH, Nasiraii LR, Varasteh AR (2016) Construction of a probiotic lactic acid bacterium that expresses acid-resistant phytase enzyme. J Agri Sci Tech 18(4):925–936
Howson SJ, Davis RP (1983) Production of phytate-hydrolysing enzyme by some fungi. Enzyme Microb Technol 5(5):377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(83)90012-1
Hur SJ, Lim BO, Decker EA, McClements DJ (2011) In vitro human digestion models for food applications. Food Chem 125:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.08.036
Khambualai O, Yamauchi K, Tangtaweewipat S, Cheva-Isarakul B (2009) Growth performance and intestinal histology in broiler chickens fed with dietary chitosan. Br Poult Sci 50(5):592–597. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071660903247182
Kim JH, Han GP, Shin JE, Kil DY (2017) Effect of dietary calcium concentrations in phytase-containing diets on growth performance, bone mineralization, litter quality, and footpad dermatitis score in broiler chickens. Anim Feed Sci Technol 229:13–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.04.008
Lee NK, Lee EK, Paik HD (2013) Potential probiotic properties of phytase-producing Lactobacillus salivarius FC113. Ann Microbiol 63:555–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0503-y
Lei XG, Weaver JD, Mullaney E, Ullah AH, Ajain MJ (2013) Phytase, a new life for an “Old” enzyme. Annu Rev Anim Biosci 1:283–309. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-animal-031412-103717
Li Q, Shi Y (2016) Feeding of phytase over-expressed Lactobacillus decreases fecal phosphate activity in chicken. Res J Biotechnol 11(3):9–16
Markiewicz LH, Honke J, Haros M, Świątecka D, Wróblewska B (2013) Diet shapes the ability of human intestinal microbiota to degrade phytate–in vitro studies. J Appl Microbiol 115(1):247–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.12204
Nielsen AVF, Meyer AS (2016) Phytate-mediated mineral solubilization from cereals under in vitro gastric conditions. J Sci Food Agric 96:3755–3761. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.7564
Nielsen AVF, Nyffenegger C, Meyer AS (2015) Performance of microbial phytases for gastric inositol phosphate degradation. J Agric Food Chem 63(3):943–950. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5050469
Priyodip P, Prakash PY, Balaji S (2017) Phytases of probiotic bacteria: characteristics and beneficial aspects. Indian J Microbiol 57(2):148–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-017-0647-3
Rocky-Salimi K, Hashemi M, Safari M, Mousivand M (2016) A novel phytase characterized by thermostability and high pH tolerance from rice phyllosphere isolated Bacillus subtilis B.S.46. J Adv Res 7:381–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2016.02.003
Sajidan R, Sari EN, Ratriyanto A, Weldekiros H, Greiner R (2015) Phytase-producing bacteria from extreme regions in Indonesia. Braz Arch Biol Technol 58(5):711–717. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132015050173
Schenk G, Korsinczky ML, Hume DA, Hamilton S, DeJersey J (2000) Purple acid phosphatases from bacteria: similarities to mammalian and plant enzymes. Gene 255(2):419–424
Shivakumar SB, Bharti D, Subbarao RB, Jang SJ, Park JS, Ullah I, Park JK, Byun JH, Park BW, Rho GJ (2016) DMSO and serum free cryopreservation of Wharton’s jelly tissue isolated from human umbilical cord. J Cell Biochem 117(10):2397–2412. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25563
Singh NK, Joshi DK, Gupta R (2013) Isolation of phytase producing bacteria and optimization of phytase production parameters. Jundishapur J Microbiol 6(5):e6419. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.6419
Tamayo-Ramos JA, Sanz-Penella JM, Yebra MJ, Monedero V, Haros M (2012) Novel phytases from Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum ATCC 27919 and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. infantis ATCC 15697. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(14):5013–5015. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00782-12
Venema K, van den Abbeele P (2013) Experimental models of the gut microbiome. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 27:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2013.03.002
Yao MZ, Zhang YH, Lu WL, Hu MQ, Wang W, Liang AH (2011) Phytases: crystal structures, protein engineering and potential biotechnological applications. J Appl Microbiol 112(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05181.x dois
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author SB acknowledges the Grant received for using ‘Foldscope as a research tool’ (Category B) under the initiative of DBT-Prakash Labs. The funding was sanctioned by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India (Sanction Order No. BT/IN/Indo-US/Foldscope/39/2015). We would also like to thank Dr. Peralam Yegneswaran Prakash, Associate Professor, Department of Microbiology, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, for his timely inputs and help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Priyodip, P., Balaji, S. Microbial degradation of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6): specificity, kinetics, and simulation. 3 Biotech 8, 268 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1302-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1302-3