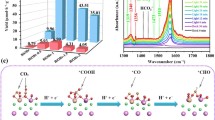
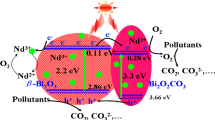
Abstract
Naphthalene sulfonic acid, which is used in the synthesis of azo dye pigments, rubber processing chemicals and pharmaceuticals, is a carcinogenic substance that pollutes water bodies. In this work, we report on the visible light-driven symmetric cleavage of naphthalene sulfonic acid group, present in methyl orange dye and its conversion into the intermediate compounds. These compounds further degrade to inorganic ions such as carbon-di-oxide, nitrates, sulfates, water, and chlorine. Complete degradation of the dye, under visible light irradiation, is attained using β-In2S3 quantum dots as photocatalyst. During homogenous precipitation process, the β-In2S3 quantum dots (~ 9 nm) self-assemble to form microflowers (~ 50 nm) with high surface-to-volume ratio. These quantum dots exhibit size-dependent, active F2g, Eg and Ag1 Raman modes with peaks at ~ 150 cm−1 (In–In stretching mode), 219 cm−1 (In–S bending mode) and 300 cm−1, corresponding to the vibrational modes of cubic phase β-In2S3. The cubic phase β-In2S3 quantum dots are photoactive under visible light exposure and releases highly oxidizing OH· radicals. They have strong band-to-band emission in ultraviolet region (~ 380 nm) and exhibit broad band defect emission with maxima at blue (~ 484 nm), green (~ 580 nm) and red (~ 600 nm) region of electromagnetic spectrum. The emission intensity from these defect energy bands, which are due to sulfur vacancy, indium interstitials and oxygen incorporation, are tuned by varying the In-to-S ratio in the sample. These defects enhance their visible light absorption coefficient and assist in improving the photocatalytic efficiency of the cubic phase β-In2S3 quantum dots. Thus, defect-assisted complete (100%) photodegradation of the azo dye is achieved using cubic β-In2S3 quantum dots with low In-to-S ratio (1:1), low mass of 20 mg and minimum irradiation time (30 min). These photocatalysts can be reused 4 times under 30-min visible light irradiation. Cubic β-In2S3 quantum dots-microflowers is a highly efficient, ecofriendly photocatalyst, which even in very low concentration can remove toxicity from the dye-contaminated water, by exposure to direct sunlight for 30 min.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bera R, Kundu S, Patra A(2015) 2D hybrid nanostructure of reduced graphene oxide–CdS nanosheets for enhance photocatalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(24):13251–13259. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03800
Cerqueira A, Russo C, Marques MRC (2008) Electroflocculation for textile wastewater treatment. Braz J Chem Eng 26:659–668. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-66322009000400004
Chai B, Peng T, Zeng P, Mao J (2011) Synthesis of floriated In2S3 decorated with TiO2 nanoparticles for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible light. J Mater Chem 21:14587–14593. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM11566A
Chen LY, Zhang ZD, Wang WZ(2008). Self-assembled porous 3D flower like β-In2S3 stuctures: synthesis, characterization and optical properties. J Phys Chem C 112(11):4117–4123. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp710074h
Cifci D (2016) Decolarisation of methylene blue and methyl orange with Ag doped TiO2 under UV–A and UV–Visible conditions: process optimization by response surface method and toxicity evaluation. Glob Nest J 16:371–380. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.001899
Dutta S, Chatterjee S, Mukherjee I, Saha R, Singh BP (2017) Fabrication of ZnS hollow spheres and RGO-ZnS nanocomposite using cysteamine as novel sulfur source: photocatalytic performance on industrial dyes and effluents. Ind Eng Chem Res 56(16):4768–4778. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b00107
Fuji T, Hayashi R, Kawasaki SJ, Suzuki A, Oshima Y (2011) Water density effects on methanol oxidation in supercritical water at high pressure upto 100 MPa. J Supercrit Fluids 58:142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2011.04.004
Gurpreet K, Bikramjeet S, Paviter S, Manpreet K, Karmjeet KB, Kulwinder S, Anup T, Rajni B, Manjeet K, Akshay K (2016) Preferentially grown nanostructured iron disulfide (FeS2) for removal of industrial pollutants. RSC Adv. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA18838A
Gurpreet K, Pooja D, Manjeet K, Anup T, Rajni B, Akshay K (2017a) Electrochemical aspects of photocatalysis: Au@FeS2 nanocomposite for removal of industrial pollutants. PhysChemChemPhys. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CP06289C
Gurpreet K, Singh B, Singh P, Singh K, Thakur A, Manjeet K, Rajini B, Akshay K (2017b) Iron disulfide (FeS2): a promising material for removal of industrial pollutants. Chem Sel 2:2166–2173. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201700087
He Y, Li D, Xiao G, Chen W, Chen Y, Sun M, Huang H, Fu X (2009) A new application of nanocrystal In2S3 in efficient degradation of organic pollutants under visible light irradiation. J Phys Chem C 113(13):5254–5262. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp809028y
Huo F, Wang Y, You C, Deng W, Yang F, Pu Y (2017) Phase and size controllable synthesis with efficient photocatalytic activity of ZnS nanoparticles. J Mater Sci 52:5626–5633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0797-z
Hwang DW, Kim HG, Lee JS, Kim J, Li W, Oh SH (2005) Photocatalytic hydrogen production from water over M-doped La2Ti2O7 (M = Cr,Fe) under visible light irradiation (λ> 420 nm). J Phys Chem B 109(6):2093–2102. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp034229n
Izadneshan H, Gremenoka VK (2014) Influence of annealing on the optical parameters of In2S30 thin films produced by thermal evaporation. J Appl Spectrosc 81:765–770
Jayakrishnan R, John TT, Kartha CS, Vijayakumar KP, Abe T, Kashiwaba Y (2005) Defect analysis of sprayed β-In2S3 thin films using photoluminescence studies. Semicond Sci Technol 20:1162. https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/20/12/003
Kayanuma Y (1988) Quantum-size effects of interacting electrons and holes in semiconductor microcrystals with spherical shape. Phys Rev B 38:9797–9805. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.38.9797
Kim J, Cai Z, Benjamin MM (2008) Effects of adsorbents on membrane fouling by natural organic matter. J Membr Sci 310:356–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.11.007
Lai CH, Lu MY, Chen LJ (2012) Metal sulfide nanostructures: synthesis, properties and applications in energy conversion and storage. J Mater Chem 22:19–30. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM13879K
Li N, Descome C, Besson M (2007) Catalytic wet air oxidation of chlorophenols over supported ruthenium catalysts. J Hazard Mater 146:602–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(18)30016-1
Liu L, Xiang W, Zhong J, Yang X, Liang X, Liu H, Cai W (2010) Flowerlike cubic β-In2S3 microspheres: synthesis and characterisation. J Alloys Compd 493:309–313
Liu H, Wu Y, Zhang J (2011) A new approach toward carbon-modified vanadium-doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3(5):1757–1764. https://doi.org/10.1021/am200248q
Liu Q, Liu Q, Wu z, Wu Y, Gao T, Yao J (2016) Efficient removal of methyl orange and alizarin reds from PH-unregulated aqueous solution by the catechol–anoine resin composite using hydrocellulose as precursors. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(2):1871–1880. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02593
Liu B, Hu X, Li X, Li Y, Chen C, Lam K (2017) Preparation of ZnS@In2S3 core @ shell composite for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of gaseous o-dicholorobenzene under visible light. Sci Rep 7:16396. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16732-4
Ma Y, Li X, Yang Z, Xu S, Zhang W, Su Y, Hu N, Lu W, Feng J, Zhang Y(2016) Morphology control and photocatalysts enhancement by in situ hybridization of cuprous oxide with nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots. Langmuir 32(37):9418–9427. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b02011
Matrix (2014) Visible-light driven photocatalytic activity of β-In2S3 quantum dots embedded in nafion. J Phys D Appl Phys 47:105103. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/10/105103
Meng A, Xing J, Li Z, Li Q (2015) Cr-doped ZnO nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, adsorption property and recyclability. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(49):27449–27457. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b09366
Mia AS, Alam NE, Ahmad F, Alam Z, Rahman (2017) Treatment of tannery wastewater by electrocoagulation technology. M JSIR 6(4):129–134
Ou XH, Wu HC, Lo AL (2006) Photo degradation of 4-chlorophenol by UV/photocatalyst: the effect of the interparticle electron transfer process. React Kinet Catal Lett 88:89–95
Prabhakaran D, Kannadasan T, Ahmed basha C (2009) Mediated electrochemical oxidation process for destruction of TOC in a batch recirculation reactor. Int J ChemTech Res 1:962–969. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/790173
Qiu W, Xu M, Yang X, Chen F, Nan Y, Zhang J, Iwaic H, Chen H (2011) Biomolecule-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of In2S3 porous films and enhanced photocatalytic properties. J Mater Chem 21:13327–13333. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JM11616A
Rengaraj S, Venkataraj S, Tai C, Kim Y, Repo E, Sillanpa M (2011) Self assembled mesoporous hierarchial-like In2S3 hollow microspheres composed of nanofibers and nanosheets and their photocatalytic activity. Langmuir 27(9):5534–5541. https://doi.org/10.1021/la104780d
Revathi N, Prathap P, Subbaiah PV, Reddy KTR (2008) Substrate temperature dependent physical properties of In2S3 films. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:155404. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/41/15/155404
Sabarinathan M, Harish S, Archana J, Navaneethan M, Ikeda H, Hayakawa Y (2017) Highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic activity of MoS2–TiO2 mixtures hybrid photocatalysts and functional properties. RSC Adv 7:24754–24763. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA03633G
Sabur MA, Khan AA, Safiullah S (2012) Treatment of textile wastewater by coagulation precipitation method. J Sci Res 4:623–633. https://doi.org/10.3329/jsr.v4i3.10777
Sall T, Nafidi A, Soucase BM, Mollar M, Hartitti B, Fahoume (2014) Synthesis of In2S3 thin films by spray pyrolysis from precursors with different [s]/[In]ratio. J Semicond 35:063002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/35/6/063002
Scholz WG, Rogue P, Bodalo A, Leitz U (2005) Desalination of mixed tannery effluent with membrane bioreactor and reverse osmosis treatment. Environ Sci Technol 39:8505–8511. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050330p
Sharma RK, Chouryal YN, Chaudhari S, Saravanakumar J, Dey SR, Ghosh P (2017a) Adsorption-driven catalytic and photocatalytic activity of phase tuned In2S3 nanocrystals synthesized via ionic liquids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(13):11651–11661. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b01092
Sharma RK, Chouryal YN, Chaudhari S, Saravanakumar J, Dev SR, Ghosh PC (2017b) Adsorption-driven photocatalytic activity of phase tuned In2S3 nanocrystal synthesized via ionic liquid. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(13):11651–11661. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b01092
Sun M, Li D, Li W, Chen Y, Chen Z, He Y, Fu X (2008) New photocatalyst, Sb2S3 for degradation of methyl orange under visible-light irradiation. J Phys Chem C 112(46):18076–18081. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp806496d
Tachikawa T, Yamashita S, Majima T (2011) Evidence for crystal-face-dependent TiO2 photocatalysis from single-molecule imaging and kinetic analysis. J Am Chem Soc 133(18):7197–7204. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja201415j
Wang L, Wu XL, Xu WH, Huang XJ, Liu JH, Xu AW (2012) Stable organic–inorganic hybrid of polyaniline/α-zirconium phosphate for efficient removal of organic pollutants in water environments. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(5):2686–2692. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300335e
Wang X, Liu J, Leong S, Lin X, Wei J, Kong B, Xu Y, Low X, Yao J, Wang H (2016) Rapid construction of ZnO@ZIF-8 heterostructures with size-selective photocatalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(14):9080–9087. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b00028
Xiang Y, He D, Jaber R, Cameron PJ, Elder KJ (2017) Sulfur-doped cubic mesostructured titania films for use as a solar photocatalyst. J Phys Chem C 121(18):9929–9937. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b01615
Yang Y, Wang G, Deng Q, Zhao H (2017) Microwave-assisted fabrication of nanoparticulate TiO2 microspheres for synergistic photocatalytic removal of Cr(VI) and methyl orange. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(2):1871–1880. https://doi.org/10.1021/am405607h
Yu ZJ, Rajesh Kumar M, Chu Y, Hao HX, Wu QY, Xie HD (2018) Photocatalytic decomposition of RhB by newly designed and highly effective CF@ZnO/CdS hierarchical heterostructures. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(1):155–164. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02005
Zhan H, Chen K, Tian H (1998) Photocatalytic degradation of acid azo dyes in aqueous TiO2 suspension II. The effect of pH values. Dyes Pigm 37:241–247
Zhang Z, Wang W, Wang L, Sun S (2012) Enhancement of visible-light photocatalysis by coupling with narrow-band-gap semiconductor: a case study on Bi2S3/Bi2WO6. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(2):593–597. https://doi.org/10.1021/am2017199
Zheng H, Liu K, Cao H, Zhang XL (2009) Lysine-assisted synthesis of ZrO2 Nanocrystals and their application in photocatalysis. J Phys Chem C 113(42):18259–18263. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9057324
Zhu Y, Li M, Liu YL, Ren TZ, Yuan ZY (2014) Carbon-doped ZnO hybridized homogeneously with graphitic carbon nitride nanocomposites for photocatalysis. J Phys Chem C 118(20):10963–10971. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp502677h
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Department of Science and Technology (DST-SERB) project (ECR/2016/000404). One of authors is grateful to Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Research (Visiting fellowship programme) for sample analysis through Prof. Chandrabhas Narayan. One of the authors (Anitha D.) acknowledge the research fellowship from DST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anitha, D., Warrier, A.R. Defect-assisted symmetric cleavage of naphthalene sulphonic acid group in azo dyes using β-In2S3 quantum dots as visible light photocatalyst. Appl Nanosci 9, 77–91 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0912-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0912-8