Abstract
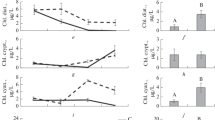
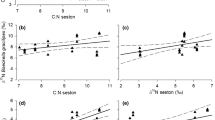
Nutrient imbalance—a mismatch in nutrient ratios between the available food supply and the demands of consumers—has the potential to be transported up food chains, exposing zooplankton to nutrient limitations. In this study, the response of Calanus sinicus (copepod), Moina mongolica (cladocera), and Brachionus plicatilis (rotifer) to nutrient-limited (no-limited, P-limited, and N-limited) food were evaluated from the perspective of growth, reproduction, and stoichiometric homoeostasis. The results indicated that the growth of three species was suppressed under nutrient-limited (especially P-limited) conditions. However, the effect of nutrient limitations on their reproduction was species-specific. For C. sinicus, the dietary UFA (unsaturated fatty acid) as a major phospholipid component affected their egg production and total FA supporting energy promoted the hatchability of eggs. Furthermore, excess carbon in the diet promoted egg production but reduced hatching success. For M. mongolica, nutritional (P and UFA) and energy (total FA) support affected their fecundity. B. plicatilis fecundity exhibited the same pattern of growth (no-limited>N-limited>P-limited). In terms of stoichiometric homeostasis, B. plicatilis’s elemental compositions were less likely to be affected by nutrient limitations than M. mongolica. We suggest that the effects of nutrient imbalances could potentially become an evolutionary force affecting ecosystem structure and stability in eutrophic waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai M N. 2001. Pelagic coelenterates and eutrophication: a review. Hydrobiologia, 451(1-3): 69–87
Augustin C B, Boersma M. 2006. Effects of nitrogen stressed algae on different Acartia species. Journal of Plankton Research, 28(4): 429–436
Becker C, Boersma M. 2005. Differential effects of phosphorus and fatty acids on Daphnia magna growth and reproduction. Limnology and Oceanography, 50(1): 388–397
Boersma M, Becker C, Malzahn A M, et al. 2009. Food chain effects of nutrient limitation in primary producers. Marine and Freshwater Research, 60(10): 983–989
Chapin III F S, Walker B H, Hobbs R J, et al. 1997. Biotic control over the functioning of ecosystems. Science, 277(5325): 500–504
Chen Mianrui, Liu Hongbin, Chen Bingzhang. 2012. Effects of dietary essential fatty acids on reproduction rates of a subtropical calanoid copepod, Acartia erythraea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 455: 95–110
Chen Xuehao, Wu Zhongqian. 2005. Effects of nutrition liquid containing Chlorella spp. on the growth and reproduction of rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences (in Chinese), 20: 21–24
Dickman E M, Newell J M, González M J, et al. 2008. Light, nutrients, and food-chain length constrain planktonic energy transfer efficiency across multiple trophic levels. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(47): 18408–18412
Elser J J. 2002. Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems: ideas, plans, and realities. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 42: 1226
Elser J J, Dobberfuhl D R, MacKay N A, et al. 1996. Organism size, life history, and N:P stoichiometry: toward a unified view of cellular and ecosystem processes. BioScience, 46(9): 674–684
Elser J J, Fagan W F, Denno R F, et al. 2000. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature, 408(6812): 578–580
Elser J J, Hayakawa K, Urabe J. 2001. Nutrient limitation reduces food quality for zooplankton: Daphnia response to seston phosphorus enrichment. Ecology, 82(3): 898–903
Færøvig P J, Hessen D O. 2003. Allocation strategies in crustacean stoichiometry: the potential role of phosphorus in the limitation of reproduction. Freshwater Biology, 48(10): 1782–1792
Goldman J C, McCarthy J J, Peavey D G. 1979. Growth rate influence on the chemical composition of phytoplankton in oceanic waters. Nature, 279(5710): 210–215
Guillard R R, Ryther J H. 1962. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana hustedt, and detonula confervacea (cleve) gran. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 8(2): 229–239
Hall S R, Smith V H, Lytle D A, et al. 2005. Constraints on primary producer N:P stoichiometry along N:P supply ratio gradients. Ecology, 86(7): 1894–1904
Harrison K E. 1990. The role of nutrition in maturation, reproduction and embryonic development of decapod crustaceans: a review. Journal of Shellfish Research, 9: 1–28
Helland S, Nejstgaard J C, Humlen R, et al. 2003. Effects of season and maternal food on Calanus finmarchicus reproduction, with emphasis on free amino acids. Marine Biology, 142(6): 1141–1151
Hessen D O, Jensen T C, Kyle M, et al. 2007. RNA responses to Nand Plimitation; reciprocal regulation of stoichiometry and growth rate in Brachionus. Functional Ecology, 21(5): 956–962
Howarth R W, Sharpley A, Walker D. 2002. Sources of nutrient pollution to coastal waters in the United States: implications for achieving coastal water quality goals. Estuaries, 25(4): 656–676
Jensen T C, Verschoor A M. 2004. Effects of food quality on life history of the rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus Pallas. Freshwater Biology, 49(9): 1138–1151
Kattner G, Hagen W, Lee R F, et al. 2007. Perspectives on marine zooplankton lipids. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 64(11): 1628–1639
Klausmeier C A, Litchman E, Levin S A. 2004. Phytoplankton growth and stoichiometry under multiple nutrient limitation. Limnology and Oceanography, 49(4): 1463–1470
Knops J M H, Bradley K L, Wedin D A. 2002. Mechanisms of plant species impacts on ecosystem nitrogen cycling. Ecology Letters, 5(3): 454–466
Lee R F, Hagen W, Kattner G. 2006. Lipid storage in marine zooplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 307: 273–306
Li Jie, Sun Song, Li Chaolun, et al. 2006. The effects of different diets on the survival and development of copepod nauplii. Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 30(12): 13–20
Lin Yuanshao, Li Song. 1984. A preliminary study on the life cycle of Calanus sinicus (Brodsky) in Xiamen Harbour. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural science) (in Chinese), 23(1): 111–117
Liu Mengtan, Li Chaolun, Sun Song. 2011. Seasonal variation in fatty acid composition of seston and the copepod Calanus sinicus (Brodsky, 1962) in Jiaozhou Bay and its trophic implications. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 29(6): 1164–1173
Malzahn A M, Boersma M. 2012. Effects of poor food quality on copepod growth are dose dependent and nonreversible. Oikos, 121(9): 1408–1416
Malzahn A M, Hantzsche F, Schoo K L, et al. 2010. Differential effects of nutrient-limited primary production on primary, secondary or tertiary consumers. Oecologia, 162(1): 35–48
Müller-Navarra D C. 1995. Biochemical versus mineral limitation in Daphnia. Limnology and Oceanography, 40(7): 1209–1214
Nixon S W. 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia, 41(1): 199–219
Purcell J E, Uye S I, Lo W T. 2007. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: a review. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 350: 153–174
Rhee G Y. 1978. Effects of N:P atomic ratios and nitrate limitation on algal growth, cell composition, and nitrate uptake. Limnology and Oceanography, 23(1): 10–25
Sargent J R, Falk-Petersen S. 1988. The lipid biochemistry of calanoid copepods. Hydrobiologia, 167(1): 101–114
Schoo K L, Aberle N, Malzahn A M, et al. 2014. The reaction of European lobster larvae (Homarus gammarus) to different quality food: effects of ontogenetic shifts and prefeeding history. Oecologia, 174(2): 581–594
Sterner R W, Elser J J. 2002. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. Princeton: Princeton University Press
Sterner R W, Hessen D O. 1994. Algal nutrient limitation and the nutrition of aquatic herbivores. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 25: 1–29
Sterner R W, Schulz K L. 1998. Zooplankton nutrition: recent progress and a reality check. Aquatic Ecology, 32(4): 261–279
Urabe J, Makino W, Hayakawa K, et al. 2002. Food quality determinants for Daphnia growth in Plimited lakes. In: Wetzel R G, ed. International Association of Theoretical and Applied Limnology, Proceedings 28th Congress Vol 28, Pt 2. Melbourne: International Association of Theoretical and Applied Limnology-Proceedings, 1089–1094
Van Nieuwerburgh L, Wänstrand I, Snoeijs P. 2004. Growth and C:N:P ratios in copepods grazing on N-or Si-limited phytoplankton blooms. Hydrobiologia, 514(1-3): 57–72
Ventura M, Catalan J. 2005. Reproduction as one of the main causes of temporal variability in the elemental composition of zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography, 50(6): 2043–2056
Vrede T, Persson J, Aronsen G. 2002. The influence of food quality (P:C ratio) on RNA:DNA ratio and somatic growth rate of Daphnia. Limnology and Oceanography, 47(2): 487–494
Wang Bodong. 2006. Cultural eutrophication in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) plume: history and perspective. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 69(3-4): 471–477
Wang Yan, He Zhihui. 2001. Effect of temperature and salinity on intrinsic increasing rate of Moina mongolica Daddy (Cladocera: Moinidae) population. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 12(1): 91–94
Weers P M M, Gulati R D. 1997. Growth and reproduction of Daphnia galeata in response to changes in fatty acids, phosphorus, and nitrogen in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Limnology and Oceanography, 42(7): 1584–1589
Yang Chunwang, Ye Jiaheng. 2000. Studies on technique for indoor culture of brachionus plicatilis with nannocholopsis. Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine (in Chinese), 17(4): 9–10
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the crew on R/V Beidou for their assistance in the field. We are grateful to Jin Xin and Ji Peng for their invaluable help during shipboard research activities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Key R & D Program of China under contract No. 2017YFC1404401; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. 41476139; the National Basic Research Program of China under contract No. 2015CB452903.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Li, C., Zhou, K. et al. Effects of nutrient limitations on three species of zooplankton. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 37, 58–68 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1122-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1122-z