Abstract
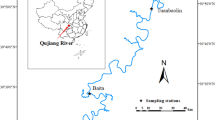
The Hangzhou Bay (HZB) and Xiangshan Bay (XSB), in northern Zhejiang Province and connect to the East China Sea (ECS) were considerably affected by the consequence of water quality degradation. In this study, we analyzed physical and biogeochemical properties of water quality via multivariate statistical techniques. Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) grouped HZB and XSB into two subareas of different pollution sources based on similar physical and biogeochemical properties. Principal component analysis (PCA) identified three latent pollution sources in HZB and XSB respectively and emphasized the importance of terrestrial inputs, coastal industries as well as natural processes in determining the water quality of the two bays. Therefore, proper measurement for the protection of aquatic ecoenvironment in HZB and XSB were of great urgency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson D M, Glibert P M, Burkholder J M. 2002. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries, 25(4): 704–726
Bianchi T S, Allison M A. 2009. Large-river delta-front estuaries as natural “recorders” of global environmental change. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(20): 8085–8092
Bierman P, Lewis M, Ostendorf B, et al. 2011. A review of methods for analysing spatial and temporal patterns in coastal water quality. Ecological Indicators, 11(1): 103–114
Borja A, Dauer D M. 2008. Assessing the environmental quality status in estuarine and coastal systems: comparing methodologies and indices. Ecological Indicators, 8(4): 331–337
Cai Xiaoxia, Pan Jianming, Yu Peisong, et al. 2013. Study of the behavior of nutrients in different harbors in coastal waters of Zhejiang Province. Marine Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 32(5): 488–493
Camargo J A, Alonso A. 2006. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: a global assessment. Environment International, 32(6): 831–849
CSCC. 1992. China’s Bays (the fifth volume) (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1–233
Dong Lixian, Su Jilan. 1999. Numerical study of water exchange in Xiangshangang Bay: II. Model application and water exchange study. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 30(5): 465–470.
Fan Ande, Jin Xisan. 1989. Tidal effects on nutrient exchange in Xiangshan Bay, China. Marine Chemistry, 27(3–4): 259–281
Gao Shengquan, Chen Jianfang, Jin Haiyan. 2011. Characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication in the Hangzhou Bay and its adjacent waters. Journal of Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 29(3): 36–47
Gao Shengquan, Yu Guohui, Wang Yuhen. 1993. Distributional features and fluxes of dissolved nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon in the Hangzhou Bay. Marine Chemistry, 43(1–4): 65–81
Gazzaz N M, Yusoff M K, Ramli M F, et al. 2012. Characterization of spatial patterns in river water quality using chemometric pattern recognition techniques. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(4): 688–698
GAQSIQ. 2007a. GB 17378.4–2007 The specification for marine monitoring— Part 4: seawater analysis (in Chinese). Beijing: China Standard Press
GAQSIQ. 2007b. GB 17378.7–2007 Specifications for marine monitoring— Part 7: Ecological survey for offshore pollution and biological monitoring (in Chinese). Beijing: China Standard Press
Herbeck L S, Unger D, Wu Ying, et al. 2013. Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China. Continental Shelf Research, 57: 92–104
Jenerette G D, Lee J, Waller D W, et al. 2002. Multivariate analysis of the ecoregion delineation for aquatic systems. Environmental Management, 29(1): 67–75
Jia Haibo, Tang Jingliang, Hu Haoyan. 2014. The variation tendency of biodiversity and cause analysis in Hangzhou Bay from 1992 to 2012. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 36(12): 111–118
Jiang Zhibing, Liao Yibo, Liu Jingjing, et al. 2013. Effects of fish farming on phytoplankton community under the thermal stress caused by a power plant in a eutrophic, semi-enclosed bay: induce toxic dinoflagellate (Prorocentrum minimum) blooms in cold seasons. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1–2): 315–324
Justic D, Rabalais N N, Turner R E, et al. 1995. Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 40(3): 339–356
Kannel P R, Lee S, Lee Y S. 2008. Assessment of spatial-temporal patterns of surface and ground water qualities and factors influencing management strategy of groundwater system in an urban river corridor of Nepal. Journal of Environmental Management, 86(4): 595–604
Kim T W, Kim D, Baek S H, et al. 2015. Human and riverine impacts on the dynamics of biogeochemical parameters in Kwangyang Bay, South Korea revealed by time-series data and multivariate statistics. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 90(1–2): 304–311
Li Xueying, Li Bin, Sun Xingli. 2014. Effects of a coastal power plant thermal discharge on phytoplankton community structure in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 81(1): 210–217
Liang Shuxiu, Han Songlin, Sun Zhaochen. 2014. Lagrangian methods for water transport processes in a long-narrow bay Xiangshan Bay, China. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 26(4): 558–567
Liu Chenwang, Lin K H, Kuo Yiming, et al. 2003. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Scicence of the Total Environment, 313(1–3): 77–89
Liu Zilin, Ning Xiuren, Cai Ming. 2001. Primary productivity and standing stock of the phytoplankton in the Hangzhou Bay to the Zhoushan Fishing Ground during autumn. Haiyang Xuebao (in Chinese), 23(2): 93–99
Milliman J D, Shen Huangting, Yang Zuosheng, et al. 1985. Transport and deposition of river sediment in the Changjiang estuary and adjacent continental shelf. Continental Shelf Research, 4(1–2): 37–45
Muylaert K, Sabbe K, Vyverman W. 2000. Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton communities in a freshwater tidal estuary (Schelde, Belgium). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 50(5): 673–687
OFAZP. 2015. Marine Environmental Quality Bulletin of Zhejiang Province 2014 (in Chinese). Hangzhou: Zhejiang Province Ocean and Fisheries Bureau
Paerl H W. 1997. Coastal eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: Importance of atmospheric deposition and groundwater as ‘new’ nitrogen and other nutrient sources. Limnology and Oceanography, 42(5part2): 1154–1165
Pauly D, Christensen V, Guénette S, et al. 2002. Towards sustainability in world fisheries. Nature, 418: 689–695
Shanthi R, Poornima D, Raja K, et al. 2015. Inter-annual and seasonal variations in hydrological parameters and its implication on chlorophyll a distribution along the southwest coast of Bay of Bengal. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34: 94–100
Shen Huanting. 2001. Material Flux of the Changjiang Estuary (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 23
Shrestha S, Kazama F. 2007. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji River basin, Japan. Environmental Modeling Software, 22: 464–475
Sin Y S, Jeong B K. 2015. Short-term variations of phytoplankton communities in response to anthropogenic stressors in a highly altered temperate estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 156: 83–91
SOA. 2014. China Marine Statistical Yearbook 2013 (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 90–98
Su Jilan, Yuan Yeli. 2005. Hydrology in China Sea (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 240–246
Thomas Y, Courties C, Helwe Y E, et al. 2010. Spatial and temporal extension of eutrophication associated with shrimp farm wastewater discharges in the New Caledonia lagoon. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 61: 387–398
Vega M, Pardo R, Barrodo E, et al. 1998. Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis. Water Research, 32: 3581–3592
Valiela I, Foreman K, La Montagne M, et al. 1992. Couplings of watersheds and coastal waters: sources and consequences of nutrient enrichment in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Estuaries and Coasts, 15: 433–457
Wang Baodong, Wang Xiulin, Zhan Run. 2003. Nutrient condition in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 58: 127–136
Wang Kui, Chen Jianfang, Jin Haiyan, et al. 2014. Summer nutrient dynamics and biological carbon uptake rate in the Changjiang River plume inferred using a three end-member mixing model. Continental Shelf Research, 91: 192–200
Wu Meilin, Wang Youshao, Sun Cuici, et al. 2010. Identification of coastal water quality by statistical analysis methods in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60: 852–860
Xie Dongfeng, Wang Zhengbing, Gao Shu, et al. 2009. Modeling the tidal channel morphodynamics in a macro-tidal embayment, Hangzhou Bay, China. Continental Shelf Research, 29: 1757–1767
Ye Ran, Liu Yanyun, Cui Yongping, et al. 2015. Temporal and spatial distributions of nutrient structure and limitation on phytoplankton in the East China Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 46: 311–320
Yeung I M H. 1999. Multivariate analysis of the Hong Kong Victoria Harbour water quality data. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 59: 331–342
Zhang Yuexia, Yu Jun, Jiang Zhibing, et al. 2015. Variations of summer phytoplankton community related to environmental factors in a macro-tidal estuarine embayment, Hangzhou Bay, China. Journal of Ocean University of China, 14: 1025–1033
Zhou Feng, Guo Huaicheng, Liu Yong, et al. 2007. Chemometrics data analysis of marine water quality and source identification in Southern Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54: 745–756
Zhou Yan, Zhao Congjiao, Gao Yuansen, et al. 2010. Variation and distribution characteristics of phytoplankton in ecology-monitoring area of Hangzhou Bay from 2005 to 2008. Journal of Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 28: 28–35
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate all the sampling staffs of Marine Environmental Monitoring Centre of Ningbo, State Oceanic Administration, for their industrious work in helping the data collection. We also thank Wang Kai from School of Marine Sciences, Ningbo University, for his help in improvement of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Marine Ecoenvironment Assessment Program of State Oceanic Administration.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, R., Liu, L., Wang, Q. et al. Identification of coastal water quality by multivariate statistical techniques in two typical bays of northern Zhejiang Province, East China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 36, 1–10 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-0981-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-0981-7