Abstract
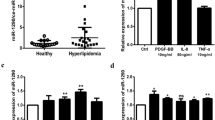
Endothelial injury, which can cause endothelial inflammation and dysfunction, is an important mechanism for the development of atherosclerotic plaque. This study aims to investigate the functional role of miR-520c-3p in vascular endothelium during inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to detect miR-520c-3p expression in in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) after treatment with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). Furthermore, the effects of miR-520c-3p overexpression and silencing on cell proliferation, adhesion, and apoptosis were assessed. Bioinformatics analysis and Biotin-labeled miRNA pull-down assay were used to confirm the targets of miR-520-3p. Then, the effects of miR-520c-3p on AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways were detected by western blot. Herein, we observed that the expression level of miR-520c-3p was downregulated in HUVECs under PDGF stimulation. Overexpression of miR-520c-3p not only decreased cell adhesion but also promoted proliferation and inhibited apoptosis to protect the viability of endothelial cells. It was confirmed that RELA is the target of miR-520c-3p. MiR-520c-3p inhibited the protein phosphorylation of AKT and RELA, and si-RELA reversed the promotion of AKT and RELA protein phosphorylation by anti-miR-520c-3p. In summary, our study suggested that miRNA-520c-3p targeting RELA through AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways regulated the proliferation, apoptosis, and adhesion of vascular endothelial cells. We conclude that miR-520c-3p may play an important role in the suppression of endothelial injury, which could serve as a biomarker and therapeutic target for atherosclerosis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adyshev DM, Moldobaeva N, Mapes B, Elangovan V, Garcia JG (2013) MicroRNA regulation of nonmuscle myosin light chain kinase expression in human lung endothelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 49(1):58–66
Andreou I, Sun X, Stone PH, Edelman ER, Feinberg MW (2015) miRNAs in atherosclerotic plaque initiation, progression, and rupture. Trends Mol Med 21(5):307–318
Aryal B, Suárez Y (2019) Non-coding RNA regulation of endothelial and macrophage functions during atherosclerosis. Vasc Pharmacol 114:64–75
Baud V, Collares D (2016) Post-translational modifications of RelB NF-κB subunit and associated functions. Cells 5(2):22
Berezin A, Zulli A, Kerrigan S, Petrovic D, Kruzliak P (2015) Predictive role of circulating endothelial-derived microparticles in cardiovascular diseases. Clin Biochem 48(9):562–568
Cai X, Zhou X, Xiao F, Ye B, Huang W, Huang Z (2018) Inhibition of hsa-miR-6086 protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against TNFα-induced proliferation inhibition and apoptosis via CDH5. Gene 661:202–208
Cheng HW, Chen YF, Wong JM, Weng CW, Chen HY, Yu SL, Chen HW, Yuan A, Chen JJ (2017) Cancer cells increase endothelial cell tube formation and survival by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1):27
Ernst O, Vayttaden SJ, Fraser IDC (2018) Measurement of NF-κB activation in TLR-activated macrophages. Methods Mol Biol 1714:67–78
Favero G, Paganelli C, Buffoli B, Rodella LF, Rezzani R (2014) Endothelium and its alterations in cardiovascular diseases: life style intervention. Biomed Res Int 2014:1–28
Gallo S, Sala V, Gatti S, Crepaldi T (2015) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of HGF/met in the cardiovascular system. Clin Sci 129(12):1173–1193
Gao W, Liu H, Yuan J, Wu C, Huang D, Ma Y, Zhu J, Ma L, Guo J, Shi H, Zou Y, Ge J (2016) Exosomes derived from mature dendritic cells increase endothelial inflammation and atherosclerosis via membrane TNF-α mediated NF-κB pathway. J Cell Mol Med 20(12):2318–2327
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, Yan M, Keyt BA, Dixit V, Ferrara N (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival throughthe phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem 273(46):30336–30343
Gorur A, Celik A, Yildirim DD, Gundes A, Tamer L (2019) Investigation of possible effects of microRNAs involved in regulation of lipid metabolism in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Mol Biol Rep 46(1):909–920
Hadi HA, Carr CS, Al Suwaidi J (2005) Endothelial dysfunction: cardiovascular risk factors, therapy, and outcome. Vasc Health Risk Manag 1(3):183–198
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2014) Regulation of NF-κB by TNF family cytokines. Semin Immunol 26(3):253–266
Hu W, Huang Y (2015) Targeting the platelet-derived growth factor signalling in cardiovascular disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 42(12):1221–1224
Karagkiozaki V, Logothetidis S, Pappa AM (2015) Nanomedicine for atherosclerosis: molecular imaging and treatment. J Biomed Nanotechnol 11(2):191–210
Keklikoglou I, Koerner C, Schmidt C, Zhang JD, Heckmann D, Shavinskaya A, Allgayer H, Gückel B, Fehm T, Schneeweiss A, Sahin Ö, Wiemann S, Tschulena U (2012) MicroRNA-520/373 family functions as a tumor suppressor in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer by targeting NF-κB and TGF-β signaling pathways. Oncogene 31(37):4150–4163
Kim JY, Chun SY, Park JS, Chung JW, Ha YS, Lee JN, Kwon TG (2018) Laminin and platelet-derived growth factor-BB promote neuronal differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med 15(2):195–209
Li X, Fu Q, Li H, Zhu L, Chen W, Ruan T, Xu W, Yu X (2019) MicroRNA-520c-3p functions as a novel tumor suppressor in lung adenocarcinoma. FEBS J 286(14):2737–2752
Li YR, Wen LQ, Wang Y, Zhou TC, Ma N, Hou ZH, Jiang ZP (2016) MicroRNA-520c enhances cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by suppressing IRF2 in gastric cancer. FEBS Open Bio 6(12):1257–1266
Libby P (2012) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(9):2045–2051
Lin N, An Y (2017) Blockade of 146b-5p promotes inflammation in atherosclerosis-associated foam cell formation by targeting TRAF6. Exp Ther Med 14(5):5087–5092
Lu QB, Wan MY, Wang PY, Zhang CX, Xu DY, Liao X, Sun HJ (2018) Chicoric acid prevents PDGF-BB-induced VSMC dedifferentiation, proliferation and migration by suppressing ROS/NFκB/mTOR/P70S6K signaling cascade. Redox Biol 14:656–668
Meng F, Liu L, Chin PC, D'Mello SR (2002) Akt is a downstream target of NF-κB. J Biol Chem 277(33):29674–29680
Miao HL, Lei CJ, Qiu ZD, Liu ZK, Li R, Bao ST, Li MY (2014) MicroRNA -520c-3p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and invasion through induction of cell apoptosis by targeting glypican-3. Hepatol Res 44(3):338–348
Nazari-Jahantigh M, Egea V, Schober A, Weber C (2015) MicroRNA-specific regulatory mechanisms in atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 89(Pt A):35–41
Parenti A, Paccosi S, Cairo F, Defraia E (2015) Treatment of periodontitis for the prevention of endothelial dysfunction: a narrative review. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 13(6):749–758
Ren J, Jin P, Wang E, Marincola FM, Stroncek DF (2009) MicroRNA and gene expression patterns in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. J Transl Med 7(1):20
Romashkova JA, Makarov SS (1999) NF-kappaB is a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signalling. Nature 401(6748):86–90
Sanli T, Strano S, Muti P (2013) Lifestyle factors and MicroRNAs: a new paradigm in Cancer chemoprevention. Microrna 2(2):82–90
Stark A, Brennecke J, Bushati N, Russell RB, Cohen SM (2005) Animal MicroRNAs confer robustness to gene expression and have a significant impact on 3'UTR evolution. Cell 123(6):1133–1146
Tao Y, Yu S, Chao M, Wang Y, Xiong J, Lai H (2019) SIRT4 suppresses the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway and attenuates HUVEC injury induced by oxLDL. Mol Med Rep 19(6):4973–4979
Wang J, Zhang C, Li C, Zhao D, Li S, Ma L, Cui Y, Wei X, Zhao Y, Gao Y (2019) MicroRNA-92a promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration through the ROCK/MLCK signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med 23(5):3696–3710
Zhou P, Lu S, Luo Y, Wang S, Yang K, Zhai Y, Sun G, Sun X (2017) Attenuation of TNF-α-induced inflammatory injury in endothelial cells by Ginsenoside Rb1 via inhibiting NF-κB, JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol 8:464
Funding
This work was supported by Liaoning Provincial Program for Top Discipline of Basic Medical Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31370800, 31070719, 30470394, 81402916), the Educational Department of Liaoning Province (2017502656), and Liaoning Provincial Program for Top Discipline of Basic Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jiao Y performed the experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. Zhao DD performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Gao FH, Hu XY, and Hu XX participated in the experiments. Cui Y, Wei XQ, Xie C, and Li M analyzed data. Zhao Y designed and supervised research. Gao Y designed and supervised research and revised the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key points
• miR-520c-3p was downregulated in PDGF-treated HUVECs.
• miR-520c-3p regulated PDGF-induced HUVECs adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis.
• miR-520c-3p decreased its target gene the expression of RELA/p65 in HUVECs.
• miR-520c-3p plays a protective role in an in vitro endothelial dysfunction model.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiao, Y., Zhao, D., Gao, F. et al. MicroRNA-520c-3p suppresses vascular endothelium dysfunction by targeting RELA and regulating the AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Physiol Biochem 77, 47–61 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00779-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-020-00779-5