Abstract
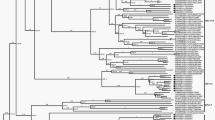
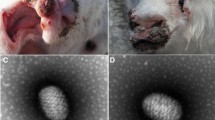
The Republic of Tatarstan is one of the most active endemic regions for nephropathia epidemica (NE) in the Russian Federation. Annually, over 1000 cases of NE are registered, with an average mortality rate of 0.43 %. NE is a zoonosis where human become infected by inhaling a hantavirus-contaminated aerosol. Puumala virus is commonly detected in NE cases. Although NE cases have been registered in the region since 1958, little is known about the genetic variability of Puumala virus circulating in Tatarstan. We conducted phylogenetic analysis of the full length (1828 nt) small (S) segment genome sequence of Puumala virus RNA isolated from four bank voles (Myodes glareolus) captured during the 2014 outbreak. These virus sequences were compared to known sequences of Puumala viruses from nearby regions such as Samara and the Republic of Bashkortostan, as well as to European isolates. We found that there was over 89 % nucleotide identity between Puumala virus sequences isolated from the bank voles captured in Tatarstan. Sequence identity between Puumala viruses from the Tatarstan bank voles and the sequences from Republic of Bashkortostan and the Samara region were 90–95 %. Less similarity was found between Tatarstan sequences and Puumala strains circulating in Europe (79.7–87.7 %). Taken together, these data suggest that Puumala viruses circulating within the bank vole population in the Republic of Tatarstan are phylogenetically closer to the viruses circulating in neighboring regions of Russia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khaiboullina, S. F., Morzunov, S. P., Jeor, S. C. S. (2005). Hantaviruses: molecular biology, evolution and pathogenesis. Current Molecular Medicine, 5(8), 773–90.
Khismatullina, N.A. et al (2015) Epidemiological dynamics of nephropathia epidemica in the Republic of Tatarstan, Russia, during the period of 1997–2013. Epidemiol Infect, p. 1–9.
Kariwa, H., et al. (2009). Epidemiological study of hantavirus infection in the Samara Region of European Russia. Journal of Veterinary Medical Science, 71, 1569–1578.
Onishchenko, G. G., & Ezhlova, E. B. (2013). Epidemiologic surveillance and prophylaxis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Russian Federation [in Russian]. Zhurnal Mikrobiologii, Epidemiologii, i Immunobiologii, 4, 23–32.
Souza, W. M., et al. (2014). Phylogeography and evolutionary history of rodent-borne hantaviruses. Infection, Genetics and Evolution, 21, 198–204.
Jonsson, C. B., et al. (2010). A global perspective on hantavirus ecology, epidemiology, and disease. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 23(2), 412–441.
Clewley, J. P. (1995). Macintosh sequence analysis software DNAStar’s LaserGene. Molecular Biotechnology, 3(3), 221–4.
Razzauti, M., et al. (2008). Accumulation of point mutations and reassortment of genomic RNA segments are involved in the microevolution of Puumala hantavirus in a bank vole (Myodes glareolus) population. The Journal of General Virology, 89(Pt 7), 1649–60.
Razzauti, M., et al. (2009). Analysis of Puumala hantavirus in a bank vole population in northern Finland: evidence for co-circulation of two genetic lineages and frequent reassortment between strains. The Journal of General Virology, 90(Pt 8), 1923–31.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation grant 15-14-00016. The work is performed according to the Russian Government Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University and subsidy allocated to Kazan Federal University for the state assignment in the sphere of scientific activities. Some of the experiments were conducted using the equipment of Interdisciplinary Center for Collective Use of Kazan Federal University supported by the Ministry of Education of Russian Federation (ID RFMEFI59414X0003) and the Pharmaceutical Research and Education Center of Kazan (Volga Region) Federal University, Kazan, Russian Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabwe, E., Davidyuk, N.Y., Morzunov, S.P. et al. Genetic Characterization of Small (s)-Segment Genome Puumala Virus Strain Kazan. BioNanoSci. 7, 316–319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0338-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0338-2