Abstract
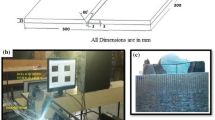
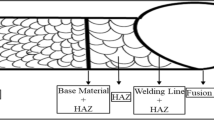
The welding of ultra-high hard armour (UHA) steel is highly challenging due to their higher hardness (600 HV) and higher carbon equivalent (0.80). In this investigation, 15-mm-thick UHA steel plates are welded by shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process using three different consumables such as austenitic stainless steel (ASS), low-hydrogen ferritic steel (LHF), and duplex stainless steel (DSS). The joints were tested against a 7.62 × 54 mm Armor-piercing (AP) projectile. All three joints successfully stopped the projectile at weld metal and interface (weld/HAZ) without perforation. The ballistic performance and mechanical properties are improved than the currently used ASS electrodes, and a new method to study the mode of failure at weld metal and interface was introduced. Striations and microcracks are preferred modes of failure than wear debris in the weld metal, and soft/hard mode is preferred over soft/soft and hard/hard modes of failure at the interface.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flores-Johnson E A, Saleh M, and Edwards L, Int J Impact Eng 38 (2011) 1022.
Ade F, Weld J 70 (1991) 53.
Madhusudhan Reddy G, and Mohandas T, J Mater Process Technol 57 (1996) 23.
McDonald B, Bornstein H, Ameri A, Daliri A, and Orifici A C, Int J Solids Struct 176–177 (2019) 135.
Trajkovski J, Kunc R, Pepel V, and Prebil I, Mater Des 66 (2015) 37.
Magudeeswaran G, Balasubramanian V, and Madhusudhan Reddy G, Int J Hydrog Energy 33 (2008) 1897.
Mittal R, and Singh BS, J Mater Process Technol 220 (2015) 76.
Magudeeswaran G, Balasubramanian V, Madhusudhan Reddy G, and Balasubramanian T S, J Iron Steel Res Int 15 (2008) 87.
Magudeeswaran G, Balasubramanian V, and Madhusudan Reddy G, Def Technol 14 (2018) 590.
Magudeeswaran G, Balasubramanian V, and Madhusudhan Reddy G, Ironmak Steelmak 35 (2008) 549.
Backman M E, and Goldsmith W, Int J Eng Sci 16 (1978) 1.
Rosenberg Z, Kositski R, and Malka-Markovitz A, Int J Impact Eng 121 (2018) 35.
Wang J, and Li Y, Bull Mater Sci 26 (2003) 295.
Xiao F, Liao B, Ren D, Shan Y, and Yang K, Mater Charact 54 (2005) 305.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to record sincere thanks to the Directorate of ERIPR, DRDO, Government of India, New Delhi, and RIC, DRDO, Chennai, for the financial support rendered through an R&D Project No: EPIR/EP/RIC/2016/1/M/01/1630. Thanks to Director, CVRDE, DRDO for providing base metal to carryout this investigation. The authors wish to thank the Director, DMRL, DRDO, India, for granting permission to conduct the ballistic test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naveen Kumar, S., Balasubramanian, V., Malarvizhi, S. et al. Influence of Microstructural Characteristics on Ballistic Performance and Its Mode of Failure in Shielded Metal Arc Welded Ultra-High Hard Armor Steel Joints. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 909–921 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02197-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02197-7