Abstract
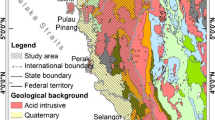
Measurement of terrestrial gamma radiation dose (TGRD) rate and activity concentrations of naturally occurring radionuclides in environmental media such as soil and air play an important role in the setting national average permissible doses to members of public. Malaysia is planning to add nuclear energy to its national electricity grid; hence the knowledge of the levels of exposure to natural background radioactivity is important for policies and law making with regards to radiological protection of both human and the environment. The aim of this work was to measure the variation of background radiation with respect to geological formations of Terengganu (Malaysia) and assess the potential health hazards that are associated with the chronic exposure to natural radiation in the area. Ludlum 19 micro survey meters with NaI[Tl] detectors and HPGe gamma ray spectrometer were used for in situ TGRD and laboratory analysis, respectively. The measured TGRD rates ranged from 35 to 340 nGy h−1 with mean value of 150 nGy h−1 and the annual effective dose to population was 0.92 mSv year−1. The mean (range) activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K in the soil samples were 79 ± 3 (20 ± 1–151 ± 5) Bq kg−1; 84 ± 3 (8 ± 1–182 ± 6) Bq kg−1; and 545 ± 55 (47 ± 5–1056 ± 107) Bq kg−1, respectively. Upon comparing these values with the world averages for specific activities of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K (i.e. 33, 36 and 474 Bq kg−1 for 226Ra, 232Th and 40K respectively), It is revealed that the mean activity concentrations of 226Ra and 232Th in the soil of Terengganu are higher than the world averages by a factor of two. The mean activity concentration of 40K in the soil of Terengganu is ~15 % higher than the world average. Acid intrusive geological formation (due to the granite composition from igneous rocks), which is the most dominant in the state was found to contained higher mean TGRD values as well as 226Ra and 232Th concentration this was consistent with some previous studies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad N, Khatibeh A (1997) Indoor radon levels and natural radioactivity in Jordanian Soils. Radiat Prot Dos 71(3):231–233
Aliyu AS, Ramli AT (2015) The world’s high background natural radiation areas (HBNRAs) revisited: a broad overview of the dosimetric, epidemiological and radiobiological issues. Radiat Meas 73:51–59
Al-Jundi J (2002) Population doses from terrestrial gamma exposure in areas near to old phosphate mine, Russaifa, Jordan. Radiat Meas 35(1):23–28
Amrani D, Tahtat M (2001) Natural radioactivity in Algerian building materials. Appl Radiat Isot 54(4):687–689
Beretka J, Mathew P (1985) Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrial wastes and by-products. Health Phy 48(1):87–95
Catelinois O, Rogel A, Laurier D, Billon S, Hemon D, Verger P, Tirmarche M (2006) Lung cancer attributable to indoor radon exposure in france: impact of the risk models and uncertainty analysis. Environ Health Perspec 114(9):1361–1366
Darby S, Hill D, Deo H, Auvinen A, Barros-Dios JM, Baysson H, Bochicchio F, Falk R, Farchi S, Figueiras A (2006) Residential radon and lung cancer—detailed results of a collaborative analysis of individual data on 7148 persons with lung cancer and 14 208 persons without lung cancer from 13 epidemiologic studies in Europe. Scandinavian J Work, Environ Health, pp 1–84
DGGS (1985) Geological map of Peninsular Malaysia. Director General Geological Survey, Malaysia, IPoh
Faanu A, Darko E, Ephraim J (2012) Determination of Natural Radioactivity and Hazard in Soil and Rock Samples in a Mining Area in Ghana. West African J Appl Ecol 19(1)
Fatima I, Zaidi J, Arif M, Daud M, Ahmad S, Tahir S (2008) Measurement of natural radioactivity and dose rate assessment of terrestrial gamma radiation in the soil of southern Punjab, Pakistan. Radiat Prot Dos 128(2):206–212
Gabdo HT, Ramli AT, Sanusi MS, Saleh MA, Garba NN (2014) Terrestrial gamma dose rate in Pahang state Malaysia. J Radioanaly Nucl Chem 299(3):1793–1798
Garba NN, Ramli AT, Saleh MA, Sanusi MS, Gabdo HT (2014) Assessment of terrestrial gamma radiation dose rate (TGRD) of Kelantan State, Malaysia: relationship between the geological formation and soil type to radiation dose rate. J Radio Nucl Chem 302(1):201–209
Garba NN, Ramli AT, Saleh MA, Sanusi MS, Gabdo HT (2015) Terrestrial gamma radiation dose rates and radiological mapping of Terengganu state, Malaysia. J Radio Nucl Chem 303(3):1785–1792
IAEA (1989) Measurement of radionuclides in food and the environment—a Guidebook Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency
IAEA (2003) Guidelines for radioelement mapping using gamma ray spectrometry data International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Ibrahiem N, El Ghani AA, Shawky S, Ashraf E, Farouk M (1993) Measurement of radioactivity levels in soil in the Nile Delta and middle Egypt. Health Phy 64(6):620–627
Karahan G, Bayulken A (2000) Assessment of gamma dose rates around Istanbul (Turkey). J Environ Radioact 47(2):213–221
Kumar V, Ramachandran T, Prasad R (1999) Natural radioactivity of Indian building materials and by-products. Appl Radiat Isot 51(1):93–96
Kurnaz A (2013) Background radiation measurements and cancer risk estimates for Sebinkarahisar. Radiat Prot Dos, Turkey. doi:10.1093/rpd/nct115
Lee SK, Wagiran H, Ramli AT, Apriantoro NH, Wood AK (2009) Radiological monitoring: terrestrial natural radionuclides in Kinta District, Perak, Malaysia. J Environ Radioact 100(5):368–374
Martin A, Harbison SA (1972) An introduction to radiation protection. Wiley, New York
Matiullah, Ahad A, ur Rehman S, ur Rehman S, Faheem M (2004) Measurement of radioactivity in the soil of Bahawalpur division, Pakistan. Radiat Prot Dos 112(3):443–447
McAulay I, Morgan D (1988) Natural radioactivity in soil in the Republic of Ireland. Radiat Prot Dos 24(1–4):47–49
Mollah A, Rahman M, Koddus M, Husain S, Malek M (1987) Measurement of high natural background radiation levels by TLD at Cox’s Bazar coastal areas in Bangladesh. Radiat Prot Dos 18(1):39–41
Møller AP, Mousseau TA (2013) The effects of natural variation in background radioactivity on humans, animals and other organisms. Biol Rev 88(1):226–254
Paramananthan S (2000) Soils of Malaysia: their characteristics and identification. (Vol. 1) Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Acad Sci Malaysia
Quindos L, Fernandez P, Soto J, Rodenas C, Gomez J (1994) Natural radioactivity in Spanish soils. Health Phy 66(2):194–200
Ramli AT (1997) Environmental terrestrial gamma radiation dose and its relationship with soil type and underlying geological formations in Pontian district, Malaysia. Appl Radiat Isot 48(3):407–412
Ramli AT, Hussein AW, Lee M (2001) Geological influence on terrestrial gamma radiation dose rate in the Malaysian State of Johore. Appl Radiat Isot 54(2):327–333
Ramli AT, Rahman ATA, Lee M (2003) Statistical prediction of terrestrial gamma radiation dose rate based on geological features and soil types in Kota Tinggi district, Malaysia. Appl Radiat Isot 59(5):393–405
Ramli AT, Hussein AW, Wood AK (2005a) Environmental 238U and 232Th concentration measurements in an area of high level natural background radiation at Palong, Johor, Malaysia. J Environ Radioact 80(3):287–304
Ramli AT, Sahrone S, Wagiran H (2005b) Terrestrial gamma radiation dose study to determine the baseline for environmental radiological health practices in Melaka state, Malaysia. J Radiol Prot 25(4):435
Ramli AT, Apriantoro NH, Wagiran H, Wood AK, Kuan LS (2009) Health risk implications of high background radiation dose rate in Kampung Sungai Durian, Kinta District, Perak, Malaysia. Global J Health Sci 1(2):P140
Saleh IH, Hafez AF, Elanany NH, Motaweh HA, Naim MA (2007) Radiological study on soils, foodstuff and fertilizers in the Alexandria region. Egypt Turk J Eng Environ Sci 31:9–17
Saleh MA, Ramli AT, Alajerami Y, Aliyu AS (2013a) Assessment of environmental 226 Ra, 232Th and 40 K concentrations in the region of elevated radiation background in Segamat District, Johor, Malaysia. J Environ Radioac 124:130–140
Saleh MA, Ramli AT, Alajerami Y, Aliyu AS (2013b) Assessment of natural radiation levels and associated dose rates from surface soils in Pontian District, Johor, Malaysia. J Ovo Res 9(1):17–26
Saleh MA, Ramli AT, Alajerami Y, Aliyu AS, Bt Basri NA (2013c) Radiological study of Mersing District, Johor, Malaysia. Radiat Phys Chem
Statistics (2010) Population and Housing Census of Malaysia 2010. 55
Tahir S, Jamil K, Zaidi J, Arif M, Ahmed N, Ahmad SA (2005) Measurements of activity concentrations of naturally occurring radionuclides in soil samples from Punjab province of Pakistan and assessment of radiological hazards. Radiat Prot Dos 113(4):421–427
Tufail M, Akhtar N, Waqas M (2006) Radioactive rock phosphate: the feed stock of phosphate fertilizers used in Pakistan. Health Phy 90(4):361–370
Tzortzis M, Svoukis E, Tsertos H (2004) A comprehensive study of natural gamma radioactivity levels and associated dose rates from surface soils in Cyprus. Radiat Prot Dos 109(3):217–224
UNSCEAR (2000) Effects of Ionizing Radiation, 2000 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes. United Nations, New York
Veiga R, Sanches N, Anjos R, Macario K, Bastos J, Iguatemy M, Aguiar J, Santos A, Mosquera B, Carvalho C (2006) Measurement of natural radioactivity in Brazilian beach sands. Radiat Meas 41(2):189–196
William Field R, Krewski D, Lubin JH, Zielinski JM, Alavanja M, Catalan VS, Klotz JB, Létourneau EG, Lynch CF, Lyon JL (2006) An overview of the North American residential radon and lung cancer case-control studies. J Toxicol and Environ Health, Part A 69(7–8):599–631
Acknowledgments
This project is funded by the Atomic Energy Licensing Board (AELB), Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation, Malaysia und project title: PEMETAAN ISODOS SINARAN GAMA DATARAN, SEMENANJUNG Malaysia, which involved Lee, M.H., Heryanshah, A., Wagiran, H., and Said, M.N. The consultancy was managed by GITM Sdn Bhd. The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE) and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) for support and funding under UTM Research University Grant; QJ130000.2526.03H67. The supports for ASA is from the Research Management Center of UTM through the post-doc research program Grant; Q.J130000.21A2.01E98.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garba, N.N., Ramli, A.T., Saleh, M.A. et al. The potential health hazards of chronic exposure to low-dose natural radioactivity in Terengganu, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 75, 431 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5217-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5217-6