Abstract
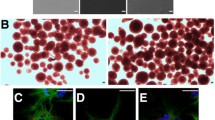
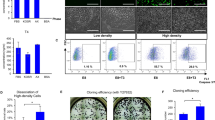
Hyperthyroidism is prevalent during pregnancy, but little is known about the effects of excess thyroid hormone on the development of embryonic neural stem/progenitor cells (NSCs), and the mechanisms underlying these effects. Previous studies indicate that STAT3 plays a crucial role in determining NSC fate during neurodevelopment. In this study, we investigated the effects of a supraphysiological dose of 3,5,3′-l-triiodothyronine (T3) on the proliferation and maintenance of NSCs derived from embryonic day 13.5 mouse neocortex, and the involvement of STAT3 in this process. Our results suggest that excess T3 treatment inhibits NSC proliferation and maintenance. T3 decreased tyrosine phosphorylation of JAK1, JAK2 and STAT3, and subsequently inhibited STAT3–DNA binding activity. Furthermore, proliferation and maintenance of NSCs were decreased by inhibitors of JAKs and STAT3, indicating that the STAT3 signalling pathway is involved in the process of NSC proliferation and maintenance. Taken together, these results suggest that the STAT3 signalling pathway is involved in the process of T3-induced inhibition of embryonic NSC proliferation and maintenance. These findings provide data for understanding the effects of hyperthyroidism during pregnancy on fetal brain development, and the mechanisms underlying these effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S (2009) The culture of neural stem cells. J Cell Biochem 106(1):1–6
Ahmed OM, El-Gareib AW, El-Bakry AM, Abd El-Tawab SM, Ahmed RG (2008) Thyroid hormones states and brain development interactions. Int J Dev Neurosci 26(2):147–209
Ahmed S, Gan HT, Lam CS, Poonepalli A, Ramasamy S, Tay Y, Tham M, Yu YH (2009) Transcription factors and neural stem cell self-renewal, growth and differentiation. Cell Adhes Migr 3(4):412–424
Ambrogini P, Cuppini R, Ferri P, Mancini C, Ciaroni S, Voci A, Gerdoni E, Gallo G (2005) Thyroid hormones affect neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult rat. Neuroendocrinology 81(4):244–253
Barnabe-Heider F, Wasylnka JA, Fernandes KJ, Porsche C, Sendtner M, Kaplan DR, Miller FD (2005) Evidence that embryonic neurons regulate the onset of cortical gliogenesis via cardiotrophin-1. Neuron 48(2):253–265
Benvenuti S, Luciani P, Cellai I, Deledda C, Baglioni S, Saccardi R, Urbani S, Francini F, Squecco R, Giuliani C, Vannelli GB, Serio M, Pinchera A, Peri A (2008) Thyroid hormones promote cell differentiation and up-regulate the expression of the seladin-1 gene in in vitro models of human neuronal precursors. J Endocrinol 197(2):437–446
Calza L, Fernandez M, Giuliani A, Aloe L, Giardino L (2002) Thyroid hormone activates oligodendrocyte precursors and increases a myelin-forming protein and NGF content in the spinal cord during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(5):3258–3263
Carreon-Rodriguez A, Charli JL, Perez-Martinez L (2009) T3 differentially regulates TRH expression in developing hypothalamic neurons in vitro. Brain Res 1305:20–30
Cattaneo E, Conti L, De-Fraja C (1999) Signalling through the JAK-STAT pathway in the developing brain. Trends Neurosci 22(8):365–369
D’Sa-Eipper C, Roth KA (2000) Caspase regulation of neuronal progenitor cell apoptosis. Dev Neurosci 22(1–2):116–124
de Escobar GM, Obregon MJ, del Rey FE (2004) Maternal thyroid hormones early in pregnancy and fetal brain development. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 18(2):225–248
Desouza LA, Ladiwala U, Daniel SM, Agashe S, Vaidya RA, Vaidya VA (2005) Thyroid hormone regulates hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult rat brain. Mol Cell Neurosci 29(3):414–426
Doe CQ (2008) Neural stem cells: balancing self-renewal with differentiation. Development 135(9):1575–1587
Fernandez M, Pirondi S, Manservigi M, Giardino L, Calza L (2004) Thyroid hormone participates in the regulation of neural stem cells and oligodendrocyte precursor cells in the central nervous system of adult rat. Eur J Neurosci 20(8):2059–2070
Fernandez M, Paradisi M, Del Vecchio G, Giardino L, Calza L (2009) Thyroid hormone induces glial lineage of primary neurospheres derived from non-pathological and pathological rat brain: implications for remyelination-enhancing therapies. Int J Dev Neurosci 27(8):769–778
Foshay KM, Gallicano GI (2008) Regulation of Sox2 by STAT3 initiates commitment to the neural precursor cell fate. Stem Cells Dev 17(2):269–278
Gu F, Hata R, Ma YJ, Tanaka J, Mitsuda N, Kumon Y, Hanakawa Y, Hashimoto K, Nakajima K, Sakanaka M (2005) Suppression of Stat3 promotes neurogenesis in cultured neural stem cells. J Neurosci Res 81(2):163–171
Haas MJ, Fishman M, Mreyoud A, Mooradian AD (2005) Thyroid hormone responsive protein (THRP) mediates thyroid hormone-induced cytotoxicity in primary neuronal cultures. Exp Brain Res 160(4):424–432
Hadj-Sahraoui N, Seugnet I, Ghorbel MT, Demeneix B (2000) Hypothyroidism prolongs mitotic activity in the post-natal mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 280(2):79–82
Hao Y, Yang X, Chen C, Yuan W, Wang X, Li M, Yu Z (2010) STAT3 signalling pathway is involved in the activation of microglia induced by 2.45 GHz electromagnetic fields. Int J Radiat Biol 86(1):27–36
He F, Ge W, Martinowich K, Becker-Catania S, Coskun V, Zhu W, Wu H, Castro D, Guillemot F, Fan G, de Vellis J, Sun YE (2005) A positive autoregulatory loop of Jak-STAT signaling controls the onset of astrogliogenesis. Nat Neurosci 8(5):616–625
Hirabayashi Y, Gotoh Y (2005) Stage-dependent fate determination of neural precursor cells in mouse forebrain. Neurosci Res 51(4):331–336
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima K, Akiyama T, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor cells. Development 131(12):2791–2801
Horn S, Heuer H (2010) Thyroid hormone action during brain development: more questions than answers. Mol Cell Endocrinol 315(1–2):19–26
Inoue M, Arata N, Koren G, Ito S (2009) Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy. Can Fam Physician 55(7):701–703
Jones SA, Jolson DM, Cuta KK, Mariash CN, Anderson GW (2003) Triiodothyronine is a survival factor for developing oligodendrocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 199(1–2):49–60
Kalani MY, Cheshier SH, Cord BJ, Bababeygy SR, Vogel H, Weissman IL, Palmer TD, Nusse R (2008) Wnt-mediated self-renewal of neural stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(44):16970–16975
Kang MK, Kang SK (2008) Interleukin-6 induces proliferation in adult spinal cord-derived neural progenitors via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway with EGF-induced MAPK phosphorylation. Cell Prolif 41(3):377–392
Kawaguchi D, Yoshimatsu T, Hozumi K, Gotoh Y (2008) Selection of differentiating cells by different levels of delta-like 1 among neural precursor cells in the developing mouse telencephalon. Development 135(23):3849–3858
Konig S, Moura Neto V (2002) Thyroid hormone actions on neural cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 22(5–6):517–544
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Luewan S, Chakkabut P, Tongsong T (2010) Outcomes of pregnancy complicated with hyperthyroidism: a cohort study. Arch Gynecol Obstet
Milosevic J, Storch A, Schwarz J (2004) Spontaneous apoptosis in murine free-floating neurospheres. Exp Cell Res 294(1):9–17
Panchision DM, McKay RD (2002) The control of neural stem cells by morphogenic signals. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12(4):478–487
Peltier J, O’Neill A, Schaffer DV (2007) PI3K/Akt and CREB regulate adult neural hippocampal progenitor proliferation and differentiation. Dev Neurobiol 67(10):1348–1361
Perra A, Simbula G, Simbula M, Pibiri M, Kowalik MA, Sulas P, Cocco MT, Ledda-Columbano GM, Columbano A (2008) Thyroid hormone (T3) and TRbeta agonist GC-1 inhibit/reverse nonalcoholic fatty liver in rats. FASEB J 22(8):2981–2989
Sarkozy G, Griesmaier E, He X, Kapelari K, Urbanek M, Simbruner G, Gressens P, Keller M (2007) T3 replacement does not prevent excitotoxic cell death but reduces developmental neuronal apoptosis in newborn mice. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 11(3):129–135
Sato A, Sunayama J, Matsuda K, Tachibana K, Sakurada K, Tomiyama A, Kayama T, Kitanaka C (2010) Regulation of neural stem/progenitor cell maintenance by PI3K and mTOR. Neurosci Lett 470(2):115–120
Schust J, Sperl B, Hollis A, Mayer TU, Berg T (2006) Stattic: a small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem Biol 13(11):1235–1242
Shimojo H, Ohtsuka T, Kageyama R (2008) Oscillations in notch signaling regulate maintenance of neural progenitors. Neuron 58(1):52–64
Sung SM, Jung DS, Kwon CH, Park JY, Kang SK, Kim YK (2007) Hypoxia/reoxygenation stimulates proliferation through PKC-dependent activation of ERK and Akt in mouse neural progenitor cells. Neurochem Res 32(11):1932–1939
Temple S (2001) The development of neural stem cells. Nature 414(6859):112–117
Viti J, Feathers A, Phillips J, Lillien L (2003) Epidermal growth factor receptors control competence to interpret leukemia inhibitory factor as an astrocyte inducer in developing cortex. J Neurosci 23(8):3385–3393
Wang B, Gao Y, Xiao Z, Chen B, Han J, Zhang J, Wang X, Dai J (2009) Erk1/2 promotes proliferation and inhibits neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells. Neurosci Lett 461(3):252–257
Yan Y, Bian W, Xie Z, Cao X, Le Roux I, Guillemot F, Jing N (2004) Stat3 signaling is present and active during development of the central nervous system and eye of vertebrates. Dev Dyn 231(2):248–257
Yoshimatsu T, Kawaguchi D, Oishi K, Takeda K, Akira S, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2006) Non-cell-autonomous action of STAT3 in maintenance of neural precursor cells in the mouse neocortex. Development 133(13):2553–2563
Zoeller RT, Rovet J (2004) Timing of thyroid hormone action in the developing brain: clinical observations and experimental findings. J Neuroendocrinol 16(10):809–818
Acknowledgments
We thank doctors Xubu Wang, Yutong Hao and Min Li for their hospitable and professional technical assistance. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 30670490) and State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. Chen and Z. Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Zhou, Z., Zhong, M. et al. Excess Thyroid Hormone Inhibits Embryonic Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells Proliferation and Maintenance through STAT3 Signalling Pathway. Neurotox Res 20, 15–25 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-010-9214-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-010-9214-y