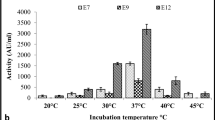
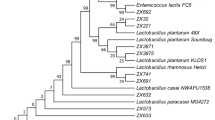
Abstract
This study aimed at characterizing two novel bacteriocin-producing enterococcal strains isolated from human intestine. A total of 200 lactic acid bacteria were isolated from a woman stool sample. Two of them were selected for characterization due to their high antimicrobial activity against five strains of Listeria monocytogenes. The selected bacteria were identified as two different strains of Enterococcus faecium and designated MT 104 and MT 162. The bacteriocins produced by MT 104 and MT 162 were stable at different pH ranging from 2 to 11 and were active after different treatments such as heat, enzymes, detergents, and γ-irradiation. The two isolated strains exhibited some probiotic properties such as survival in simulated gastric fluid and intestinal fluid, lack of expression of bile salt hydrolase or hemolytic activity, adhesion to Caco-2 cells efficiently, and sensitivity to clinical antimicrobial agents. Thus, the two isolated strains of E. faecium could become new probiotic bacteria and their bacteriocins could be used for controlling L. monocytogenes in combination with irradiation for food preservation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noguchi N, Nakaminami H, Nakase K, Sasatsu M (2011) Characterization of enterococcus strains contained in probiotic products. Biol Pharm Bull 34(9):1469–1473
Agerholm-Larsen L, Bell ML, Grunwald GK, Astrup A (2000) The effect of a probiotic milk product on plasma cholesterol: a meta-analysis of short-term intervention studies. Eur J Clin Nutr 54(11):856–860
Dunne C, O’Mahony L, Murphy L, Thornton G, Morrissey D, O’Halloran S, Feeney M, Flynn S, Fitzgerald G, Daly C, Kiely B, O’Sullivan GC, Shanahan F, Collins JK (2001) In vitro selection criteria for probiotic bacteria of human origin: correlation with in vivo findings. Am J Clin Nutr 73(2 Suppl):386S–392S
Foulquie Moreno MR, Sarantinopoulos P, Tsakalidou E, De Vuyst L (2006) The role and application of enterococci in food and health. Int J Food Microbiol 106(1):1–24
Almeida T, Brandao A, Munoz-Atienza E, Goncalves A, Torres C, Igrejas G, Hernandez PE, Herranz C, Cintas LM, Poeta P (2011) Identification of bacteriocin genes in enterococci isolated from game animals and saltwater fish. J Food Prot 74(8):1252–1260
Cintas LM, Rodríguez JM, Fernández MF, Sletten K, Nes IF, Hernández PE, Holo H (1995) Isolation and characterization of pediocin L50, a new bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici with a broad inhibitory spectrum. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(7):2643–2648
Nes IF, Diep DB, Holo H (2007) Bacteriocin diversity in Streptococcus and Enterococcus. J Bacteriol 189(4):1189–1198
Ananou S, Garriga M, Hugas M, Maqueda M, Martinez-Bueno M, Galvez A, Valdivia E (2005) Control of Listeria monocytogenes in model sausages by enterocin AS-48. Int J Food Microbiol 103(2):179–190
Laukova A, Czikkova S, Laczkova S, Turek P (1999) Use of enterocin CCM 4231 to control Listeria monocytogenes in experimentally contaminated dry fermented Hornad salami. Int J Food Microbiol 52(1–2):115–119
Lauková A, Vlaemynck G, Czikková S (2001) Effect of enterocin CMM 4231 on Listeria monocytogenes in Saint-Paulin cheese. Folia Microbiol 46(2):157–160
Aymerich T, Artigas MG, Garriga M, Monfort JM, Hugas M (2000) Effect of sausage ingredients and additives on the production of enterocin A and B by Enterococcus faecium CTC492. Optimization of in vitro production and anti-listerial effect in dry fermented sausages. J Appl Microbiol 88(4):686–694
Aymerich T, Garriga M, Ylla J, Vallier J, Monfort JM, Hugas M (2000) Application of enterocins as biopreservatives against Listeria innocua in meat products. J Food Prot 63(6):721–726
Millette M, Dupont C, Archambault D, Lacroix M (2007) Partial characterization of bacteriocins produced by human Lactococcus lactis and Pediococccus acidilactici isolates. J Appl Microbiol 102(1):274–282
Scheilfer KH, Kilpper-Bälz R (1984) Transfer of Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium to the genus Enterococcus nom. Rev as Enterococcus faecalis comb. Nov. and Enterococcus faecalis comb. Nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 34(1):31–34
Labbe N, Juteau P, Parent S, Villemur R (2003) Bacterial diversity in a marine methanol-fed denitrification reactor at the montreal biodome, Canada. Microbial Ecol 46(1):12–21
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Schillinger U, Lucke FK (1989) Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus sake isolated from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol 55(8):1901–1906
Zamfir M, Callewaert R, Cornea PC, Savu L, Vatafu I, De Vuyst L (1999) Purification and characterization of a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus IBB 801. J Appl Microbiol 87(6):923–931
Biedenbach DJ, Schermer IH, Jones RN (1997) Validation of Etest for seven antimicrobial agents using regulatory criteria for the assessment of antimicrobial susceptibility devices. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 27(1–2):1–5
Succi M, Tremonte P, Reale A, Sorrentino E, Grazia L, Pacifico S, Coppola R (2005) Bile salt and acid tolerance of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains isolated from Parmigiano Reggiano cheese. FEMS Microbiol Lett 244(1):129–137
Chauviere G, Coconnier MH, Kerneis S, Fourniat J, Servin AL (1992) Adhesion of human Lactobacillus acidophilus strain LB to human enterocyte-like Caco-2 cells. J Gen Microbiol 138:1689–1696
Alander M, Satokari R, Korpela R, Saxelin M, Vilpponen-Salmela T, Mattila-Sandholm T, von Wright A (1999) Persistence of colonization of human colonic mucosa by a probiotic strain, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG, after oral consumption. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(1):351–354
Hosseini SV, Arlindo S, Bohme K, Fernandez-No C, Calo-Mata P, Barros-Velazquez J (2009) Molecular and probiotic characterization of bacteriocin-producing Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from nonfermented animal foods. J Appl Microbiol 107(4):1392–1403
Belguesmia Y, Choiset Y, Prevost H, Dalgalarrondo M, Chobert JM, Drider D (2010) Partial purification and characterization of the mode of action of enterocin S37: a bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecalis S37 isolated from poultry feces. J Environ Public Health 2010:986460
Franz CM, Holzapfel WH, Stiles ME (1999) Enterococci at the crossroads of food safety? Int J Food Microbiol 47(1–2):1–24
Franz CM, van Belkum MJ, Holzapfel WH, Abriouel H, Galvez A (2007) Diversity of enterococcal bacteriocins and their grouping in a new classification scheme. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31(3):293–310
Lyon WJ, Olson DG, Murano EA (1995) Isolation and purification of Enterocin El1, a bacteriocin produced by a strain of Enterococcus Faecium. J Food Prot 58(8):890–898
Ivanova I, Miteva V, Stefanova T, Pantev A, Budakov I, Danova S, Moncheva P, Nikolova I, Dousset X, Boyaval P (1998) Characterization of a bacteriocin produced by Streptococcus thermophilus 81. Int J Food Microbiol 42(3):147–158
De Kwaadsteniet M, Todorov SD, Knoetze H, Dicks LM (2005) Characterization of a 3944 Da bacteriocin, produced by Enterococcus mundtii ST15, with activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 105(3):433–444
Bayoub K, Mardad I, Ammar E, Serrano A, Soukri A (2011) Isolation and purification of two bacteriocins 3D produced by Enterococcus faecium with inhibitory activity against Listeria monocytogenes. Curr Microbiol 62(2):479–485
Cintas LM, Casaus P, Holo H, Hernandez PE, Nes IF, Havarstein LS (1998) Enterocins L50A and L50B, two novel bacteriocins from Enterococcus faecium L50, are related to staphylococcal hemolysins. J Bacteriol 180(8):1988–1994
Floriano B, Ruiz-Barba JL, Jimenez-Diaz R (1998) Purification and genetic characterization of enterocin I from Enterococcus faecium 6T1a, a novel antilisterial plasmid encoded bacteriocin which does not belong to the pediocin family of bacteriocins. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4883–4890
Sung C, Kim BG, Kim S, Joo HS, Kim PI (2010) Probiotic potential of Staphylococcus hominis MBBL 2–9 as anti-Staphylococcus aureus agent isolated from the vaginal microbiota of a healthy woman. J Appl Microbiol 108(3):908–916
Ouwehand AC, Niemi P, Salminen SJ (1999) The normal faecal microflora does not affect the adhesion of probiotic bacteria in vitro. FEMS Microbiol Lett 177(1):35–38
Ruiz-Moyano S, Martin A, Benito MJ, Aranda E, Casquete R, Cordoba Mde G (2009) Safety and functional aspects of preselected enterococci for probiotic use in Iberian dry-fermented sausages. J Food Sci 74(7):M398–M404
Klingberg TD, Axelsson L, Naterstad K, Elsser D, Budde BB (2005) Identification of potential probiotic starter cultures for Scandinavian-type fermented sausages. Int J Food Microbiol 105(3):419–431
Galvez A, Lopez RL, Abriouel H, Valdivia E, Omar NB (2008) Application of bacteriocins in the control of foodborne pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. Crit Rev Biotechnol 28(2):125–152
Turgis M, Borsa J, Millette M, Salmieri S, Lacroix M (2008) Effect of selected plant essential oils or their constituents and modified atmosphere packaging on the radiosensitivity of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhi in ground beef. J Food Prot 71(3):516–521
Turgis M, Han J, Borsa J, Lacroix M (2008) Combined effect of natural essential oils, modified atmosphere packaging, and gamma radiation on the microbial growth on ground beef. J Food Prot 71(6):1237–1243
Turgis M, Han J, Millette M, Salmieri S, Borsa J, Lacroix M (2009) Effect of selected antimicrobial compounds on the radiosensitization of Salmonella Typhi in ground beef. Lett Appl Microbiol 48(6):657–662
Farkas J (1998) Irradiation as a method for decontaminating food. A review. Int J Food Microbiol 44(3):189–204
Aymerich T, Holo H, Havarstein LS, Hugas M, Garriga M, Nes IF (1996) Biochemical and genetic characterization of enterocin A from Enterococcus faecium, a new antilisterial bacteriocin in the pediocin family of bacteriocins. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(5):1676–1682
Franz CM, Schillinger U, Holzapfel WH (1996) Production and characterization of enterocin 900, a bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecium BFE 900 from black olives. Int J Food Microbiol 29(2–3):255–270
Purve WK, Sadava DE, Orians GH, Heller HC (2003) Life: the sicence of biology, 7th edn. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates and Freeman, New York, pp 961–984
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and BSA Food Ingredients s.e.c/l.p (Montreal, Qc, Canada) under a research contract agreement with INRS. The authors are grateful to Nordion Inc. for irradiation treatment. M. Turgis is a scholarship recipient of the Fondation Armand-Frappier. The Institute of Nutraceuticals and Functional Foods (INAF) is acknowledged for giving a supplemented scholarship to post-doc K.D.V.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turgis, M., Vu, K.D. & Lacroix, M. Partial Characterization of Bacteriocins Produced by Two New Enterococcus faecium Isolated from Human Intestine. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 5, 110–120 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-013-9129-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-013-9129-z