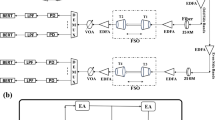
Abstract
The conversion of binary data to its equivalent decimal counterpart and the vice-versa is very essential and necessary for all optical/electrical computing and data processing systems. In this paper, the authors propose a new scheme for the optical conversion of frequency encoded binary data to its equivalent frequency encoded decimal form based on the optical tree architecture. This is completely associated with frequency encoding technique because of its salient advantages. The scheme is implemented with all optical nonlinear switch like Mach–Zehnder interferometer-based semiconductor optical amplifier (MZI-SOA) to get a faster conversion rate.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Mukhopadhyay, Role of optics in super-fast information processing. Indian J. Phys. 84(8), 1069–1074 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-010-0101-4
B. Ghosh, R.R. Pal, S. Mukhopadhyay, An all-optical integrated system for implementing arithmetic operation in 2’s complement method with the active participation of non-linear material based switches. Indian J. Phys. 84(8), 1101–1109 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-010-0105-0
S. Dey, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical high frequency clock pulse generator using the feedback mechanism in Toffoli gate with Kerr material. J. Nonlinear Opt. Phys. Mater. Matter 25, 1650012 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218863516500120
S. Sen, S. Mukhopadhyay, ‘A noble technique of using a specially cut LiNbO3 for achieving a greater amount phase difference between the components of light rays. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 124(11), 1011–1013 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.01.021
T. Yabu, M. Geshiro, T. Kitamura et al., All-optical logic gates containing a two-mode nonlinear waveguide. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 38(1), 37–46 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/3.973317
T. Fujisawa, M. Koshiba, All-optical logic gates based on nonlinear slot-waveguide couplers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 23(4), 684–691 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.23.000684
S.K. Garai, A. Pal, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical frequency-encoded inversion operation with tristate logic using reflecting semiconductor optical amplifiers. Optik (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2009.02.011
J.N. Roy, A.K. Maiti, S. Mukhopadhyay, Designing of an all-optical time division multiplexing scheme with the help of nonlinear material based tree-net architecture. Chin. Opt. Lett. 4(8), 483–486 (2006)
A. Sinha, H. Bhowmik, P. Kuila, S. Mukhopadhyay, New method of controlling the power of a Gaussian optical pulse through an electro-optic modulator and a nonlinear waveguide for generation of solitons. Opt. Eng. 44(6), 065003 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1117/1.1921207
K. Mallick, R. Mukherjee, B. Das, G.C. Mandal, A.S. Patra, Bidirectional hybrid OFDM based wireless-over-fiber transport system using reflective semiconductor amplifier and polarization multiplexing technique. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 96, 260–266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2018.09.041
R. Mukherjee, B. Das, G.C. Mandal, A.S. Patra, A full-duplex WDM hybrid fiber-wired/fiber-wireless/fiberVLC/fiber-IVLC transmission system based on a self-injection locked quantum dash laser and a RSOA. Opt. Commun. 427, 202–208 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2018.06.048
R. Mukherjee, B. Das, G.C. Mandal, A.S. Patra, Bidirectional and simultaneous transmission of baseband and wireless signals over RSOA based WDM radio-over-fiber passive optical network using incoherent light injection technique. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 80, 193–198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2017.07.030
A.S. Das, A.S. Patra, Bidirectional transmission of 10 Gbps using RSOA based WDM-PON and optical carrier suppression scheme. J. Opt. Commun. 35(3), 239–243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1515/joc-2013-0166
A.S. Das, P.K. Kuiri, A.S. Patra, A RSOA based full-duplex 80 channel CATV signal with 1.25 Gbps data-stream transmission system using optical carrier suppression and injection-locked FPLDs. SPIE Proc. 9654, 96541T-T96551 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2182645
A.S. Das, A.S. Patra, RSOA-based full-duplex WDM-PON for 20 Gbps transmission in two channels over a long-haul smf using external modulation scheme. J. Opt. Commun. 36(3), 231–235 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/joc-2014-0059
M.J. Connelly, Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 2002)
N.K. Dutta, Q. Wang, Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, 2006)
K. Obermann, S. Kindt, D. Breuer et al., Performance analysis of wavelength converters based on cross-gain modulation in semiconductor optical amplifiers. J. Lightwave Technol. 16(1), 78–85 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/50.654987
S.K. Chandra, S. Mukhopadhyay, An all-optical approach of implementing a different kind of phase encoded XOR and XNOR logic operations with the help of four wave mixing in SOA. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 124(6), 505–507 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2011.12.048
D.-X. Wang, J.A. Buck, K. Brennan et al., Numerical model of wavelength conversion through cross-gain modulation in semiconductor optical amplifiers. Appl. Opt. 45(19), 4701–4708 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.45.004701
S.K. Chandra, S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, Phase-encoded all-optical reconfigurable integrated multi logic unit using phase information processing of four-wave mixing in semiconductor optical amplifier. IET Optoelectron. 10(1), 1–6 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-opt.2014.0066
S. Singh, R.S. Kaler, ‘All optical wavelength converters based on cross phase modulation in SOA-MZI configuration. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 118(8), 390–394 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2006.04.010
A.K. Maiti, J.N. Roy, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical conversion scheme from binary to its MTN form with the help of nonlinear material based tree net architecture. Chin. Opt. Lett. 5(8), 480–483 (2007)
S. Dutta, S. Mukhopadhyay, All optical frequency encoding method for converting a decimal number to its equivalent binary number using tree architecture. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 122(2), 125–127 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2009.11.018
S. Dutta, S. Mukhopadhyay, All-optical approach for conversion of a binary number having a fractional part to its decimal equivalent and vice-versa. Opt. Photonics Lett. 03(01), 51–59 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793528810000104
S. Mukhopadhyay, An optical conversion systems from binary to decimal and decimal to binary. Opt. Commun. 76(5–6), 309–312 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0030-4018(90)90257-T
S. Saha, S. Biswas, S. Mukhopadhyay, Optical scheme of conversion of a positionally encoded decimal digit to frequency encoded Boolean form using Mach–Zehnder interferometer-based semiconductor optical amplifier. IET Optoelectron. 11(5), 201–207 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-opt.2016.0078
B. Ghosh, R.R. Pal, S. Mukhopadhyay, A new approach to all-optical half-adder by utilizing semiconductor optical amplifier based MZI wavelength converter. Optik Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 122(20), 1804 (2011)
Wu. Jian-Wei, A.K. Sarma, Ultrafast all-optical XOR logic gate based on a symmetrical Mach–Zehnder interferometer employing SOI waveguides. Opt. Commun. 283(14), 2914–2917 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2010.02.045
C. Reis, R. Dionísio, B. Neto, A. Teixeira, P.S. André, All optical xor based on integrated mzi-soa with co and counter propagation scheme, in International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks, Mediterranean Winter Conference, 3, Angers, Dezembro 2009. Angèrs: IEEE, 2009. p. 1–4, URL: http://hdl.handle.net/10400.11/470
S. Saha, S. Dey, S. Mukhopadhyay, All optical wavelength encoded 1-bit memory unit exploiting the nonlinear character of asymmetric mzi-soa switch. Accepted for poster presentation in The International Conference on Fiber Optics and Photonics (Photonics 2016), December, https://doi.org/10.1364/PHOTONICS.2016.Th3A.32
M. Spyropoulou, N. Pleros, A. Miliou, SOA-MZI-based nonlinear optical signal processing: a frequency domain transfer function for wavelength conversion, clock recovery, and packet envelope detection. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/JQE.2010.2071411
W. Wu, S. Campbell, S. Zhou et al., Polarization-encoded optical logic operations in photorefractive media. Opt. Lett. 18(20), 1742–1744 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.18.001742
K.W. Wong, L.M. Cheng, M.C. Poon, Design of digital–optical processors by using both intensity and polarization–encoding schemes. Appl. Opt. 31(17), 3225–3232 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.31.003225
B. Chakarborty, S. Mukhophahyay, All-optical method of developing half and full subtractor by the use of phase encoding principle. Optik Int. J. Light Electron. Opt. 122(24), 2207–2210 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2011.01.014
Y. Guan, Demonstration of an optical switch based on SOA-MZI operation at 10 Gbit/s, in International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Software Engineering (ICAISE 2013), The authors-Published by Atlantis Press
V. Krishnamurthy, Y. Chen, Q. Wang, MZI-semiconductor-based all-optical switch with switching gain. J. Lightwave Technol. 32(13), 2433 (2014)
M. Ding, A. Wonfor, Q. Cheng, R.V. Penty, I.H. White, Hybrid MZI-SOA InGaAs/InP photonic integrated switches. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 24(1), 1–8 (2017). https://doi.org/10.17863/CAM.13398
A. Abd El Aziz, W.P. Ng, Z. Ghassemlooy, M.H. Aly, M.F. Chiang, Optimisation of the key SOA parameters for amplification and switching. Academia, RN 2, 3, 2008
C. Michie, A.E. Kelly, I. Armstrong, I. Andonovic, C. Tombling, An Adjustable gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier (AGC-SOA). J. Lightwave Technol. 25(6), 1466 (2007)
N. Pleros, C. Bintjas, M. Kalyvas, G. Theophilopoulos, K. Yiannopoulos, S. Sygletos, H. Avramopoulos, Multiwavelength and power equalized SOA laser sources. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 14(5), 693 (2002)
R.A. Johni, D.I. Forsyth, K.R. Tariq, Effects on semiconductor optical amplifier gain quality for applications in advanced all-optical communication systems. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 7(16), 3414–3418 (2014)
J. Kurumida, H. Uenohara, K. Kobayashi, All-optical label recognition for time-domain signal using multistage switching scheme based on SOA-MZIs. Electron. Lett. 42(2), 1362 (2006)
T. Segawa, S. Matsuo, T. Ishii, Y. Ohiso, Y. Shibata, H. Suzuki, High-speed wavelength-tunable optical filter using cascaded Mach–Zehnder interferometers with apodized sampled gratings. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 44(10), 922–930 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/JQE.2008.2000920
O. Aharon, I. Abdulhalim, Tunable optical filter having a large dynamic range. Opt. Lett. 34(14), 2114 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. Subhendu Biswas, Assistant Professor, UIT-Burdwan, for his contribution to the simulation part of the present scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, S., Biswas, S. & Mukhopadhyay, S. An alternative approach for binary to decimal conversion of frequency encoded optical data using MZI-SOA Switch. J Opt 51, 357–370 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-021-00786-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-021-00786-9