Abstract
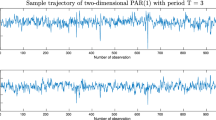
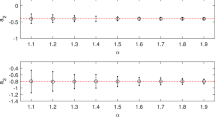
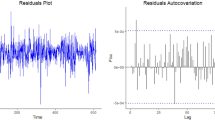
Many real data exhibit periodic behavior. The periodic autoregressive moving average (PARMA) is one of the most common and useful model to describe these data. In the classical case, the PARMA model is considered by the assumption of Gaussian (or finite-variance) distribution of the noise. However, the Gaussian distribution seems to be unsuitable in many real applications, especially when the corresponding data exhibit impulsive-like behavior. Therefore, the extensions of the classical PARMA models are considered and the Gaussian distribution of the noise is replaced by the so-called heavy-tailed distribution. One of the most known distribution that can be used here is the \(\alpha -\) stable one. In this paper, we introduce a new estimation technique for the parameters of the multidimensional periodic autoregressive time series of order 1 (i.e., PAR(1)), which is based on fractional lower-order covariance, the alternative dependence measure adequate for \(\alpha -\)stable distributed models. From theoretical point of view, the use of this technique is justified as in this case the classical measure (i.e., covariance) is not defined. The practical aspect of this technique is discussed. The efficiency of the technique on simulated data is demonstrated using the Monte Carlo approach in different contexts, including the sample size and index of stability \(\alpha \) of the noise’s distribution. Lastly, we present the real data analysis.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data are free available.
References
Broszkiewicz-Suwaj, E., Makagon, A., Weron, R., Wyłomańska, A.: On detecting and modeling periodic correlation in financial data. Physica A Stat. Mech. Appl. 336(1–2), 196–205 (2004)
Franses, P.: Periodicity and Stochastic Trends in Economic Time Series. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1996)
Brelsford, M., Jones, R.: Time series with periodic structure. Biometrika 54, 403–407 (1967)
Bukofzer, D.: Optimum and suboptimum detector performance for signals in cyclostationary noise. J. Ocean. Eng. 12, 97–115 (1987)
Donohue, K., Bressler, J., Varghese, T., Bilgutay, N.: Spectral correlation in ultrasonic pulse-echo signal processing. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 40, 330–337 (1993)
Fellingham, L., Sommer, F.: Ultrasonic characterization of tissue structure in the in vivo human liver and spleen. IEEE Trans. Son. Ultrason. 31, 418–428 (1984)
Antoni, J.: Cyclostationarity by examples. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 23(4), 987–1036 (2009)
Antoni, J., Bonnardot, F., Raad, A., El Badaoui, M.: Cyclostationary modelling of rotating machine vibration signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 18(6), 1285–1314 (2004)
Bloomfield, P., Hurd, H., Lund, R.: Periodic correlation in stratospheric ozone time series. J. Time Series Anal. 15, 127–150 (1994)
Dargaville, R., Doney, S., Fung, I.: Inter-annual variability in the interhemispheric atmospheric CO2 gradient. Tellus B 15, 711–722 (2003)
Jones, R., Brelsford, W.: Time series with periodic structure. Biometrika 54, 403–8 (1968)
Troutman, B.: Some results in periodic autoregression. Biometrika 66, 219–228 (1979)
Hipel,K. W. , McLeod,A. I.: Chapter 14 Periodic Models, in: Time Series Modelling of Water Resources and Environmental Systems, Vol. 45 of Developments in Water Science, Elsevier, pp. 483–524 (1994)
Adams, G.J., Goodwin, G.C.: Parameter estimation for periodic ARMA models. J. Time Series Anal. 16(2), 127–145 (1995)
Lund, R., Basawa, I.V.: Recursive prediction and likelihood evaluation for periodic ARMA models. J. Time Series Anal. 21(1), 75–93 (2000)
Basawa, I.V., Lund, R.: Large sample properties of parameter estimates for periodic ARMA models. J. Time Series Anal. 22(6), 651–663 (2001)
Shao, Q., Lund, R.: Computation and characterization of autocorrelations and partial autocorrelations in periodic ARMA models. J. Time Series Anal. 25(3), 359–372 (2004)
Anderson, P.L., Meerschaert, M.M.: Parameter estimation for periodically stationary time series. J. Time Series Anal. 26(4), 489–518 (2005)
Ursu, E., Turkman, K.F.: Periodic autoregressive model identification using genetic algorithms. J. Time Series Anal. 33(3), 398–405 (2012)
Anderson, P.L., Meerschaert, M.M., Zhang, K.: Forecasting with prediction intervals for periodic autoregressive moving average models. J. Time Series Anal. 34(2), 187–193 (2013)
Brockwell, P.J., Davis, R.A.: Introduction to Time Series and Forecasting. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Jachan, M., Matz, G., Hlawatsch, F.: Time-frequency ARMA models and parameter estimators for underspread nonstationary random processes. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(9), 4366–4381 (2007)
Makagon, A., Weron, A., Wyłomańska, A.: Bounded solutions for ARMA model with varying coefficients. Appl. Math. 31, 273–285 (2004)
Zielinski, J., Bouaynaya, N., Schonfeld, D., O Neill, W.: Time-dependent ARMA modeling of genomic sequences. BMC Bioinform. 9(Suppl 9), S14 (2008)
Hurd, H.L., Miamee, A.: Periodically Correlated Random Sequences: Spectral Theory and Practice, vol. 355. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (2007)
Nowicka-Zagrajek, J., Weron, R.: Modeling electricity loads in California: ARMA models with hyperbolic noise. Signal Process. 82(12), 1903–1915 (2002)
Palacios, M.B., Steel, M.F.J.: Non-Gaussian Bayesian geostatistical modeling. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 101(474), 604–618 (2006)
Gosoniu, L., Vounatsou, P., Sogoba, N., Smith, T.: Bayesian modelling of geostatistical malaria risk data. Geospat. Health 1(1), 127–139 (2006)
Mittnik, S., Rachev, S.T.: Stable Paretian Models in Finance. Wiley, New York (2000)
Żak, G., Wyłomańska, A., Zimroz, R.: Periodically impulsive behaviour detection in noisy observation based on generalised fractional order dependency map. Appl. Acoust. 144, 31–39 (2019)
Żak,G., Wyłomańska,A., Zimroz,R.: Data driven iterative vibration signal enhancement strategy using alpha-stable distribution, Shock and Vibration 2017 Article ID 3698370 (2017) 11 pages
Chen, Z., Ding, S.X., Peng, T., Yang, C., Gui, W.: Fault detection for non-Gaussian processes using generalized canonical correlation analysis and randomized algorithms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(2), 1559–1567 (2018)
Takayasu, H.: Stable distribution and Lévy process in fractal turbulence. Prog. Theo. Phys. 72(3), 471–479 (1984)
Kruczek, P., Zimroz, R., Wyłomańska, A.: How to detect the cyclostationarity in heavy-tailed distributed signals. Signal Process. 172, 107514 (2020)
Kruczek, P., Wyłomańska, A., Teuerle, M., Gajda, J.: The modified Yule-Walker method for alpha-stable time series models. Physica A 469, 588–603 (2017)
Nowicka-Zagrajek, J., Wylomanska, A.: The dependence structure for parma models with alpha-stable innovations. Acta Physica Polonica 37(1), 3071–3081 (2006)
Samorodnitsky, G., Taqqu, M.: Stable Non-Gaussian Random Processes: Stochastic Models with Infinite Variance. Chapman and Hall, London (1994)
Kozubowski, T.J., Panorska, A.K., Rachev, S.T.: Statistical issues in modeling multivariate stable portfolios. In: Rachev, S.T. (ed.) Handbook of Heavy Tailed Distributions in Finance. Handbooks in Finance, vol. 1, pp. 131–167. North-Holland, Amsterdam (2003)
Nolan, J.P., Panorska, A.K.: Data analysis for heavy tailed multivariate samples. Commun. Stat. Stoch. Models 13(4), 687–702 (1997)
Kozubowski, T.J., Panorska, A.K.: Multivariate geometric stable distributions in financial applications. Math. Comput. Modell. 29(10–12), 83–92 (1999)
Stoyanov, S.V., Samorodnitsky, G., Rachev, S., Ortobelli, S.: Computing the portfolio conditional Value-at-Risk in the alpha-stable case. Probab. Math. Stat. 26, 1–22 (2006)
Samorodnitsky, G., Taqqu, M.S.: Stable Non-Gaussian Random Processes: Stochastic Models with Infinite Variance. Chapman & Hall, New York (1994)
Nowicka, J.: Asymptotic behavior of the covariation and the codifference for ARMA models with stable innovations. Commun. Stat. Stoch. Models 13(4), 673–685 (1997)
Kokoszka, P.S., Taqqu, M.S.: Fractional ARIMA with stable innovations. Stoch. Process. Appl. 60(1), 19–47 (1995)
Rosadi, D., Deistler, M.: Estimating the codifference function of linear time series models with infinite variance. Metrika 73, 395–429 (2011)
Rosadi, D.: Order identification for Gaussian moving averages using the codifference function. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 76(6), 553–559 (2006)
Wyłomańska, A., Chechkin, A., Sokolov, I.M., Gajda, J.: Codifference as a practical tool to measure interdependence. Physica A 421, 412–429 (2015)
Liu, T.-H., Mendel, J.M.: A subspace-based direction finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49(8), 1605–1613 (2001)
Chen, Z., Geng, X., Yin, F.: A harmonic suppression method based on fractional lower order statistics for power system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(6), 3745–3755 (2016)
Aalo, V.A., Ackie, A.-B.E., Mukasa, C.: Performance analysis of spectrum sensing schemes based on fractional lower order moments for cognitive radios in symmetric \(\alpha \)-stable noise environments. Signal Process. 154, 363–374 (2019)
Grzesiek,A., Teuerle,M., Wyłomańska,A.: Cross-codifference for bidimensional VAR(1) models with infinite variance, Published online in Communications in Statistics - Simulation and Computation https://doi.org/10.1080/03610918.2019.1670840
Grzesiek, A., Teuerle, M., Sikora, G., Wyłomańska, A.: Spatial-temporal dependence measures for \(\alpha -\)stable bivariate AR(1). J. Time Series Anal. 41(3), 454–475 (2020)
Stoica, P.: Generalized yule-walker equations and testing the orders of multivariate time series. Int. J. Control 37(5), 1159–1166 (1983)
Basu, R.G.S.: A note on properties of spatial yule-walker estimators. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 41(3–4), 243–255 (1992)
Choi, B.: On the covariance matrix estimators of the white noise process of a vector autoregressive model. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 23, 249–256 (1994)
Choi, B.: The asymptotic joint distribution of the yule-walker estimators of a causal multidimensional ar process. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 30, 609–614 (2001)
Gallagher, C.M.: A method for fitting stable autoregressive models using the autocovariation function. Stat. Probab. Lett. 53, 381–390 (2001)
Kruczek, P., Żuławiński, W., Pagacz, P., Wyłomańska, A.: Fractional lower order covariance based-estimator for ornstein-uhlenbeck process with stable distribution. Math. Appl. 47(2), 259–292 (2019)
Grzesiek, A., Sundar, S., Wyłomańska, A.: Fractional lower order covariance-based estimator for bidimensional AR(1) model with stable distribution. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. Appl. Math. 11, 217–229 (2019)
Miller, G.: Properties of certain symmetric stable distributions. J. Multivar. Anal. 8(3), 346–360 (1978)
Weron, A.: Stable processes and measures; a survey. In: Szynal, D., Weron, A. (eds.) Probability Theory on Vector Spaces III, pp. 306–364. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (1984)
Zolotarev, V.M.: One-dimensional stable distributions, Translations of Mathematical Monographs. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1986)
Nowicka-Zagrajek, J., Wyłomańska, A.: Measures of dependence for stable AR(1) models with time-varying coefficients. Stoch. Models 24(1), 58–70 (2008)
Grzesiek, A., Giri, P., Sundar, S., Wyłomańska, A.: Measures of cross-dependence for bidimensional periodic AR(1) model with \(\alpha -\)stable distribution. J. Time Series Anal. 41(6), 785–807 (2020)
Grzesiek, A., Wylomanska, A.: Asymptotic behavior of the cross-dependence measures for bidimensional AR(1) model with \(\alpha -\)stable noise. Banach Center Publ. 122, 133–157 (2020)
Zak, G., Teuerle, M., Wylomanska, A., Zimroz, R.: Measures of dependence for alpha-stable distributed processes and its application to diagnostics of local damage in presence of impulsive noise. Shock Vib. 6, 1–9 (2017)
Ma, N.C.X.: Joint estimation of time delay and frequency delay in impulsive noise using fractional lower order statistics. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 44, 2669–2687 (1996)
Peiris, M.S., Thavansewaran, A.: Multivariate stable ARMA processes with time dependent coefficients. Metrika 54, 131–138 (2001)
Hourly elspot prices and volumes (hourly) in SE3 area, 14th August 2019 - 11th November 2019, available for free on https://www.nordpoolgroup.com/historical-market-data/ (column SE3)
McCulloch,J. H.: Financial applications of stable distributions, in: Statistical Methods in Finance, Vol. 14 of Handbook of Statistics, Elsevier, (1996), pp. 393–425
Borak, S., Misiorek, A., Weron, R.: Models for heavy-tailed asset returns. In: Statistical Tools for Finance and Insurance, pp. 21–55. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Ocłoń, P., Łopata, S., Nowak, M.: Comparative study of conjugate gradient algorithms performance on the example of steady-state axisymmetric heat transfer problem. Arch. Thermodyn. 3, 15–44 (2013)
Saad,Y.: Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, (2003)
Barrett,R., Berry,M., Chan,T., Demmel, J., Donato,J., Dongarra,J., Eijkhout,V., Pozo,R., Romine,C., van der Vorst,H.: Templates for the Solution of Linear Systems: Building Blocks for Iterative Methods, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, (1994)
van der Vorst, H.: Bi-cgstab: a fast and smoothly converging variant of bi-cg for the solution of nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 13(2), 631–644 (1992)
Funding
The work of P. Giri and S. Sundar was supported by Indian Institute of Technology Madras, India, under the Project No. SB20210848MAMHRD008558 ”Centre for Computational Mathematics and Data Science, Department of Mathematics, IIT Madras Chennai India.” The work of A. Wyłomańska was supported by the National Center of Science under Opus Grant 2020/37/B/HS4/00120 ”Market risk model identification and validation using novel statistical, probabilistic, and machine learning tools.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
[ S.S, A.W, P.G] contributed to conceptualization, [A.W, P.G] contributed to methodology, [ P.G] contributed to formal analysis and investigation, [P.G, A.W] contributed to writing—original draft preparation, [P.G, A.W] contributed to writing—review and editing, and [S.S, A.W] contributed to supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
A Algorithms and additional tables
A Algorithms and additional tables
In this section, we show that how to solve the consistent system of Eq. (38). Since the FLOC-based matrix can be singular or non-singular, i.e., \(\widehat{\mathbf {R_d}}^{v-1}(0)\) may be singular or non-singular for each \(v = 1,\ldots ,T\). The following procedure (algorithm) can be used to solve the system of Eq. (38) in any case.

where BICGSTAB is a procedure (algorithm) for solving linear systems of equations \(\mathbf{A} x = b \) (for example) with preconditioning, where \(\mathbf{A} \) is the coefficient matrix, which may be singular or non-singular, \(\mathbf{x} \) is the unknown vector, and \(\mathbf{b} \) is the known vector. It is the most recent and up-to-date process. For more information on BICGSTAB, see [72,73,74,75].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giri, P., Sundar, S. & Wyłomańska, A. Fractional lower-order covariance (FLOC)-based estimation for multidimensional PAR(1) model with \(\alpha -\)stable noise. Int J Adv Eng Sci Appl Math 13, 215–235 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12572-021-00301-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12572-021-00301-0