Abstract
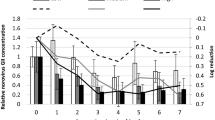
Bivalve mollusks as filter-feeders concentrate in their digestive tissue microorganisms likely present in the harvesting water, thus becoming risky food especially if consumed raw or poorly cooked. To eliminate bacteria and viruses eventually accumulated, they must undergo a depuration process which efficacy on viruses is on debate. To better clarify the worth of the depuration process on virus elimination from mussels, in this study we investigated rotavirus kinetics of accumulation and depuration in Mytilus galloprovincialis experimentally contaminated. Depuration process was monitored for 9 days and virus residual presence and infectivity were evaluated by real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, cell culture and electron microscopy at days 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9 of depuration. Variables like presence of ozone and of microalgae feeding were also analyzed as possible depuration enhancers. Results showed a two-phase virus removal kinetic with a high decrease in the first 24 h of depuration and 5 days necessary to completely remove rotavirus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoroso, M. G., Salzano, C., Cioffi, B., Napoletano, M., Garofalo, F., Guarino, A., & Fusco, G. (2011). Validation of a real-time PCR assay for fast and sensitive quantification of Brucella spp. in water buffalo milk. Food Control, 22(8), 1466–1470,
Araud, E., Di Caprio, E., Yang, Z., Li, X., Lou, F., Hughes, J. H., et al. (2015). High-pressure inactivation of rotaviruses: Role of treatment temperature and strain diversity in virus inactivation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,81(19), 6669–6678. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01853-15.
Araud, E., DiCaprio, E., Ma, Y., Lou, F., Gao, Y., Kingsley, D., et al. (2016). Thermal inactivation of enteric viruses and bioaccumulation of enteric foodborne viruses in live oysters (Crassostrea virginica). Applied and Environmental Microbiology,82(7), 2086–2099. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03573-15.
Bongiorno, T., Iacumin, L., Tubaro, F., Marcuzzo, E., Sensidoni, A., & Tulli, F. (2015). Seasonal changes in technological and nutritional quality of Mytilus galloprovincialis from suspended culture in the Gulf of Trieste (North Adriatic Sea). Food Chemistry,173, 355–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.029.
Boxman, I. L., Verhoef, L., Vennema, H., Ngui, S. L., Friesema, I. H., Whiteside, C., et al. (2016). International linkage of two food-borne hepatitis A clusters through traceback of mussels, The Netherlands, 2012. Euro Surveillance: Bulletin Europeen Sur Les Maladies Transmissibles = European Communicable Disease Bulletin, 21(3), 30113. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2016.21.3.30113.
Butt, A. A., Aldridge, K. E., & Sanders, C. V. (2004). Infections related to the ingestion of seafood. Part I: Viral and bacterial infections. The Lancet: Infectious Diseases, 4(4), 201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(04)00969-7.
Cho, H. G., Lee, S. G., Lee, M. Y., Hur, E. S., Lee, J. S., Park, P. H., et al. (2016). An outbreak of norovirus infection associated with fermented oyster consumption in South Korea. Epidemiology and Infection,144(13), 2759–2764. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268816000170.
Costafreda, M. I., Bosch, A., & Pinto, R. M. (2006). Development, evaluation, and standardization of a real-time TaqMan reverse transcription-PCR assay for quantification of hepatitis A virus in clinical and shellfish samples. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,72(6), 3846–3855.
Croci, L., Ciccozzi, M., De Medici, D., Di Pasquale, S., Fiore, A., Mele, A., et al. (1999). Inactivation of hepatitis A virus in heat-treated mussels. Journal of Applied Microbiology,87(6), 884–888.
De Medici, D., Ciccozzi, M., Fiore, A., Di Pasquale, S., Parlato, A., Ricci-Bitti, P., et al. (2001). Closed-circuit system for the depuration of mussels experimentally contaminated with hepatitis A virus. Journal of Food Protection,64(6), 877–880. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028x-64.6.877.
Fusco, G., Di Bartolo, I., Cioffi, B., Ianiro, G., Palermo, P., Monini, M., et al. (2017). Prevalence of foodborne viruses in mussels in southern Italy. Food and Environmental Virology,9(2), 187–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-016-9277-x.
Gentry, J., Vinje, J., & Lipp, E. K. (2009). A rapid and efficient method for quantitation of genogroups I and II norovirus from oysters and application in other complex environmental samples. Journal of Virological Methods,156(1–2), 59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2008.11.001.
Hu, L., Crawford, S. E., Czako, R., Cortes-Penfield, N. W., Smith, D. F., Le Pendu, J., et al. (2012). Cell attachment protein VP8* of a human rotavirus specifically interacts with A-type histo-blood group antigen. Nature,485(7397), 256–259. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10996.
Huang, P., Xia, M., Tan, M., Zhong, W., Wei, C., Wang, L., et al. (2012). Spike protein VP8* of human rotavirus recognizes histo-blood group antigens in a type-specific manner. Journal of Virology,86(9), 4833–4843. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.05507-11.
Ianiro, G., Delogu, R., Bonomo, P., Fiore, L., Ruggeri, F. M., & RotaNet-Italy Study Group. (2014). Molecular analysis of group A rotaviruses detected in adults and adolescents with severe acute gastroenteritis in Italy in 2012. Journal of Medical Virology,86(6), 1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.23871.
Keller, R., Justino, J. F., & Cassini, S. T. (2013). Assessment of water and seafood microbiology quality in a mangrove region in Vitoria. Brazil. Journal of Water and Health,11(3), 573–580. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2013.245.
Le Guyader, F. S., Le Saux, J. C., Ambert-Balay, K., Krol, J., Serais, O., Parnaudeau, S., et al. (2008). Aichi virus, norovirus, astrovirus, enterovirus, and rotavirus involved in clinical cases from a French oyster-related gastroenteritis outbreak. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,46(12), 4011–4017. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01044-08.
Le Guyader, F. S., Atmar, R. L., & Le Pendu, J. (2012). Transmission of viruses through shellfish: When specific ligands come into play. Current Opinion in Virology,2(1), 103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.029.
Lodder, W. J., & de Roda Husman, A. M. (2005). Presence of noroviruses and other enteric viruses in sewage and surface waters in The Netherlands. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,71(3), 1453–1461.
Love, D. C., Lovelace, G. L., & Sobsey, M. D. (2010). Removal of Escherichia coli, Enterococcus fecalis, coliphage MS2, poliovirus, and hepatitis A virus from oysters (Crassostrea virginica) and hard shell clams (Mercinaria mercinaria) by depuration. International Journal of Food Microbiology,143(3), 211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.08.028.
Lunestad, B. T., Maage, A., Roiha, I. S., Myrmel, M., Svanevik, C. S., & Duinker, A. (2016). An outbreak of norovirus infection from shellfish soup due to unforeseen insufficient heating during preparation. Food and Environmental Virology,8(4), 231–234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-016-9245-5.
Maalouf, H., Zakhour, M., Le Pendu, J., Le Saux, J. C., Atmar, R. L., & Le Guyader, F. S. (2010). Distribution in tissue and seasonal variation of norovirus genogroup I and II ligands in oysters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,76(16), 5621–5630. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00148-10.
Mattison, K., Harlow, J., Morton, V., Cook, A., Pollari, F., Bidawid, S., et al. (2010). Enteric viruses in ready-to-eat packaged leafy greens. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 16(11), 1815–1817, discussion 1817. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1611.100877.
McLeod, C., Hay, B., Grant, C., Greening, G., & Day, D. (2009). Inactivation and elimination of human enteric viruses by Pacific oysters. Journal of Applied Microbiology,107(6), 1809–1818. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04373.x.
McLeod, C., Polo, D., Le Saux, J. C., & Le Guyader, F. S. (2017). Depuration and relaying: A review on potential removal of Norovirus from oysters. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,16, 692–706.
Mezzanotte, V., Marazzi, F., Bissa, M., Pacchioni, S., Binelli, A., Parolini, M., et al. (2016). Removal of enteric viruses and Escherichia coli from municipal treated effluent by zebra mussels. The Science of the Total Environment,539, 395–400.
Nappier, S. P., Graczyk, T. K., & Schwab, K. J. (2008). Bioaccumulation, retention, and depuration of enteric viruses by Crassostrea virginica and Crassostrea ariakensis oysters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,74(22), 6825–6831. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01000-08.
Oliveira, A. R., Sykes, A. V., Hachero-Cruzado, I., Azeiteiro, U. M., & Esteves, E. (2015). A sensory and nutritional comparison of mussels (Mytilus sp.) produced in NW Iberia and in the Armona Offshore Production Area (Algarve, Portugal). Food Chemistry,168, 520–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.082.
Parada-Fabian, J. C., Juarez-Garcia, P., Natividad-Bonifacio, I., Vazquez-Salinas, C., & Quinones-Ramirez, E. I. (2016). Identification of enteric viruses in foods from Mexico City. Food and Environmental Virology,8(3), 215–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-016-9244-6.
Park, H., Jung, S., Shin, H., Ha, S. D., Park, T. J., Park, J. P., et al. (2019). Localization and persistence of hepatitis A virus in artificially contaminated oysters. International Journal of Food Microbiology,299, 58–63.
Polo, D., Alvarez, C., Longa, A., & Romalde, J. L. (2014a). Effectiveness of depuration for hepatitis A virus removal from mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). International Journal of Food Microbiology,180, 24–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.04.001.
Polo, D., Avarez, C., Vilarino, M. L., Longa, A., & Romalde, J. L. (2014b). Depuration kinetics of hepatitis A virus in clams. Food Microbiology,39, 103–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2013.11.011.
Polo, D., Feal, X., Varela, M. F., Monteagudo, A., & Romalde, J. L. (2014c). Depuration kinetics of murine norovirus in shellfish. Food Research International (Ottawa, Ontario),64, 182–187.
Polo, D., Feal, X., & Romalde, J. L. (2015a). Mathematical model for viral depuration kinetics in shellfish: An useful tool to estimate the risk for the consumers. Food Microbiology,49, 220–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2015.02.015.
Polo, D., Varela, M. F., & Romalde, J. L. (2015b). Detection and quantification of hepatitis A virus and norovirus in Spanish authorized shellfish harvesting areas. International Journal of Food Microbiology,193, 43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.10.007.
Powell, A., & Scolding, J. W. (2018). Direct application of ozone in aquaculture systems. Reviews in Aquaculture,10(2), 424–438.
Prevost, B., Lucas, F. S., Goncalves, A., Richard, F., Moulin, L., & Wurtzer, S. (2015). Large scale survey of enteric viruses in river and waste water underlines the health status of the local population. Environment International,79, 42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.03.004.
Purpari, G., Macaluso, G., Di Bella, S., Gucciardi, F., Mira, F., Di Marco, P., et al. (2019). Molecular characterization of human enteric viruses in food, water samples, and surface swabs in Sicily. International Journal of Infectious Diseases: Official Publication of the International Society for Infectious Diseases,80, 66–72.
Quiroz-Santiago, C., Vazquez-Salinas, C., Natividad-Bonifacio, I., Barron-Romero, B. L., & Quinones-Ramirez, E. I. (2014). Rotavirus G2P[4] detection in fresh vegetables and oysters in Mexico City. Journal of Food Protection,77(11), 1953–1959. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-13-426.
Ramani, S., & Giri, S. (2019). Influence of histo blood group antigen expression on susceptibility to enteric viruses and vaccines. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1097/QCO.0000000000000571.
Raposo, M. F., de Morais, R. M., & Bernardo de Morais, A. M. (2013). Bioactivity and applications of sulphated polysaccharides from marine microalgae. Marine Drugs,11(1), 233–252. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010233.
Richards, G. P., McLeod, C., & Le Guyader, F. S. (2010). Processing strategies to inactivate viruses in shellfish. Food and Environmental Virology,2, 183–193.
Romalde, J. L., Rivadulla, E., Varela, M. F., & Barja, J. L. (2018). An overview of 20 years of studies on the prevalence of human enteric viruses in shellfish from Galicia, Spain. Journal of Applied Microbiology,124(4), 943–957. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13614.
Ruggeri, F. M., & Greenberg, H. B. (1991). Antibodies to the trypsin cleavage peptide VP8 neutralize rotavirus by inhibiting binding of virions to target cells in culture. Journal of Virology,65(5), 2211–2219.
Souza, D. S., Piazza, R. S., Pilotto, M. R., do Nascimento Mde, A., Moresco, V., Taniguchi, S., & Barardi, C. R. (2013). Virus, protozoa and organic compounds decay in depurated oysters. International Journal of Food Microbiology,167(3), 337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.09.019.
Souza, D. S. M., Dominot, A. F. A., Moresco, V., & Barardi, C. R. M. (2018). Presence of enteric viruses, bioaccumulation and stability in Anomalocardia brasiliana clams (Gmelin, 1791). International Journal of Food Microbiology,266, 363–371.
Tate, J. E., Patel, M. M., Cortese, M. M., Payne, D. C., Lopman, B. A., Yen, C., et al. (2016). Use of patients with diarrhea who test negative for rotavirus as controls to estimate rotavirus vaccine effectiveness through case–control studies. Clinical Infectious Diseases: An Official Publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America,62(Suppl 2), S106–S114. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ1014.
Ueki, Y., Shoji, M., Suto, A., Tanabe, T., Okimura, Y., Kikuchi, Y., et al. (2007). Persistence of caliciviruses in artificially contaminated oysters during depuration. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,73(17), 5698–5701.
Van Trang, N., Vu, H. T., Le, N. T., Huang, P., Jiang, X., & Anh, D. D. (2014). Association between norovirus and rotavirus infection and histo-blood group antigen types in Vietnamese children. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,52(5), 1366–1374. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02927-13.
Yanuhar, U., Nurdiani, R., & Hertika, A. M. S. (2011). Potency of Nannochloropsis oculata as antibacterial, antioxidant and antiviral on humpback grouper infected by Vibrio alginolyticus and viral nervous necrotic. Journal of Food Science and Engineering,1(5), 323–330.
Zeng, S. Q., Halkosalo, A., Salminen, M., Szakal, E. D., Puustinen, L., & Vesikari, T. (2008). One-step quantitative RT-PCR for the detection of rotavirus in acute gastroenteritis. Journal of Virological Methods,153(2), 238–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jviromet.2008.08.004.
Zhang, X. F., Long, Y., Tan, M., Zhang, T., Huang, Q., Jiang, X., et al. (2016). P[8] and P[4] rotavirus infection associated with secretor phenotypes among children in south China. Scientific Reports,6, 34591. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34591.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Roberta Pellicanò for statistical analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by Grant RC015/IZSME from Italian Ministry of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amoroso, M.G., Langellotti, A.L., Russo, V. et al. Accumulation and Depuration Kinetics of Rotavirus in Mussels Experimentally Contaminated. Food Environ Virol 12, 48–57 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-019-09413-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-019-09413-0