Abstract
Background
The mechanism of regulation of PD-L1 expression by ALK translocation remains unclear. We detected PD-L1 protein expression and its regulation in lung adenocarcinoma patients with EML4-ALK fusion gene.
Methods
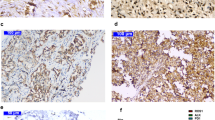
PD-L1 and ALK expression at protein level in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and tumor tissue specimens was evaluated by immunohistochemistry analysis and Western blotting. The expression at DNA level and RNA level was indicated by quantitative real-time PCR analysis. The signal pathway was indicated at protein level by western blotting.
Results
The PD-L1 protein expression was higher in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines with EML4-ALK fusion gene than that without this fusion gene. Induced expression of EML4-ALK in A549 cells significantly increased PD-L1 protein expression, whereas PD-L1 protein expression was downregulated after crizotinib and pembrolizumab successively. Significant positive correlations between PD-L1 and p-ERK, p-STAT3 or p-AKT expression were observed in ALK-translocated tumors. PD-L1 overexpression was significantly associated with shorter progressive survival and overall survival after crizotinib in ALK-translocated patients.
Conclusions
We demonstrate that ALK translocation can upregulate PD-L1 expression by activating ERK, STAT3 and AKT pathways. ALK inhibitor combined with a PD-L1-targeted therapy may be a potential strategy in ALK-translocated lung adenocarcinoma patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- EML4-ALK:
-
Echinoderm microtubule-associated protein like4-an aplastic lymphoma kinase
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
References
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J (2016) Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66(2):115–132
Zheng R, Zeng H, Zuo T, Zhang S, Qiao Y, Zhou Q, Chen W (2016) Lung cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2011. Thorac Cancer 7(1):94–99
Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T, Iyer S, Reisman A, Wilner KD, Tursi J, Blackhall F, PROFILE 1014 Investigators (2014) First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 371(23):2167–2177
Zhang NN, Liu YT, Ma L, Wang L, Hao XZ, Yuan Z, Lin DM, Li D, Zhou YJ, Lin H, Han XH, Sun Y, Shi Y (2014) The molecular detection and clinical significance of ALK rearrangement in selected advanced non-small cell lung cancer: ALK expression provides insights into ALK targeted therapy. PLoS One 9(1):e84501
Hida T, Nokihara H, Kondo M, Kim YH, Azuma K, Seto T, Takiguchi Y, Nishio M, Yoshioka H, Imamura F, Hotta K, Watanabe S, Goto K, Satouchi M, Kozuki T, Shukuya T, Nakagawa K, Mitsudomi T, Yamamoto N, Asakawa T, Asabe R, Tanaka T, Tamura T (2017) Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 390(10089):29–39
Shaw AT, Friboulet L, Leshchiner I, Gainor JF, Bergqvist S, Brooun A, Burke BJ, Deng YL, Liu W, Dardaei L, Frias RL, Schultz KR, Logan J, James LP, Smeal T, Timofeevski S, Katayama R, Iafrate AJ, Le L, McTigue M, Getz G, Johnson TW, Engelman JA (2016) Resensitization to crizotinib by the lorlatinib ALK resistance mutation L1198F. N Engl J Med 374(1):54–61
Azzato EM, Deshpande C, Aikawa V, Aggarwal C, Alley E, Jacobs B, Morrissette J, Daber R (2015) Rare complex mutational profile in an ALK inhibitor-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 35(5):3007–3012
Dempke WC, Sellmann L, Fenchel K, Edvardsen K (2015) Immunotherapies for NSCLC: are we cutting the gordian helix? Anticancer Res 35(11):5745–5757
Valecha GK, Vennepureddy A, Ibrahim U, Safa F, Samra B, Atallah JP (2017) Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in non-small cell lung cancer: the era of immunotherapy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 17(1):47–59
Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crino L, Eberhardt WE, Poddubskaya E, Antonia S, Pluzanski A, Vokes EE, Holgado E, Waterhouse D, Ready N, Gainor J, Arén Frontera O, Havel L, Steins M, Garassino MC, Aerts JG, Domine M, Paz-Ares L, Reck M, Baudelet C, Harbison CT, Lestini B, Spigel DR (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:123–135
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, Barlesi F, Kohlhäufl M, Arrieta O, Burgio MA, Fayette J, Lena H, Poddubskaya E, Gerber DE, Gettinger SN, Rudin CM, Rizvi N, Crinò L, Blumenschein GR Jr, Antonia SJ, Dorange C, Harbison CT, Graf Finckenstein F, Brahmer JR (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:1627–1639
Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Pérez-Gracia JL, Han JY, Molina J, Kim JH, Arvis CD, Ahn MJ, Majem M, Fidler MJ, de Castro G, Jr Garrido M, Lubiniecki GM, Shentu Y, Im E, Dolled-Filhart M, Garon EB (2016) Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387(10027):1540–1550
McDermott DF, Atkins MB (2013) PD-1 as a potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Med 2(5):662–673
Velcheti V, Schalper KA, Carvajal DE, Anagnostou VK, Syrigos KN, Sznol M, Herbst RS, Gettinger SN, Chen L, Rimm DL (2014) Programmed death ligand-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Lab Invest 94(1):107–116
Schalper KA, Velcheti V, Carvajal D, Wimberly H, Brown J, Pusztai L, Rimm DL (2014) In situ tumor PD-L1 mRNA expression is associated with increased TILs and better outcome in breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 20(10):2773–2782
Robainas M, Otano R, Bueno S, Ait-Oudhia S (2017) Understanding the role of PD-L1/PD1 pathway blockade and autophagy in cancer therapy. Onco Targets Ther 10:1803–1807
Okita R, Maeda A, Shimizu K, Nojima Y, Saisho S, Nakata M (2017) PD-L1 overexpression is partially regulated by EGFR/HER2 signaling and associated with poor prognosis in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 66(7):865–876
Tanizaki J, Okamoto I, Takezawa K, Sakai K, Azuma K, Kuwata K, Yamaguchi H, Hatashita E, Nishio K, Janne PA, Nakagawa K (2012) Combined effect of ALK and MEK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancercells. Br J Cancer 106(4):763–767
Yang H, Chen H, Luo S, Li L, Zhou S, Shen R, Lin H, Xie X (2017) The correlation between programmed death-ligand 1 expression and driver gene mutations in NSCLC. Oncotarget 8(14):23517–23528
Ma L, Li W, Zhu HP, Li Z, Sun ZJ, Liu XP, Zhao J, Zhang JS, Zhang YQ (2010) Localization and androgen regulation of metastasis-associated protein 1 in mouse epididymis. PLoS One 5(11):e15439
Ma L, Han XH, Wang S, Wang JF, Shi YK (2012) Effects of icotinib hydrochloride on the proliferation and apoptosis of human lung cancer cell lines. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 92(36):2561–2564
Liu Y, Ma L, Liu D, Yang Z, Yang C, Hu Z, Chen W, Yang Z, Chen S, Zhang Z (2013) Impact of polysomy 17 on HER2 testing of invasive breast cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(1):163–173
Somasundaram A, Burns TF (2017) The next generation of immunotherapy: keeping lung cancer in check. J Hematol Oncol 10(1):87
Giroux Leprieur E, Dumenil C, Julie C, Giraud V, Dumoulin J, Labrune S, Chinet T (2017) Immunotherapy revolutionises non-small-cell lung cancer therapy: results, perspectives and new challenges. Eur J Cancer 78:16–23
Boland JM, Kwon ED, Harrington SM, Wampfler JA, Tang H, Yang P, Aubry MC (2013) Tumor B7-H1 and B7-H3 expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Clin Lung Cancer 14:157–163
Chen YY, Wang LB, Zhu HL, Li XY, Zhu YP, Yin YL, Lu FZ, Wang ZL, Qu JM (2013) Relationship between programmed death-ligand 1 and clinicopathological characteristics in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Chin Med Sci J 28:147–151
Marzec M, Zhang Q, Goradia A, Raghunath PN, Liu X, Paessler M, Wang HY, Wysocka M, Cheng M, Ruggeri BA (2008) Oncogenic kinase NPM/ALK induces through STAT3 expression of immunosuppressive protein CD274 (PD-L1, B7-H1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:20852–20857
Lastwika KJ, Wilson W, Li QK, Norris J, Xu H, Ghazarian SR, Kitagawa H, Kawabata S, Taube JM, Yao S, Liu LN, Gills JJ, Dennis PA (2016) Control of PD-L1 expression by oncogenic activation of the AKT-mTOR pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 76(2):227–238
Koh J, Jang JY, Keam B, Kim S, Kim MY, Go H, Kim TM, Kim DW, Kim CW, Jeon YK, Chung DH (2015) EML4-ALK enhances programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression in pulmonary adenocarcinoma via hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and STAT3. Oncoimmunology 5(3):e1108514
Hong S, Chen N, Fang W, Zhan J, Liu Q, Kang S, He X, Liu L, Zhou T, Huang J, Chen Y, Qin T, Zhang Y, Ma Y, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Zhang L (2015) Upregulation of PD-L1 by EML4-ALK fusion protein mediates the immune escape in ALK positive NSCLC: implication for optional for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune therapy for ALK-TKIs sensitive and resistant NSCLC patients. Oncoimmunology 5(3):e1094598
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Guanting Lv PhD. for his helpful advice regarding to the possible relationship between PD-L1 and ALK. We would like to thank all patients in our study. We are indebted to Dr. Muhammad Jabran for his careful English assistance during the preparation of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by Capital health development scientific research fund-the young talents program (2018-4-1043); Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals’ Youth program (QML20181602); Backbone talents project in Beijing Chest Hospital & Beijing Tuberculosis and Thoracic Tumor Research Institute (212-20180307); Municipal Administration of Beijing Chest Hospitals’ Incubating Program (PYZL201706).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: LM, JW and SZ. Performed the experiments: LM, HZ, XL, QZ, XY and YD. Analyzed the data: LM and JL. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: XZ, JN, and YD. Wrote the paper: LM and JL.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, L., Lv, J., Dong, Y. et al. PD-L1 Expression and Its Regulation in Lung Adenocarcinoma with ALK Translocation. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 11, 266–272 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-019-00331-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-019-00331-0