Abstract
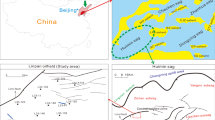
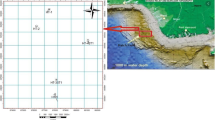
Geological facies modeling is a crucial problem for reservoir characterization as it affects the reservoir heterogeneities and fluid flow performance prediction. The main purpose of this research is to adopt a stochastic simulation to construct 3D lithofacies models of the tidal/estuarine depositional environment of the upper sandstone member in south Rumaila oil field, located in Iraq. Based on core measurements, the upper sandstone member has three main lithofacies: sand, shaly sand, and shale. Literature review indicates that the formation is encompassed of mainly sandstone with some inter-bedded shale zones. To reconstruct the 3D lithofacies model, the sequential indicator simulation (SISIM) was adopted to build the categorical image, pixel by pixel, considering the nonparametric condition distribution. Specifically, SISIM depends on the variogram to address and model the variation between any two spatial points from the available data. Therefore, 12 different variograms were constructed given the three lithofacies in four different azimuth directions: 0°, 45°, 90°, and 135°.The resulting lithofacies models in the four selected azimuth directions have shown frequent tidal lithofacies channeling and indicate an approximate matching with the original description of the formation depositional environment of the tidal-dominated and sand-rich environment. The generated lithofacies model in 135° direction has sand channels prevailing towards the southeast shoreline of the reservoir. The created lithofacies model also preserves the reservoir complexity and heterogeneity because it was created using a high-resolution gridding system with approximately two million grids. Additionally, the resulting tidal lithofacies model ensures reservoir heterogeneity as the petrophysical properties are then distributed given each lithofacies with distinct indicator variograms.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Naqib KM (1967) Geology of the Arabian peninsula southwestern Iraq. Paper 560-G, U.S. Geological Survey Professional. United States Government Printing Office, Washington
Alabert FG, Massonnat GJ (1990) Heterogeneity in a complex turbiditic reservoir: stochastic modelling of facies and petrophysical variability. SPE-20604-MS paper presented at the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana, 23–26 September 1990
Alabert FG, Modot V (1992) Stochastic models of reservoir heterogeneity: impact on connectivity and average permeabilities. SPE-24893-MS paper presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, Washington, D.C., 4–7 October 1992
Al-Ameri TK, Al-Khafaji AJ, Zumberge J (2009) Petroleum system analysis of the Mishrif reservoir in the Ratawi, Zubair, North and South Rumaila oil fields, southern Iraq. GeoArabia 14:91–108
Al-Ansari R (1993) The petroleum geology of the upper sandstone member of the Zubair formation in the Rumaila south. Geological Study, Ministry of Oil, Baghdad
Al-Mudhafar WJ (2015) Integrating component analysis & classification techniques for comparative prediction of continuous & discrete lithofacies distributions. Offshore technology conference. doi:10.4043/25806-MS
Al-Mudhafar WJ (2017) Integrating kernel support vector machines for efficient rock facies classification in the main pay of Zubair formation in South Rumaila oil field, Iraq. Model Earth Syst Environ 3:12. doi:10.1007/s40808-017-0277-0
Al-Muhailan M, Hussain I, Maliekkal H, Ghoneim O, Nair P, Fayed M (2013) New HTHP cutter technology coupled with FEA-based bit selection system improves rop by 60% in abrasive Zubair formation. IPTC-17122, paper presented at the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Beijing, China
Al-Obaidi RY (2009) Identification of Palynozones and age evaluation of Zubair Formation, Southern Iraq. Journal of Al-Nahrain University 12(3):16–22
Al-Obaidi RY (2010) Determination of Palynofades to assess depositional environments and hydrocarbons potential, Lower Cretaceolls, Zubair Formation South Iraq. Journal of College of Education 5:163–174
Begg SH, Kay A, Gustason ER, Angert PF (1996) Characterization of a complex fluvial-deltaic reservoir for simulation. SPE Form Eval 11(03):47–154
Caers J (2000) Direct sequential indicator simulation. In the 6th International Geostatistics Congress, South Africa, 10–14 April 2000
Caers J (2005) Petroleum geostatistics. Society of Petroleum Engineers, Richardson
Caers J, Zhang T (2004) Multiple-point geostatistics: a quantitative vehicle for integrating geologic analogs into multiple reservoir models. AAPG Mem 80:383394
Deutsch CV, Journel AG (1998) GSLIB. Geostatistical software library and user’s guide, New York
Goovaerts P (1997) Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. Oxford University Press, New York
Gringarten E, Deutsch CV (1999) Methodology for variogram interpretation and modeling for improved reservoir characterization. In SPE annual technical conference
Harris GD, Wellner RW, Catterall V, Kairo S, Liu C, Chen Y (2012) Stratigraphy and depositional environment of the upper Zubair sandstone (Main Pay), West Qurna 1 Field, Iraq. IR17, paper presented at the EAGE Work- shop on Iraq: Hydrocarbon Exploration and Field Development, Istanbul, Turkey
Isaaks EH, Srivastava RM (1989) An introduction to applied geostatistics. Oxford University Press, New York
Journel AG (1989) Geostatistical characterization of reservoir heterogeneities. In SEG annual meeting, Dallas, Texas, 29 October–2 November 1989
Journel AG (1990) Geostatistics for reservoir characterization. SPE-20750-MS, presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, New Orleans, Louisiana
Journel AG, Alabert FG (1990) New method for reservoir mapping. J Pet Technol 42(02):212–218
Journel AG, Gomez-Hernandez JJ (1993) Stochastic imaging of the Wilmington clastic sequence. SPE Form Eval 8(01):33–40
D. Kitching, Farmer R, Abuzaid M (2013) In search of the remaining oil in the “Main Pay” member of the Zubair Formation through surveillance oil mapping, Rumaila Field, Southern Iraq, Second EAGE Workshop on Iraq. doi:10.3997/2214-4609.20131456
Liu Y, Harding A, Abriel W, Strebelle S (2004) Multiple-point simulation integrating wells, three-dimensional seismic data, and geology. AAPG Bull 88(7):905–921
Massonnat GJ, Alabert FG, Giudicelli CB (1992) Anguille Marine, a deepsea-fan reservoir offshore Gabon: from geology to stochastic modelling. SPE-24709-MS paper presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, Washington, D.C., 4–7 October 1992
Mikes D, Geel CR (2006) Standard facies models to incorporate all heterogeneity levels in a reservoir model. Mar Pet Geol 23:943–959
Mohammed WJ, Al Jawad MS Al-Shamaa DA (2010) Reservoir flow simulation study for a sector in main pay-south rumaila oil field. SPE Oil and Gas India conference and exhibition, Mumbai, India
Overeem I (2008) Geological modeling introduction: lecture, community surface dynamic modeling system. University of Colorado, Boulder
Pyrcz MJ, Deutsch CV (2014) Geostatistical reservoir modeling, 2nd edition. Oxford University Press, New York
Seifert D, Jensen JL (1999) Using sequential indicator simulation as a tool in reservoir description: issues and uncertainties. Math Geol 31(5)
Srivastava RM (1994) An overview of stochastic methods for reservoir characterization. In: Yarus JM, Chambers RL (eds) AAPG computer applications in geology no. 3, stochastic modeling and geostatistics: principles, methods and case studies, vol 316. American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa
Walker RG (1992) Facies, facies models and modern stratigraphic concepts. Geological Association of Canada, St. John’s, pp 1–14
Wells M, D Kitching, D Finucane, B Kostic (2013) An integrated description of the stratigraphy and depositional environment of the “Main Pay” member of the Zubair Formation, Rumaila, Iraq. IR21, paper presented at the Second EAGE Workshop on Iraq, Dead sea, Jordan. doi:10.3997/2214-4609.20131455
White CD, Royer SA (2003) Experimental design as a framework for reservoir studies. SPE reservoir simulation symposium, Houston, Texas, USA
Zhang T (2008) Incorporating geological conceptual models and interpretations into reservoir modeling using multiple-point geostatistics. Earth Sci Front 15(1):26–35
Acknowledgements
The author would like to present his thanks and appreciation to the Institute of International Education for granting the Fulbright Science and Technology Awards that has funded the PhD Research. Thanks also go to Schlumberger Co. for granting the university a free version of Petrel Software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Mudhafar, W.J. Geostatistical lithofacies modeling of the upper sandstone member/Zubair formation in south Rumaila oil field, Iraq. Arab J Geosci 10, 153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2951-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2951-y