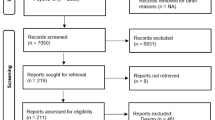
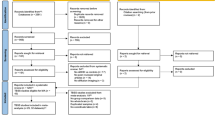
Abstract
Executive function (EF) is a multifaceted construct that has been defined as a set of higher-order cognitive processes that allow for flexibility, self-regulation, strategic planning, and goal-directed behaviors. EFs have been studied in numerous clinical disorders using a variety of neuropsychological tasks and, more recently, neuroimaging techniques. The underlying physiological substrates of EF were historically attributed to the frontal lobes; however, recent studies suggest more widespread involvement of additional brain regions. The purpose of the present study was to conduct a systematic review (using PRISMA 2009 guidelines) of neuroimaging studies employing functional magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor imaging methods investigating the physiological substrates of EFs in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder compared to other clinical groups and non-clinical participants. Research articles were retrieved using PsycINFO, PsycARTICLES, MEDLINE, and ScienceDirect, beginning February 2015 through May 2016. A total of 42 studies met eligibility. Of those 42 studies, 22 studies included clinical participants and 20 studies included non-clinical participants. Results revealed increased activation of the frontal brain region in the majority of non-clinical studies and approximately 50% of the clinical studies, albeit with some inconsistencies across subregions, tasks, and age groups. Implications, methodological limitations, and suggestions for future research are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baillieux H, De Smet HJ, Dobbeleir A, Paquier PF, De Deyn PP, Mariën P (2010) Cognitive and affective disturbances following focal cerebellar damage in adults: a neuropsychological and SPECT study. Cortex 46:869–879
Ball G, Stokes PR, Rhodes RA, Bose SK, Rezek I, Wink AM, Turkheimer FE (2011) Executive functions and prefrontal cortex: a matter of persistence? Front Syst Neurosci 5:3
Banich M, Burgess G, Depue B, Ruzic L, Bidwell L, Hitt-Lausten S, Willcutt E (2009) The neural basis of sustained and transient attentional control in young adults with ADHD. Neuropsychologia 47:3095–3104
Bendlin BB, Newman LM, Ries ML, Puglielli L, Carlsson CM, Johnson SC (2010) NSAIDs may protect against age-related brain atrophy. Front Aging Neurosci 2:35. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2010.00035
Bobb DS, Adinoff B, Laken SJ, McClintock SM, Rubia K, Huang HW, Gopinath K (2012) Neural correlates of successful response inhibition in unmedicated patients with late-life depression. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 20(12):1057–1069
Braet W, Johnson KA, Tobin CT, Acheson R, McDonnell C, Garavan H (2011) fMRI activation during response inhibition and error processing: the role of the DAT1 gene in typically developing adolescents and those diagnosed with ADHD. Neuropsychologia 49:1641–1650. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2011.01.001
Braun U, Schäfer A, Walter H, Erk S, Romanczuk-Seiferth N, Haddad L, Meyer-Lindenberg A (2015) Dynamic reconfiguration of frontal brain networks during executive cognition in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112(37):11678–11683
Brown TE (2002) DSM-IV: ADHD and executive function impairments. Adv Stud Med 2(25):910–914
Bunford N, Brandt NE, Golden C, Dykstra JB, Suhr JA, Owens JS (2015) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms mediate the association between deficits in executive functioning and social impairment in children. J Abnorm Child Psychol 43(1):133–147
Castellanos FX, Sonuga-Barke EJ, Milham MP, Tannock R (2006) Characterizing cognition in ADHD: beyond executive dysfunction. Trends Cognit Sci 10(3):117–123
Chikazoe J, Jimura K, Asari T, Yamashita K, Morimoto H, Konishi S (2009) Functional dissociation in right inferior frontal cortex during performance of go/no-go task. Cereb Cortex 19:146–152. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn065
Depue BE, Burgess GC, Willcutt EG, Bidwell LC, Ruzic L, Banich MT (2010) Symptom-correlated brain regions in young adults with combined-type ADHD: Their organization, variability, and relation to behavioral performance. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 182(2):96–102
Dibbets P, Evers EA, Hurks PP, Bakker K, Jolles J (2010) Differential brain activation patterns in adult attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) associated with task switching. Neuropsychology 24:413–423. doi:10.1037/a0018997
Dodds CM, Morein-Zamir S, Robbins TW (2011) Dissociating inhibition, attention and response control in the frontoparietal network using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Cereb Cortex 21:1155–1165. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq187
Doyle AE (2006) Executive functions in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 67(suppl 8):1–478
Drobyshevsky A, Baumann SB, Schneider W (2006) A rapid fMRI task battery for mapping of visual, motor, cognitive, and emotional function. Neuroimage 31:732–744. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.12.016
Dubois B, Pillon B (1996) Cognitive deficits in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 244(1):2–8. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9007738
Dunai J, Labuschagne I, Castle DJ, Kyrios M, Rossell SL (2010) Executive function in body dysmorphic disorder. Psychol Med 40:1541–1548. doi:10.1017/S003329170999198X
Fletcher JM (1996) Executive functions in children: introduction to the special series. Develop Neuropsychol 12(1):1–3
Fuentes-Claramonte P, Ávila C, Rodríguez-Pujadas A, Costumero V, Ventura-Campos N, Bustamante JC, Barrós-Loscertales A (2016) Inferior frontal cortex activity is modulated by reward sensitivity and performance variability. Biol Psychol 114:127–137
Fuglestad AJ, Whitley ML, Carlson SM, Boys CJ, Eckerle JK, Fink BA, Wozniak JR (2015) Executive functioning deficits in preschool children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Child Neuropsychol 21:716–731
Godinez DA, Willcutt EG, Burgess GC, Depue BE, Andrews-Hanna JR, Banich MT (2015) Familial risk and ADHD-specific neural activity revealed by case-control, discordant twin pair design. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 233(3):458–465
Goldberg TE, Goldman RS, Burdick KE, Malhotra AK, Lencz T, Robinson DG (2007) Cognitive improvement after treatment with second-generation antipsychotic medications in first-episode schizophrenia: is it a practice effect. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:1115–1122
Goldman-Rakic PS (1987) Development of cortical circuitry and cognitive function. Child Dev 58:601–622
Graham S, Jiang J, Manning V, Nejad AB, Zhisheng K, Salleh SR, McKenna PJ (2010) IQ-related fMRI differences during cognitive set shifting. Cereb Cortex 20(3):641–649. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhp130
Gruner P, Vo A, Ikuta T, Mahon K, Peters BD, Malhotra AK, Szeszko PR (2012) White matter abnormalities in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 37(12):2730–2739
Hale T, Bookheimer S, McGough J, Phillips J, McCracken J (2007) Atypical brain activation during simple & complex levels of processing in adult ADHD: an fMRI study. J Atten Disord 11:125–140
Harvey PO, Fossati P, Pochon JB, Levy R, LeBastard G, Lehéricy S, Dubois B (2005) Cognitive control and brain resources in major depression: an fMRI study using the n-back task. Neuroimage 26(3):860–869
He N, Li F, Li Y, Guo L, Chen L, Huang X, Gong Q (2015) Neuroanatomical deficits correlate with executive dysfunction in boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neurosci Lett 600:45–49
Hobson CW, Scott S, Rubia K (2011) Investigation of cool and hot executive function in ODD/CD independently of ADHD. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 52:1035–1043
Hu S, Li CS (2012) Neural processes of preparatory control for stop signal inhibition. Human Brain Mapp 33:2786–2796. doi:10.1002/hbm.21399
Ide JS, Li CR (2011) A cerebellar thalamic cortical circuit for error-related cognitive control. Neuroimage 54:455–464. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.07.042
Jimura K, Hirose S, Kunimatsu A, Ohtomo K, Koike Y, Konishi S (2014) Late enhancement of brain-behavior correlations during response inhibition. Neuroscience 274:383–392. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.058
Kikuchi T, Miller JM, Schneck N, Oquendo MA, Mann JJ, Parsey RV, Keilp JG (2012) Neural responses to incongruency in a blocked-trial Stroop fMRI task in major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 143(1):241–247
Li Q, Sun J, Guo L, Zang Y, Feng Z, Huang X, Gong Q (2010) Increased fractional anisotropy in white matter of the right frontal region in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroendocrinol Lett 31:747–753
Luria AR (1969) Brain research and human behavior. Hyg Mental 58:1–19
Massat I, Slama H, Kavec M, Sylvie L, Mary A, Baleriaux D, Peigneux P (2012) Working memory-related functional brain patterns in never medicated children with ADHD. PLoS ONE 7:e49392. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049392
Maltby N, Tolin DF, Worhunsky P, O'keefe TM, Kiehl KA (2005) Dysfunctional action monitoring hyperactivates frontal–striatal circuits in obsessive–compulsive disorder: an event-related fMRI study. Neuroimage 24(2):495–503
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed1000097
Morein-Zamir S, Voon V, Dodds CM, Sule A, van Niekerk J, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (2015) Divergent subcortical activity for distinct executive functions: stopping and shifting in obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychol Med 46:1–12
Mulligan RC, Kristjansson SD, Reiersen AM, Parra AS, Anokhin AP (2014) Neural correlates of inhibitory control and functional genetic variation in the dopamine D4 receptor gene. Neuropsychologia 62:306–318. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.07.033
Mumford JA (2012) A power calculation guide for fMRI studies. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci 7(6):738–742. doi:10.1093/scan/nss059
Nakao T, Nakagawa A, Yoshiura T, Nakatani E, Nabeyama M, Yoshizato C, Kawamoto M (2005) A functional MRI comparison of patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder and normal controls during a Chinese character Stroop task. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 139(2):101–114. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2014.07.033
Østgård HF, Sølsnes AE, Bjuland KJ, Rimol LM, Martinussen M, Brubakk AM, Håberg AK, Skranes J, Løhaugen GCC (2016) Executive function relates to surface area of frontal and temporal cortex in very-low-birth-weight late teenagers. Early Hum Dev 95:47–53
Page LA, Rubia K, Deeley Q, Daly E, Toal F, Mataix-Cols D, Murphy DG (2009) A functional magnetic resonance imaging study of inhibitory control in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 174(3):202–209
Penadés R, Catalán R, Andrés S, Salamero M, Gastó C (2005) Executive function and nonverbal memory in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res 133(1):81–90
Pennington BF, Orzonoff S (1996) Executive functions and Developmental Psychopathology. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 37(1):51–87
Perry RJ, Hodges JR (1999) Attention and executive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 122(3):383–404
Pritchard AE, Kalback S, McCurdy M, Capone GT (2015) Executive functions among youth with Down Syndrome and co‐existing neurobehavioural disorders. J Intell Disabil Res
Roth RM, Baribeau J, Milovan DL, O’Connor K (2004) Speed and accuracy on tests of executive function in obsessive–compulsive disorder. Brain Cogn 54(3):263–265
Roth RM, Saykin AJ, Flashman LA, Pixley HS, West JD, Mamourian AC (2007) Event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging of response inhibition in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 62(8):901–909
Sasson E, Doniger GM, Pasternak O, Tarrasch R, Assaf Y (2013) White matter correlates of cognitive domains in normal aging with diffusion tensor imaging. Front Neurosci 7:32. doi:10.3389/fnins.2013.00032
Satterthwaite TD, Elliott MA, Gerraty RT, Ruparel K, Loughead J, Wolf DH (2013) An improved framework for confound regression and filtering for control of motion artifact in the preprocessing of resting-state functional connectivity data. Neuroimage 64:240–256. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.08.052
Schwam DM, King TZ, Greenberg D (2015) Characteristics of executive functioning in a small sample of children with tourette syndrome. Appl Neuropsychol Child 4(4):297–308
Sebastian C, Fontaine N, Bird G, Blakemore S, De Brito S, McCrory E, Viding E (2012) Neural processing associated with cognitive and affective Theory of Mind in adolescents and adults. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci 7(1):53–63. doi:10.1093/scan/nsr023
Seghete KLM, Herting MM, Nagel BJ (2013) White matter microstructure correlates of inhibition and task-switching in adolescents. Brain Res 1527:15–28
Shallice T (1982) Specific Impairments of Planning. PHILOS T R SOC B 298(1089):199–209
Snyder HR (2013) Major depressive disorder is associated with broad impairments on neuropsychological measures of executive function: a meta-analysis and review. Psychol Bull 139(1):81
Sparding T, Silander K, Pålsson E, Östlind J, Sellgren C, Ekman CJ, Landén M (2015). Cognitive functioning in clinically stable patients with bipolar disorder I and II. PloS one 10(1)
Spinelli S, Joel S, Nelson T, Vasa R, Pekar J, Mostofsky S (2011) Different neural patterns are associated with trials preceding inhibitory errors in children with and without attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 50:705–715. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.03.014
Steele VR, Claus ED, Aharoni E, Harenski C, Calhoun VD, Pearlson G, Kiehl KA (2014) A large scale (N = 102) functional neuroimaging study of error processing in a Go/NoGo task. Behav Brain Res 268:127–138
Suskauer S, Simmonds D, Fotedar S, Blankner J, Pekar J, Denckla M, Mostofsky S (2008) Functional magnetic resonance imaging evidence for abnormalities in response selection in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: differences in activation associated. J Cogn Neurosci 20:478–493. doi:10.1162/jocn.2008.20032
Van Eylen L, Boets B, Steyaert J, Wagemans J, Noens I (2015) Executive functioning in autism spectrum disorders: influence of task and sample characteristics and relation to symptom severity. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 1–19
van Rooij D, Hoekstra PJ, Mennes M, von Rhein D, Thissen AJ, Heslenfeld D, Rommelse N (2015) Distinguishing adolescents with ADHD from their unaffected siblings and healthy comparison subjects by neural activation patterns during response inhibition. Am J Psychiatry
Wagner G, Sinsel E, Sobanski T, Köhler S, Marinou V, Mentzel HJ, Schlösser RG (2006) Cortical inefficiency in patients with unipolar depression: an event-related FMRI study with the Stroop task. Biol Psychiatry 59(10):958–965
Watkins E, Brown RG (2002) Rumination and executive function in depression: an experimental study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72(3):400–402
Weyandt LL (2005) Executive function in children, adolescents, and adults with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: introduction to the special issue. Dev Neuropsychol 27(1):1–10. doi:10.1207/s15326942dn2701_1
Weyandt LL (2006) An ADHD Primer, 2nd ed. Lawrence Erlbaum and Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Weyandt LL, Oster DR, Marraccini ME, Gudmundsdottir GG, Munro BA, Kuhar B (2014) Pharmacological interventions for adolescents and adults with ADHD: stimulant and nonstimulant medications and misuse of prescription stimulants.Psychol Res Behav Manag 7:223–249. doi:10.2147/PRBM.S4701
White CN, Congdon E, Mumford JA, Karlsgodt KH, Sabb FW, Freimer NB, Poldrack RA (2014) Decomposing decision components in the stop-signal task: a model-based approach to individual differences in inhibitory control. J Cogn Neurosci 26(8):1601–1614
Willcutt EG et al (2005) Validity of the executive function theory of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analytic review. Biol Psychiatry 57:1336–1346
Witt ST, Stevens MC (2012) Overcoming residual interference in mental set switching: neural correlates and developmental trajectory. Neuroimage 62(3):2055–2064
Zhang S, Li CSR (2010) A neural measure of behavioral engagement: task-residual low-frequency blood oxygenation level-dependent activity in the precuneus. Neuroimage 49(2):1911–1918
Zhang S, Li CSR (2012) Functional networks for cognitive control in a stop signal task: independent component analysis. Hum Brain Mapp 33(1):89–104
Acknowledgements
Research supported by the National Center for Research Resources of the National Institutes of Health under Award G20RR030883. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munro, B.A., Weyandt, L.L., Hall, L.E. et al. Physiological substrates of executive functioning: a systematic review of the literature. ADHD Atten Def Hyp Disord 10, 1–20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-017-0226-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12402-017-0226-9