Abstract
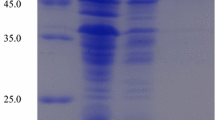
A recombinant Escherichia coli clone expressing an endoglucanase was identified from a genomic library of the halophilic bacterium Halomonas sp. S66-4, and the enzyme was designated Cel8H. The cel8H gene consisted of 1,053 bp and encoded 350 amino acids sharing the highest identity of 48% to other known endoglucanases. The protein was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) and purified to homogeneity. The purified recombinant enzyme had an optimal activity of 4.9 U/mg at pH 5 and 45°C toward the substrate carboxymethylcellulose. It exhibited extraordinary properties which differed from endoglucanases reported previously at the point of high salt tolerance above 5 M, simultaneously with high pH stability at pH 4–12 and high temperature stability at 40–60°C. Various substrate tests indicated that the enzyme hydrolyzes β-1,4-glucosidic bonds specifically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akita, M., K. Kayatama, Y. Hatada, S. Ito, and K. Horikoshi. 2005. A novel β-glucanase gene from Bacillus halodurans C-125. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 248, 9–15.
Alzari, P.M., H. ne Souchon, and R. Dominguez. 1996. The crystal structure of endoglucanase CelA, a family 8 glycosyl hydrolase from Clostridium thermocellum. Structure 4, 265–275.
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–259.
Cao, S., Z. Liu, A. Guo, Y. Li, C. Zhang, W. Gaobing, F. Chunfang, Y. Tan, and H. Chen. 2008. Efficient production and characterization of Bacillus anthracis lethal factor and a novel inactive mutant rLFm-Y236F. Protein Expr. Purif. 59, 25–30.
Cho, S., S. Par, M. Kim, W. Lim, S. Ryu, C. An, S. Hong, H. Kim, Y. Cho, and H. Yun. 2002. Cloning of the cel8Y gene from Pectobacterium chrysanthemi PY35 and its comparison to cel genes of softrot Pectobacterium. Mol. Cells 13, 28–34.
Dobson, S., T. McMeekin, and P. Franzmann. 1993. Phylogenetic relationships between some members of the genera Deleya, Halomonas, and Halovibrio. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43, 665–673.
Dym, O., M. Mevarech, and J. Sussman. 1995. Structural features that stabilize halophilic malate dehydrogenase from an archaebacterium. Science 267, 1344–1346.
Endo, K., Y. Hakamada, S. Takizawa, H. Kubota, N. Sumitomo, T. Kobayashi, and S. Ito. 2001. A novel alkaline endoglucanase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus isolate: enzymatic properties, and nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57, 109–116.
Fukuchi, S., K. Yoshimune, M. Wakayama, M. Moriguchi, and K. Nishikawa. 2003. Unique amino acid composition of proteins in halophilic bacteria. J. Mol. Biol. 327, 347–357.
Garcia, M., E. Mellado, J. Ostos, and A. Ventosa. 2004. Halomonas organivorans sp. nov., a moderate halophile able to degrade aromatic compounds. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54, 1723–1728.
Gole, A., S. Vyas, S.R. Sainkar, A. Lachke, and M. Sastry. 2001. Enhanced temperature and pH stability of fatty amine-endoglucanase composites: fabrication, substrate protection, and biological activity. Langmuir 17, 5964–5970.
Halldorsdottir, S., E. Thorolfsdottir, R. Spilliaert, M. Johansson, S. Thorbjarnardottir, A. Palsdóttir, G. Hreggvidsson, J. Kristjansson, O. Holst, and G. Eggertsson. 1998. Cloning, sequencing and overexpression of a Rhodothermus marinus gene encoding a thermostable cellulase of glycosyl hydrolase family 12. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 49, 277–284.
Hirasawa, K., K. Uchimura, M. Kashiwa, W. Grant, S. Ito, T. Kobayashi, and K. Horikoshi. 2006. Salt-activated endoglucanase of a strain of alkaliphilic Bacillus agaradhaerens. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 89, 211–219.
Karnchanatat, A., A. Petsom, P. Sangvanich, J. Piapukiew, A.J.S. Whalley, C.D. Reynolds, G.M. Gadd, and P. Sihanonth. 2008. A novel thermostable endoglucanase from the wood-decaying fungus Daldinia eschscholzii (Ehrenb.: Fr.) Rehm. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 42, 404–413.
Kim, K., L. Jin, H. Yang, and S. Lee. 2007. Halomonas gomseomensis sp. nov., Halomonas janggokensis sp. nov., Halomonas salaria sp. nov. and Halomonas denitrificans sp. nov., moderately halophilic bacteria isolated from saline water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 675–681.
Lanyi, J. 1974. Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 38, 272–290.
Li, Y.H., M. Ding, J. Wang, G. Xu, and F. Zhao. 2006. A novel thermoacidophilic endoglucanase, Ba-EGA, from a new cellulosedegrading bacterium, Bacillus sp. AC-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 70, 430–436.
Lynd, L., P. Weimer, W. van Zyl, and I. Pretorius. 2002. Microbial cellulose utilization: fundamentals and biotechnology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 66, 506–577.
Matthysse, A., S. White, and R. Lightfoot. 1995. Genes required for cellulose synthesis in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 177, 1069–1075.
Min, H., Y. Choi, K. Cho, J. Ha, and J. Woo. 1994. Cloning of the endoglucanase gene from Actinomyces sp. 40 in Escherichia coli and some properties of the gene products. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 4, 102–107.
Murashima, K., T. Nishimura, Y. Nakamura, J. Koga, T. Moriya, N. Sumida, T. Yaguchi, and T. Kono. 2002. Purification and characterization of new endo-1,4-β-D-glucanases from Rhizopus oryzae. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 30, 319–326.
Nakamura, K., N. Misawa, and K. Kitamura. 1986. Sequence of a cellulase gene of Cellulomonas uda CB4. J. Biotechnol. 4, 247–254.
Singh, J., N. Batra, and R.C. Sobti. 2004. Purification and characterisation of alkaline cellulase produced by a novel isolate, Bacillus sphaericus JS1. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31, 51–56.
Teather, R. and P. Wood. 1982. Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 43, 777–780.
Voget, S., H. Steele, and W. Streit. 2006. Characterization of a metagenome-derived halotolerant cellulase. J. Biotechnol. 126, 26–36.
Wang, C., Y. Hsieh, C. Ng, H. Chan, H. Lin, W. Tzeng, and Y. Shyu. 2009. Purification and characterization of a novel halostable cellulase from Salinivibrio sp. strain NTU-05. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 44, 373–379.
Yasutake, Y., S. Kawano, K. Tajima, M. Yao, Y. Satoh, M. Munekata, and I. Tanaka. 2006. Structural characterization of the Acetobacter xylinum endo-β-1,4-glucanase CMCax required for cellulose biosynthesis. Proteins 64, 1069–1077.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Shao, Z., Hong, Y. et al. Cel8H, a novel endoglucanase from the halophilic bacterium Halomonas sp. S66-4: Molecular cloning, heterogonous expression, and biochemical characterization. J Microbiol. 48, 318–324 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-009-0188-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-009-0188-5