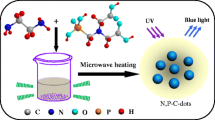
Abstract
Heteroatom-doped carbon dots (CDs) with a high photoluminescent quantum yield (PLQY) have recently attracted attention due to their applications in chemical sensors, photocatalysis, bioimaging, and drug delivery. Nitrogen and phosphorus are in close proximity to carbon in the periodic table and are key tracking elements in the field of biomedical imaging. These two elements alter the optical and electronic properties of CDs and help improve the fundamental understanding of their PLQY. This can also lead to multifunctional usage in photoimaging and photothermal therapy. However, most PLQYs resulting from the synthesis of P-doped CDs are currently below 50%. These CDs have limited usefulness in the fields of bioimaging and drug delivery. In this study, a single-step, high-efficiency hydrothermal method was applied to synthesize nitrogen and phosphorous-doped carbon dots ((N,P)-CDs) with a PLQY of up to 53.8% with independent emission behavior. Moreover, the CDs presented high monodispersity, robust excitation-independent luminescence, and stability over a large pH range. Spectroscopic investigations indicated that the PLQY of the (N,P)-CDs was primarily due to the addition of P and the passivation effect of the oxidized surface. The excellent fluorescence properties of (N,P)-CDs can be effectively and selectively quenched by Hg2+ ions. Such systems show a linear response in the 0–900 nM concentration range with a short response time, indicating their potential for applications in the fields of chemistry and biology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, X. Y.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y. L.; Ploehn, H. J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W. A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737.
Lim, S. Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Q. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381.
Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A. G.; Cai, C. Z.; Lin, H. W. Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: Full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363.
Yan, F. Y.; Zou, Y.; Wang, M.; Mu, X. L.; Yang, N.; Chen, L. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots-based fluorescent chemosensors for sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions and application of imaging in living cells. Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 2014, 192, 488–495.
Xu, Q.; Zhao, J. G.; Liu, Y.; Pu, P.; Wang, X. S.; Chen, Y. S.; Gao, C.; Chen, J. R.; Zhou, H. J. Enhancing the luminescence of carbon dots by doping nitrogen element and its application in the detection of Fe(III). J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 2571–2576.
Yang, S. W.; Sun, J.; Li, X. B.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z. Y.; He, P.; Ding, G. Q.; Xie, X. M.; Kang, Z. H.; Jiang, M. H. Large-scale fabrication of heavy doped carbon quantum dots with tunable-photoluminescence and sensitive fluorescence detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8660–8667.
Yang, X. M.; Luo, Y. W.; Zhu, S. S.; Feng, Y. J.; Zhuo, Y.; Dou, Y. One-pot synthesis of high fluorescent carbon nanoparticles and their applications as probes for detection of tetracyclines. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 6–11.
Posthuma-Trumpie, G. A.; Wichers, J. H.; Koets, M.; Berëndsen, L. B. J. M.; van Amerongen, A. Amorphous carbon nanoparticles: A versatile label for rapid diagnostic (immuno)assays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 593–600.
Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Su, R. G.; Cai, L. L.; Li, B. F.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Zhang, L. Z.; Wang, Y. J.; Wang, Y.; Li, N. et al. Highly fluorescent Zn-doped carbon dots as Fenton reaction-based bio-sensors: An integrative experimental-theoretical consideration. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17919–17927.
Liu, R. H.; Li, H. T.; Kong, W. Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Tong, C. Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Z. H. Ultra-sensitive and selective Hg2+ detection based on fluorescent carbon dots. Mater. Res. Bull. 2013, 48, 2529–2534.
Tang, D.; Liu, J.; Wu, X. Y.; Liu, R. H.; Han, X.; Han, Y. Z.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. K. Carbon quantum dot/NiFe layered double-hydroxide composite as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for water oxidation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7918–7925.
Ruan, S. B.; Qian, J.; Shen, S.; Zhu, J. H.; Jiang, X. G.; He, Q.; Gao, H. L. A simple one-step method to prepare fluorescent carbon dots and their potential application in non-invasive glioma imaging. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 10040–10047.
Xing, X. H.; Zhang, B. B.; Wang, X. H.; Liu, F. J.; Shi, D. L.; Cheng, Y. S. An “imaging-biopsy” strategy for colorectal tumor reconfirmation by multipurpose paramagnetic quantum dots. Biomaterials 2015, 48, 16–25.
Yang, W. T.; Guo, W. S.; Le, W. J.; Lv, G. X.; Zhang, F. H.; Shi, L.; Wang, X. L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Chang, J. et al. Albumin-bioinspired Gd:CuS nanotheranostic agent for in vivo photoacoustic/magnetic resonance imaging-guided tumor-targeted photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10245–10257.
Yuan, F. L.; Li, S. H.; Fan, Z. T.; Meng, X. Y.; Fan, L. Z.; Yang, S. H. Shining carbon dots: Synthesis and biomedical and optoelectronic applications. Nano Today 2016, 11, 565–586.
Yuan, F. L.; Wang, Z. B.; Li, X. H.; Li, Y. C.; Tan, Z. A.; Fan, L. Z.; Yang, S. H. Bright multicolor bandgap fluorescent carbon quantum dots for electroluminescent light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604436.
Wang, Z. F.; Yuan, F. L.; Li, X. H.; Li, Y. C.; Zhong, H. Z.; Fan, L. Z.; Yang, S. H. 53% efficient red emissive carbon quantum dots for high color rendering and stable warm white-light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702910.
Liu, R. L.; Wu, D. Q.; Liu, S. H.; Koynov, K.; Knoll, W.; Li, Q. An aqueous route to multicolor photoluminescent carbon dots using silica spheres as carriers. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 121, 4668–4671.
Wang, X.; Cao, L.; Lu, F. S.; Meziani, M. J.; Li, H. T.; Qi, G.; Zhou, B.; Harruff, B. A.; Kermarrec, F.; Sun, Y. P. Photoinduced electron transfers with carbon dots. Chem. Commun. 2009, 3774–3776.
Zhu, S. J.; Meng, Q. N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. H.; Song, Y. B.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H. C.; Wang, H. Y.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3953–3957.
Dong, Y. Q.; Pang, H. C.; Yang, H. B.; Guo, C. X.; Shao, J. W.; Chi, Y. W.; Li, C. M.; Yu, T. Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7800–7804.
Xu, Q.; Kuang, T. R.; Liu, Y.; Cai, L. L.; Peng, X. F.; Sreenivasan, T. S.; Zhao, P.; Yu, Z. Q.; Li, N. Heteroatomdoped carbon dots: Synthesis, characterization, properties, photoluminescence mechanism and biological applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7204–7219
Gong, Y. Q.; Yu, B.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X. L. Phosphorus, and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for real-time measurement of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species inside macrophages. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 822–828.
Wang, C.; Zhou, J. D.; Ran, G. X.; Li, F.; Zhong, Z.; Song, Q. J.; Dong, Q. C. Bi-functional fluorescent polymer dots: A one-step synthesis via controlled hydrothermal treatment and application as probes for the detection of temperature and Fe3+. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 434–443.
Liang, Q. H.; Ma, W. J.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. M. Easy synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon quantum dots from gelatin and their luminescent properties and applications. Carbon 2013, 60, 421–428.
Paraknowitsch, J. P.; Zhang, Y. J.; Wienert, B.; Thomas, A. Nitrogen- and phosphorus-co-doped carbons with tunable enhanced surface areas promoted by the doping additives. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49,1208–1210.
Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, C.; Wei, J. F.; Zhou, H. J.; Chen, Y. S.; Dong, C. B.; Sreeprasad, T. S.; Li, N.; Xia, Z. H. Synthesis, mechanistic investigation, and application of photoluminescent sulfur and nitrogen co-doped carbon dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 9885–9893.
Wu, M. B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W. T.; Hu, C.; Wang, X. N.; Zheng, J. T.; Li, Z. T.; Jiang, B.; Qiu, J. S. Preparation of functionalized water-soluble photoluminescent carbon quantum dots from petroleum coke. Carbon 2014, 78, 480–489.
Simões, E. F. C.; da Silva, J. C. G. E.; Leitão, J. M. M. Carbon dots from tryptophan doped glucose for peroxynitrite sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 852, 174–180.
Sun, Y. P.; Zhou, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Shiral Fernando, K. A.; Pathak, P.; Meziani, M. J.; Harruff, B. A.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. et al. Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7756–7757.
Liang, J.; Jiao, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Sulfur and nitrogen dual-doped mesoporous graphene electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction with synergistically enhanced performance. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11496–11500.
Nolan, E. M.; Lippard, S. J. Tools and tactics for the optical detection of mercuric ion. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3443–3480.
Harris, H. H.; Pickering, I. J.; George, G. N. The chemical form of mercury in fish. Science 2003, 301, 1203–1203.
Qu, K. G.; Wang, J. S.; Ren, J. S.; Qu, X. G. Carbon dots prepared by hydrothermal treatment of dopamine as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the label-free detection of iron(III) ions and dopamine. Chem.-Eur. J. 2013, 19, 7243–7249.
Li, S. H.; Li, Y. C.; Cao, J.; Zhu, J.; Fan, L. Z.; Li, X. H. Sulfur-doped graphene quantum dots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of Fe3+. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10201–10207.
Zhang, H. J.; Chen, Y. L.; Liang, M. J.; Xu, L. F.; Qi, S. D.; Chen, H. L.; Chen, X. G. Solid-phase synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for sensitive and selective probing ferric ions in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9846–9852.
Shi, B. F.; Su, Y. B.; Zhang, L. L.; Huang, M. J.; Liu, R. Q.; Zhao, S. L. Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon nanodots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of Fe3+ in human serum and living cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10717–10725.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Beijing Nova Program (No. Z171100001117058), Beijing Nova program Interdisciplinary Studies Cooperative Project, Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (No. Z161100001316010), State Key Laboratory of Silicate Materials for Architecture (No. SYSJJ2016-05), Medical Science Youth Training Program (No. 16PNQ145), Defense Technology Project Fund (No. 3408080), Translational Medicine Project of PLAGH (No. 2016TM-019), and the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (No. 81402216) for the support. This work was obtained with the resources and financial support of National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory in Hefei.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1937_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Synthesis, mechanical investigation, and application of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots with a high photoluminescent quantum yield
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Li, B., Ye, Y. et al. Synthesis, mechanical investigation, and application of nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon dots with a high photoluminescent quantum yield. Nano Res. 11, 3691–3701 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1937-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1937-0