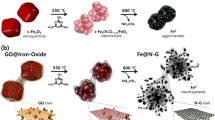
Abstract
Atomically dispersed catalysts have attracted attention in energy conversion applications because their efficiency and chemoselectivity for special catalysis are superior to those of traditional catalysts. However, they have limitations owing to the extremely low metal-loading content on supports, difficulty in the precise control of the metal location and amount as well as low stability at high temperatures. We prepared a highly doped single metal atom hybrid via a single-step thermal pyrolysis of glucose, dicyandiamide, and inorganic metal salts. High-angle annular dark field-scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (XAFS) revealed that nitrogen atoms doped into the graphene matrix were pivotal for metal atom stabilization by generating a metal-Nx coordination structure. Due to the strong anchoring effect of the graphene matrix, the metal loading content was over 4 wt.% in the isolated atomic hybrid (the Pt content was as high as 9.26 wt.% in the Pt-doped hybrid). Furthermore, the single iron-doped hybrid (Fe@N-doped graphene) showed a remarkable electrocatalytic performance for the oxygen reduction reaction. The peak power density was ∼199 mW·cm−2 at a current density of 310 mA·cm−2 and superior to that of a commercial Pt/C catalyst when it was used as a cathode catalyst in assembled zinc-air batteries. This work offered a feasible approach to design and fabricate highly doped single metal atoms (SMAs) catalysts for potential energy applications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, L. C.; Díaz, U.; Arenal, R.; Agostini, G.; Concepción, P.; Corma, A. Generation of subnanometric platinum with high stability during transformation of a 2D zeolite into 3D. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 132–138.
Liu, P. X.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, R. X.; Mo, S. G.; Chen, G. X.; Gu, L.; Chevrier, D. M.; Zhang, P.; Guo, Q.; Zang, D. D. et al. Photochemical route for synthesizing atomically dispersed palladium catalysts. Science 2016, 352, 797–801.
Yan, H.; Cheng, H.; Yi, H.; Lin, Y.; Yao, T.; Wang, C. L.; Li, J. J.; Wei, S. Q.; Lu, J. L. Single-atom Pd1/graphene catalyst achieved by atomic layer deposition: Remarkable performance in selective hydrogenation of 1,3-butadiene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 10484–10487.
Yang, S.; Kim, J.; Tak, Y. J.; Soon, A.; Lee, H. Single-atom catalyst of platinum supported on titanium nitride for selective electrochemical reactions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2058–2062.
Huang, X. H.; Xia, Y. J.; Cao, Y. J.; Zheng, X. S.; Pan, H. B.; Zhu, J. F.; Ma, C.; Wang, H. W.; Li, J. J.; You, R. et al. Enhancing both selectivity and coking-resistance of a single-atom Pd1/C3N4 catalyst for acetylene hydrogenation. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 1302–1312.
Fei, H. L.; Dong, J. C.; Arellano-Jiménez, M. J.; Ye, G. L.; Dong Kim, N.; Samuel, E. L. G.; Peng, Z. W.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, F. M.; Bao, J. M. et al. Atomic cobalt on nitrogen-doped graphene for hydrogen generation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8668.
Wei, H. S.; Liu, X. Y.; Wang, A. Q.; Zhang, L. L.; Qiao, B. T.; Yang, X. F.; Huang, Y. Q.; Miao, S.; Liu, J. Y.; Zhang, T. FeOx-supported platinum single-atom and pseudo-single-atom catalysts for chemoselective hydrogenation of functionalized nitroarenes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5634.
Yang, X. F.; Wang, A. Q.; Qiao, B. T.; Li, J.; Liu, J. Y.; Zhang, T. Single-atom catalysts: A new frontier in heterogeneous catalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1740–1748.
Yin, P. Q.; Yao, T.; Wu, Y. E.; Zheng, L. R.; Lin, Y.; Liu, W.; Ju, H. X.; Zhu, J. F.; Hong, X.; Deng, Z. X. et al. Single cobalt atoms with precise N-coordination as superior oxygen reduction reaction catalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10800–10805.
Chen, X. Q.; Yu, L.; Wang, S. H.; Deng, D. H.; Bao, X. H. Highly active and stable single iron site confined in graphene nanosheets for oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 353–358.
Choi, C. H.; Kim, M.; Kwon, H. C.; Cho, S. J.; Yun, S.; Kim, H. T.; Mayrhofer, K. J.; Kim, H.; Choi, M. Tuning selectivity of electrochemical reactions by atomically dispersed platinum catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10922.
Cheng, N. C.; Stambula, S.; Wang, D.; Banis, M. N.; Liu, J.; Riese, A.; Xiao, B. W.; Li, R. Y.; Sham, T. K.; Liu, L. M. et al. Platinum single-atom and cluster catalysis of the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13638.
Deng, J.; Li, H. B.; Xiao, J. P.; Tu, Y. C.; Deng, D. H.; Yang, H. X.; Tian, H. F.; Li, J. Q.; Ren, P. J.; Bao, X. H. Triggering the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity of the inert two-dimensional MoS2 surface via single-atom metal doping. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 1594–1601.
Hackett, S. F. J.; Brydson, R. M.; Gass, M. H.; Harvey, I.; Newman, A. D.; Wilson, K.; Lee, A. F. High-activity, singlesite mesoporous Pd/Al2O3 catalysts for selective aerobic oxidation of allylic alcohols. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8593–8596.
Matthey, D.; Wang, J. G.; Wendt, S.; Matthiesen, J.; Schaub, R.; Laegsgaard, E.; Hammer, B.; Besenbacher, F. Enhanced bonding of gold nanoparticles on oxidized TiO2(110). Science 2007, 315, 1692–1696.
Kwak, J. H.; Hu, J. Z.; Mei, D. H.; Yi, C. W.; Kim, D. H.; Peden, C. H. F.; Allard, L. F.; Szanyi, J. Coordinatively unsaturated Al3+ centers as binding sites for active catalyst phases of platinum on γ-Al2O3. Science 2009, 325, 1670–1673.
Ortalan, V.; Uzun, A.; Gates, B. C.; Browning, N. D. Direct imaging of single metal atoms and clusters in the pores of dealuminated HY zeolite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 506–510.
Maiti, U. N.; Lee, W. J.; Lee, J. M.; Oh, Y.; Kim, J. Y.; Kim, J. E.; Shim, J.; Han, T. H.; Kim, S. O. 25th anniversary article: Chemically modified/doped carbon nanotubes & graphene for optimized nanostructures & nanodevices. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 40–66.
Liu, X. E.; Dai, L. M. Carbon-based metal-free catalysts. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16064.
Deng, D. H.; Novoselov, K. S.; Fu, Q.; Zheng, N. F.; Tian, Z. Q.; Bao, X. H. Catalysis with two-dimensional materials and their heterostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 218–230.
Li, X. H.; Kurasch, S.; Kaiser, U.; Antonietti, M. Synthesis of monolayer-patched graphene from glucose. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9689–9692.
Li, Y. R.; Wang, Z. W.; Xia, T.; Ju, H. X.; Zhang, K.; Long, R.; Xu, Q.; Wang, C. M.; Song, L.; Zhu, J. F. et al. Implementing metal-to-ligand charge transfer in organic semiconductor for improved visible-near-infrared photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6959–6965.
Zhang, G. G.; Huang, C. J.; Wang, X. C. Dispersing molecular cobalt in graphitic carbon nitride frameworks for photocatalytic water oxidation. Small 2015, 11, 1215–1221.
Wang, X. C.; Chen, X. F.; Thomas, A.; Fu, X. Z.; Antonietti, M. Metal-containing carbon nitride compounds: A new functional organic-metal hybrid material. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1609–1612.
Midgley, P. A.; Weyland, M. 3D electron microscopy in the physical sciences: The development of Z-contrast and EFTEM tomography. Ultramicroscopy 2003, 96, 413–431.
Jiang, H. L.; Yao, Y. F.; Zhu, Y. H.; Liu, Y. Y.; Su, Y. H.; Yang, X. L.; Li, C. Z. Iron carbide nanoparticles encapsulated in mesoporous Fe-N-doped graphene-like carbon hybrids as efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21511–21520.
Wang, J.; Wang, G. X.; Miao, S.; Jiang, X. L.; Li, J. Y.; Bao, X. H. Synthesis of Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles encapsulated in nitrogen-doped carbon with single-source molecular precursor for the oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon 2014, 75, 381–389.
Liu, X. W.; Zhao, S.; Meng, Y.; Peng, Q.; Dearden, A. K.; Huo, C. F.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. W.; Wen, X. D. Mössbauer spectroscopy of iron carbides: From prediction to experimental confirmation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26184.
Vij, V.; Tiwari, J. N.; Lee, W. G.; Yoon, T.; Kim, K. S. Hemoglobin-carbon nanotube derived noble-metal-free Fe5C2-based catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20132.
Lin, L.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, A. W. Noble-metal-free Fe-N/C catalyst for highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction under both alkaline and acidic conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11027–11033.
Guo, Z. Y.; Xiao, Z.; Ren, G. Y.; Xiao, G. Z.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, L. M.; Jiang, L. Natural tea-leaf-derived, ternary-doped 3D porous carbon as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1244–1255.
Jiang, W. J.; Gu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. J.; Wang, J. Q.; Hu, J. S.; Wei, Z. D.; Wan, L. J. Understanding the high activity of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts in oxygen reduction: Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles boost the activity of Fe-Nx. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3570–3578.
Cao, R. G.; Thapa, R.; Kim, H.; Xu, X. D.; Gyu Kim, M.; Li, Q.; Park, N.; Liu, M. L.; Cho, J. Promotion of oxygen reduction by a bio-inspired tethered iron phthalocyanine carbon nanotube-based catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2076.
Sun, Z. H.; Liu, Q. H.; Yao, T.; Yan, W. S.; Wei, S. Q. X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy in nanomaterials. Sci. China Mater. 2015, 58, 313–341.
Zhou, J. G.; Duchesne, P. N.; Hu, Y. F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y. G.; Regier, T.; Dai, H. J. Fe–N bonding in a carbon nanotube-graphene complex for oxygen reduction: An XAS study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 15787–15791.
Miedema, P. S.; van Schooneveld, M. M.; Bogerd, R.; Rocha, T. C. R.; Hävecker, M.; Knop-Gericke, A.; de Groot, F. M. F. Oxygen binding to cobalt and iron phthalocyanines as determined from in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 25422–25428.
Jia, Q. Y.; Ramaswamy, N.; Hafiz, H.; Tylus, U.; Strickland, K.; Wu, G.; Barbiellini, B.; Bansil, A.; Holby, E. F.; Zelenay, P. et al. Experimental observation of redox-induced Fe–N switching behavior as a determinant role for oxygen reduction activity. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 12496–12505.
Zitolo, A.; Goellner, V.; Armel, V.; Sougrati, M. T.; Mineva, T.; Stievano, L.; Fonda, E.; Jaouen, F. Identification of catalytic sites for oxygen reduction in iron- and nitrogen-doped graphene materials. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 937–942.
Ravel, B.; Newville, M. ATHENA, ARTEMIS, HEPHAESTUS: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2005, 12, 537–541.
Yu, H. J.; Shang, L.; Bian, T.; Shi, R.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Zhao, Y. F.; Zhou, C.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C. H.; Zhang, T. R. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets templated from g-C3N4 as metal-free electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5080–5086.
Wu, G.; Santandreu, A.; Kellogg, W.; Gupta, S.; Ogoke, O.; Zhang, H. G.; Wang, H. L.; Dai, L. M. Carbon nanocomposite catalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions: From nitrogen doping to transition-metal addition. Nano Energy 2016, 29, 83–110.
Yan, H. J.; Meng, M. C.; Wang, L.; Wu, A. P.; Tian, C. G.; Zhao, L.; Fu, H. G. Small-sized tungsten nitride anchoring into a 3D CNT-rGO framework as a superior bifunctional catalyst for the methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 329–343.
Yu, H. J.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. X.; Bian, T.; Zhao, Y. F.; Zhou, C.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C. H.; Zhang, T. R. Alkali-assisted synthesis of nitrogen deficient graphitic carbon nitride with tunable band structures for efficient visible-light-driven hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605148.
Guo, S. J.; Yang, Y. M.; Liu, N. Y.; Qiao, S.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. H. One-step synthesis of cobalt, nitrogen-codoped carbon as nonprecious bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 68–77.
Lefèvre, M.; Proietti, E.; Jaouen, F.; Dodelet, J. P. Iron-based catalysts with improved oxygen reduction activity in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Science 2009, 324, 71–74.
Yang, J.; Sun, H. Y.; Liang, H. Y.; Ji, H. X.; Song, L.; Gao, C.; Xu, H. X. A highly efficient metal-free oxygen reduction electrocatalyst assembled from carbon nanotubes and graphene. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4606–4613.
Shang, L.; Yu, H. J.; Huang, X.; Bian, T.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. F.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C. H.; Zhang, T. R. Well-dispersed ZIF-derived Co,N-Co-doped carbon nanoframes through mesoporous-silica-protected calcination as efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1668–1674.
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported partly by Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) (Nos. 2017YFA0303500 and 2014CB848900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Nos. U1532112, 11574280 and 11605201 ), CAS Interdisciplinary Innovation Team and CAS Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (No. QYZDB-SSW-SLH018). L. S. acknowledges the recruitment program of global experts, the CAS Hundred Talent Program and Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry (Ministry of Education) Nankai University. We thank the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (14W1, SSRF), the Beijing Synchrotron Radiation Facility (1W1B and soft-X-ray endstation, BSRF), the Hefei Synchrotron Radiation Facility (Photoemission, MCD and Catalysis/Surface Science Endstations, NSRL), and the USTC Center for Micro and Nanoscale Research and Fabrication for helps in characterizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1840_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
In situ trapped high-density single metal atoms within graphene: Iron-containing hybrids as representatives for efficient oxygen reduction
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Wu, C., Chen, S. et al. In situ trapped high-density single metal atoms within graphene: Iron-containing hybrids as representatives for efficient oxygen reduction. Nano Res. 11, 2217–2228 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1840-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1840-8