Abstract
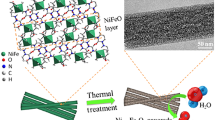
The development of efficient and stable non-noble metal-based electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is one of the essential challenges for the upcoming hydrogen economy. Herein, 3D mesoporous nickel iron selenide with rose-like microsphere architecture was directly grown on Ni foam via a successive two-step hydrothermal method. The unique 3D mesoporous rose-like morphology leads to a higher number of active sites as well as fast mass and electron transport through the entire electrode, and facilitates the release of O2 bubbles formed during the OER catalysis. As a result, the synthesized Ni0.76Fe0.24Se exhibits superior OER performances, with an ultralow overpotential of 197 mV needed to produce a current density of 10 mA·cm–2 in 1 M KOH, outperforming all transition metal selenide OER catalysts reported to date.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for asustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303.
Zou, X. X.; Zhang, Y. Noble metal-free hydrogen evolution catalysts for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5148–5180.
Liu, T. T.; Liu, D. N.; Qu, F. L.; Wang, D. X.; Zhang, L.; Ge, R. X.; Hao, S.; Ma, Y. J.; Du, G.; Asiri, A. M. et al. Enhanced electrocatalysis for energy-efficient hydrogen production over CoP catalyst with nonelectroactive Zn as a promoter. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700020.
Yang, F. L.; Chen, Y. T.; Cheng, G, Z.; Chen, S. L.; Luo, W. Ultrathin nitrogen-doped carbon coated with CoP for efficient hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 3824–3831.
Long, X.; Li, G. X.; Wang, Z. L.; Zhu, H. Y.; Zhang, T.; Xiao. S.; Guo, W. Y.; Yang, S. H. Metallic iron–nickel sulfide ultrathin nanosheets as a highly active electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic media. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11900–11903.
Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, N. Y.; Han, Y. Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Lifshitz, Y.; Lee, S. T.; Zhong, J.; Kang, Z. H. Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting via a two-electron pathway. Science 2015, 347, 970–974.
Du, C.; Yang, L.; Yang, F. L.; Cheng, G. Z.; Luo, W. Nest-like NiCoP for highly efficient overall water splitting. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4131–4137.
Wu, Y. Y.; Liu, Y. P.; Li, G. D.; Zou, X.; Lian, X. R.; Wang, D. J.; Sun, L.; Asefa, T.; Zou, X. X. Efficient electrocatalysis of overall water splitting by ultrasmall NixCo3–xS4 coupled Ni3S2 nanosheet arrays. Nano Energy 2017, 35, 161–170.
Sun, C. C.; Dong, Q. C.; Yang, J.; Dai, Z. Y.; Lin, J. J.; Chen, P.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. C. Metal–organic framework derived CoSe2 nanoparticles anchored on carbon fibers as bifunctional electrocatalysts for efficient overall water splitting. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2234–2243.
Wang, J.; Zhong, H. X.; Wang, Z. L.; Meng, F. L.; Zhang, X. B. Integrated three-dimensional carbon paper/carbon tubes/cobalts-sulfide sheets as an efficient electrode for overall water splitting. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2342–2348.
Chen, P. Z.; Xu, K.; Fang, Z. W.; Tong, Y.; Wu, J. C.; Lu, X. L.; Peng, X.; Ding, H.; Wu, C. Z.; Xie, Y. Metallic Co4N porous nanowire arrays activated by surface oxidation as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14710–14714.
Zhang, W.; Wu, Y. Z.; Qi, J.; Chen, M. X.; Cao, R. A thin NiFe hydroxide film formed by stepwise electrodeposition strategy with significantly improved catalytic water oxidation efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602547.
Wan, S. H.; Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W. N.; Zhang, S. K.; Liu, K. Q.; Zheng, H. Q.; Sun, J. L.; Wang, S. Y.; Cao, R. Hierarchical Co(OH)F superstructure built by low-dimensional substructures for electrocatalytic water oxidation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700286.
Chen, M. X.; Wu, Y. Z.; Han, Y. Z.; Lin, X. H.; Sun, J. L.; Zhang, W.; Cao, R. An iron-based film for highly efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution from neutral aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 21852–21859.
Guo, D. Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, W.; Cao, R. Surface electrochemical modification of a nickel substrate to prepare a NiFe-based electrode for water oxidation. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 394–400.
Stern, L. A.; Feng, L. G.; Song, F.; Hu, X. L. Ni2P as a Janus catalyst for water splitting: The oxygen evolution activity of Ni2P nanoparticles. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2347–2351.
Xu, X.; Song, F.; Hu, X. L. A nickel iron diselenide-derived efficient oxygen-evolution catalyst. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12324.
Zhao, X.; Zhang, H. T.; Yan. Y.; Cao, J. H.; Li, X. Q.; Zhou, S. M.; Peng, Z. M.; Zeng, J. Engineering the electrical conductivity of lamellar silver-doped cobalt(II) selenide nanobelts for enhanced oxygen evolution. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 328–332.
Gong, M.; Dai, H. J. A mini review of NiFe-based materials as highly active oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 23–39.
Lee, Y.; Suntivich, J.; May, K. J.; Perry, E. E.; Shao-Horn, Y. Synthesis and activities of rutile IrO2 and RuO2 nanoparticles for oxygen evolution in acid and alkaline solutions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 399–404.
Wang, J.; Zhong, H. X.; Qin, Y. L.; Zhang, X. B. An efficient three-dimensional oxygen evolution electrode. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5248–5253.
Fan, X. J.; Peng, Z. W.; Ye, R. Q.; Zhou, H. Q.; Guo, X. M3C (M: Fe, Co, Ni) nanocrystals encased in graphene nanoribbons: An active and stable bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reactions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7407–7418.
McCrory, C. C. L.; Jung, S.; Peters, J. C.; Jaramillo, T. F. Benchmarking heterogeneous electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16977–16987.
Masa, J.; Weide, P.; Peeters, D.; Sinev, I.; Xia, W.; Sun, Z. Y.; Somsen, C.; Muhler, M.; Schuhmann, W. Amorphous cobalt boride (Co2B) as a highly efficient nonprecious catalyst for electrochemical water splitting: Oxygen and hydrogen evolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502313.
Yan, K.; Wu, G. S.; Jin, W. Recent advances in the synthesis of layered, double-hydroxide-based materials and their applications in hydrogen and oxygen evolution. Energy Technol. 2016, 4, 354–368.
Bai, Y. J.; Fang, L.; Xu, H. T.; Gu, X.; Zhang, H. J.; Wang, Y. Strengthened synergistic effect of metallic MxPy (M = Co, Ni, and Cu) and carbon layer via peapod-like architecture for both hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. Small 2017, 13, 1603718.
Yan, Y.; Xia, B. Y.; Li, N.; Xu, Z. C.; Fisher, A.; Wang, X. Vertically oriented MoS2 and WS2 nanosheets directly grown on carbon cloth as efficient and stable 3-dimensional hydrogen-evolving cathodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 131–135.
Xia, C.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Hedhili, M. N.; Alshareef, H. N. Selenide-based electrocatalysts and scaffolds for water oxidation applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 77–85.
Liu, X. B.; Liu, Y. C.; Fan, L. Z. MOF-derived CoSe2 microspheres with hollow interiors as high-performance electrocatalysts for enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15310–15314.
Sivanantham, A.; Shanmugam, S. Nickel selenide supported on nickel foam as an efficient and durable non-precious electrocatalyst for the alkaline water electrolysis. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2017, 203, 485–493.
Liu, T. T.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Electrodeposited Co-doped NiSe2 nanoparticles film: A good electrocatalyst for efficient water splitting. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3911–3915.
Zhao, Q.; Zhong, D. Z.; Liu, L.; Li, D. D.; Hao, G. Y.; Li, J. P. Facile fabrication of robust 3D Fe-NiSe nanowires supported on nickel foam as a highly efficient, durable oxygen evolution catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14639–14645.
Du, Y. S.; Cheng, G. Z.; Luo, W. Colloidal synthesis of urchin-like Fe doped NiSe2 for efficient oxygen evolution. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 6821–6825.
Xie, J. F.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, R. X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, J. F.; Lou, X. W.; Xie, Y. Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5807–5813.
You, B.; Jiang, N.; Sheng, M. L.; Bhushan, M. W.; Sun, Y. J. Hierarchically porous urchin-like Ni2P superstructures supported on nickel foam as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 714–721.
Wang, D. Y.; Gong, M.; Chou, H. L.; Pan, C. J.; Chen, H. A.; Wu, Y. P.; Lin, M. C.; Guan, M. Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, C. W. et al. Highly active and stable hybrid catalyst of cobalt-doped FeS2 nanosheets–carbon nanotubes for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1587–1592.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, N. Y.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Self-supported Cu3P nanowire arrays as an integrated highperformance three-dimensional cathode for generating hydrogen from water. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9577–9581.
Wang, Z. Q.; Zeng, S.; Liu, W. H.; Wang, X. W.; Li, Q. W.; Zhao, Z. G.; Geng, F. X. Coupling molecularly ultrathin sheets of NiFe-layered double hydroxide on NiCo2O4 nanowire arrays for highly efficient overall water-splitting activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1488–1495.
Liu, J.; Wang, J. S.; Zhang, B.; Ruan, Y. J.; Lv, L.; Ji, X.; Xu, K.; Miao, L.; Jiang, J. J. Hierarchical NiCo2S4@NiFe LDH heterostructures supported on nickel foam for enhanced overall-water-splitting activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15364–15372.
Lu, Z. Y.; Xu, W. W.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Q.; Lei, X. D.; Liu, J. F.; Li, Y. P.; Sun, X. M.; Duan, X. Three-dimensional NiFe layered double hydroxide film for high-efficiency oxygen evolution reaction. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 6479–6482.
Tang, C.; Gan, L. F.; Zhang, R.; Lu, W. B.; Jiang, X. E.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Ternary Fe1–xCoxP nanowire array as a robust hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst with Pt-like activity: Experimental and theoretical insight. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6617–6621.
Yu, J.; Li, Q. Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, C. Y.; Zhen, L.; Dravid, V. P.; Wu, J. S. Ternary metal phosphide with triple-layered structure as a low-cost and efficient electrocatalyst for bifunctional water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7644–7651.
Song, J. H.; Zhu, C. Z.; Xu, B. Z.; Fu, S. F.; Engelhard, M. H.; Ye, R. F.; Du, D.; Beckman, S. P.; Lin, Y. H. Bimetallic cobalt-based phosphide zeoliticimidazolate framework: CoPx phase-dependent electrical conductivity and hydrogen atom adsorption energy for efficient overall water splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601555.
Chen, G. F.; Ma, T. Y.; Liu, Z. Q.; Li, N.; Su, Y. Z.; Davey, K.; Qiao, S. Z. Efficient and stable bifunctional electrocatalysts Ni/NixMy(M = P, S) for overall water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3314–3323.
Chen, W.; Liu, Y. Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Qiu, Y. C.; Liu, C.; Zhou, G. M.; Cui, Y. In situ electrochemically derived nanoporous oxides from transition metal dichalcogenides for active oxygen evolution catalysts. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7588–7596.
Panda, C.; Menezes, P. W.; Walter, C.; Yao, S. L.; Miehlich, M. E.; Gutkin, V.; Meyer, K.; Driess, M. From a molecular 2Fe-2Se precursor to a highly efficient iron diselenide electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10506–10510.
Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Liu, K. Q.; Cao, R. A nickel-based integrated electrode from an autologous growth strategy for highly efficient water oxidation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502489.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.21571145, 21633008), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and Large-scale Instrument and Equipment Sharing Foundation of Wuhan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1832_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
3D mesoporous rose-like nickel-iron selenide microspheres as advanced electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Cheng, G. & Luo, W. 3D mesoporous rose-like nickel-iron selenide microspheres as advanced electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Nano Res. 11, 2149–2158 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1832-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1832-8